
U.S. Hydrogen Generation Market Size, Share, Trends, and Forecast by Technology, Application, Systems Type, and Region, 2025-2033
U.S. Hydrogen Generation Market Size and Share:
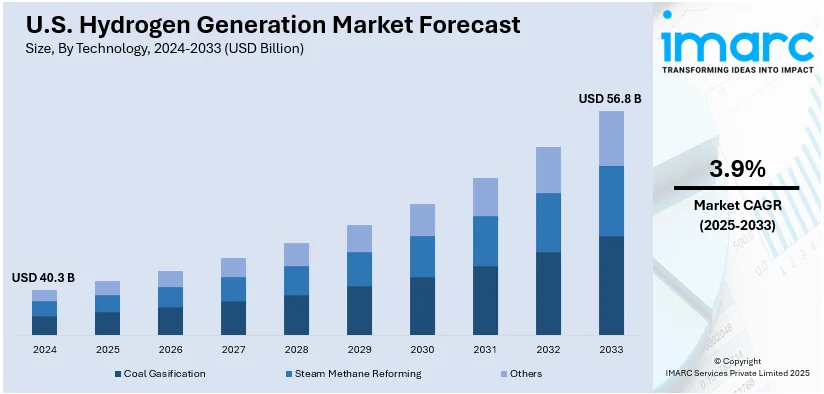
The U.S. hydrogen generation market size was valued at USD 40.3 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 56.8 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025-2033. The market is primarily driven by the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions, significant government fundings for hydrogen infrastructure, innovations in cost-effective production methods such as electrolysis, broader use in transportation fuel cells, a heightened focus on energy security, and initiatives to decrease dependence on fossil fuels.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 40.3 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 56.8 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 3.9% |
The global market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for clean energy solutions aimed at reducing carbon emissions. For example, the U.S. Gulf Coast region, producing 3.5 million tons of hydrogen annually, is positioned to be a natural fit for the clean hydrogen industry due to its extensive pipeline network and substantial CO₂ storage capacity. Moreover, production of green hydrogen is on the rise due to increased utilization of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. This is deemed one of the most significant methods through which industries such as transportation and industrial manufacturing can be decarbonized. Lastly, government programs like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act are speeding up the building of hydrogen infrastructure. Further driving market adoption is cost-effectiveness and efficiency through technological advancements in electrolysis and steam methane reforming (SMR).
Other drivers in the U.S. market include the growth in energy security and away from fossil fuels. Following this, there is also a growing emphasis on hydrogen as a versatile energy carrier that may be used across various industries. Moreover, the scaling up of hydrogen storage and distribution networks is enhancing the scalability of hydrogen solutions, enabling its integration into the energy mix. In addition, the growing interest in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, along with rising investments in related infrastructure, is opening up vast opportunities for market growth. According to the U.S. Department of Energy's January 2024 presentation on the National Clean Hydrogen Strategy, the United States, hydrogen and fuel cell technology has reached some remarkable deployment milestones: over 500 MW of backup power, more than 60,000 forklifts, over 18,000 fuel cell buses, around 50 hydrogen retail stations, and between 80 to 150 fuel cell cars. The U.S. hosts electrolyzers with a capacity of over 3.7 GW, produces 10 million metric tons of hydrogen annually, and operates the world's largest hydrogen storage cavern alongside more than 1,600 miles of hydrogen pipelines.
U.S. Hydrogen Generation Market Trends:
Increasing investments in green hydrogen production
The market is mainly fueled by the rapid shift as investments in green hydrogen production are going up continuously. Furthermore, an increased focus on the commitment of the country to cut down carbon emissions and switch to renewable energy is also driving the market. Furthermore, government funding into hydrogen technologies is rising to speed up the green energy transition and is fueling the market further. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy has awarded USD 2.2 Billion to centers in the Gulf Coast and Midwest to develop hydrogen as a clean energy source. This funding aims to promote the production of low-carbon hydrogen to combat climate change and fuel heavy industries and transportation. Also, government favorable initiatives such as tax incentives and subsidies for hydrogen production are also further supporting this market. Furthermore, green hydrogen is increasingly being seen as a solution to sectors that are harder to decarbonize like heavy industry, transportation, and power generation. With improvements in production technologies, the cost of green hydrogen is anticipated to come down and therefore be more competitive with other energy sources.
Technological advancements in hydrogen generation
The continuous technological developments in hydrogen generation are driving the market for both production efficiency and scalability. Another significant growth-inducing factor for the market is the development of water electrolysis technology, which separates water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. Increasing electrolysis efficiency, especially when using renewable energy sources, makes cost-effective hydrogen production possible, thereby fostering the market further. With the increase in demand for hydrogen in a wide range of industries, these developments are necessary which are also supporting the market even more. The industry is also expanding due to recent advancements in hydrogen transportation and storage. Toyota is advancing hydrogen-powered vehicle technology with a liquid hydrogen system that includes a self-pressurizer to save and reuse escaping gas as fuel for increased engine efficiency. The system, introduced in the GR Corolla H2 Concept, keeps hydrogen at -253 degrees Celsius to prevent boiling. Toyota showcased a "self-pressurizer" at a race, which uses boil-off gas pressure to produce reusable fuel without additional energy. These technological developments will not only reduce costs but also significantly increase the feasibility of using hydrogen as an energy source across various industries because the industry is shifting more towards these clean and sustainable energy alternatives.
Rising demand for hydrogen in industrial applications
Major growth in the market in the United States comes from the increased need for hydrogen in industrial applications. Additionally, hydrogen is increasingly being utilized in fossil fuel-based industries, such as steel, chemicals, and refining, to reduce carbon footprint in their respective operations, hence leading to the expansion of the market. For instance, the U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that developers plan to expand hydrogen production using electrolyzers, increasing capacity from 116 megawatts to 4,524 megawatts. This expansion could boost annual hydrogen production via electrolysis to approximately 0.72 million metric tons, compared to the current 10 million metric tons produced from fossil fuels. Ammonia and methanol, crucial feedstocks of fertilizers and polymers, are derived from hydrogen through the chemical manufacturing process. Meanwhile, hydrogen is increasingly identified as a key enabler of energy transitions in heavy industries where, for instance, it may be seamlessly integrated into existing infrastructure with minimal negative impact on operational performance. The increasing demand in industrial applications is driving adoption of hydrogen generation systems and supporting the on-going growth of the market in the United States.
U.S. Hydrogen Generation Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the U.S. hydrogen generation market, along with forecasts at the regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on technology, application, and systems type.
Analysis by Technology:
- Coal Gasification
- Steam Methane Reforming
- Others
Coal gasification is a crucial process in the U.S. hydrogen generation market as it provides an approach to generate hydrogen from coal. The developments in CCS (carbon capture and storage) technologies are helping reduce environmental impacts. Coal gasification is still significant because of owing to its cost-effectiveness, and the abundance of coal resources in the U.S. supports hydrogen production at a large scale.
SMR uses natural gas as feedstock, where the steam is used as reagent to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen from it. It is an efficient process with a large carbon dioxide emission rate. With research still underway in improving carbon capture technologies, it will be a vital supply contributor, mainly industrial application, to come in to meet this growing need.
Analysis by Application:
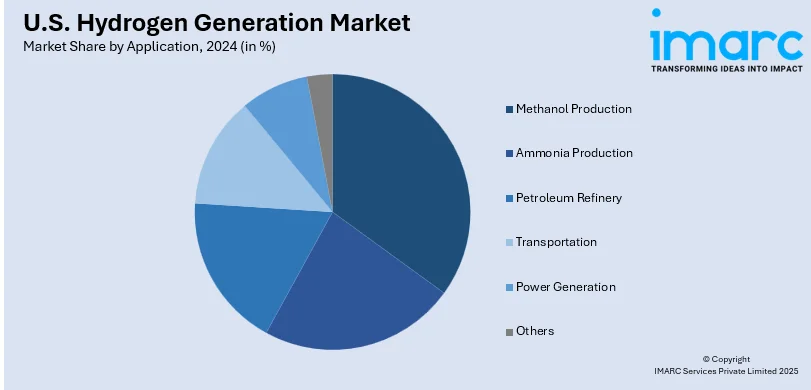
- Methanol Production
- Ammonia Production
- Petroleum Refinery
- Transportation
- Power Generation
- Others
Methanol production is vital to hydrogen generation, as hydrogen is widely used in methanol production. Hydrogen acts as a feedstock in the synthesis of methanol, which is used to produce various chemicals and fuels. As there is an increased demand for green fuels and chemicals, hydrogen's use in the production of methanol has gained momentum, especially green methanol that is obtained from renewable sources, driving the production technologies of hydrogen in the U.S.
Hydrogen is also an important byproduct in the production of ammonia, which is an important commodity for the agricultural industry, especially in the preparation of fertilizers. In the United States, ammonia is a major consumer of hydrogen as part of the Haber-Bosch process used to synthesize ammonia; it reacts with nitrogen using hydrogen. With the ever-increasing need for fertilizers, specifically with the growing global push for sustainable farming, hydrogen in ammonia production is expected to increase. This will give a boost to innovation in the hydrogen generation market.
A central chemical entity in the petroleum refining sector is hydrogen, used not only for hydrocracking, an essential desulfurizing process, but also necessary to crack crude oil in the production of high-quality fuels like gasoline, diesel fuel, and jet fuel through removing sulfur compounds that negatively affect the environment. Advances of modern refineries toward becoming environmentally friendly are making refineries increase their demand of hydrogen, thus forcing generation technologies to improve, consequently providing clean fuels for US energy consumers.
Analysis by Systems Type:
- Merchant
- Captive
The merchant hydrogen production system plays a crucial role in managing fluctuating demand and providing support for decarbonizing sectors in transition to cleaner energy solutions. Improving transportation and storage technologies, and growing investments in renewable production of hydrogen, are accelerating the growth of the merchant segment.
Captive hydrogen generation systems are becoming increasingly important in the U.S. as industries look for reliable, on-site hydrogen production solutions. These systems allow companies, particularly in sectors such as refining and chemicals, to produce hydrogen in-house to meet their energy demands. By generating hydrogen captively, companies reduce their dependency on external suppliers, ensuring greater control over production costs and supply chain reliability. Captive generation also supports industries in achieving sustainability goals by utilizing cleaner production technologies.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
The Northeast region of the U.S. is emerging as a key player in the hydrogen generation market due to its progressive energy policies and strong focus on renewable energy adoption. States like New York and Massachusetts are integrating hydrogen into their clean energy strategies to decarbonize industries and transportation. The region's infrastructure development for hydrogen refueling stations is also progressing, driven by partnerships between private companies and government initiatives.
The Midwest is a significant contributor to the U.S. hydrogen market, leveraging its robust agricultural and industrial base. This region is well-suited for hydrogen production from biomass and natural gas reforming, supported by abundant feedstock availability. States such as Illinois and Ohio are exploring hydrogen’s potential in manufacturing and transportation, aiming to modernize traditional industries with cleaner alternatives. Public-private collaborations in research and development further strengthen the Midwest's position in advancing hydrogen technologies.
The South holds a significant position in the U.S. hydrogen generation market, driven by its extensive refining and petrochemical industries. The region is witnessing substantial investments in blue hydrogen projects that capture and store carbon dioxide emissions, aligning with decarbonization goals. Moreover, the South’s growing interest in renewable hydrogen aligns with its solar and wind energy resources, offering significant potential for green hydrogen production in the future.
The Western region plays a pivotal role with its comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure, including refueling stations and production facilities. Additionally, the West is at the forefront of technological advancements, with pilot projects and partnerships exploring innovative hydrogen applications in energy storage, grid stabilization, and heavy-duty transportation.
Competitive Landscape:
The U.S. hydrogen generation market is quite competitive, with big, established energy companies as well as innovative startups competing for market share. Competition is driven more by the progress made in hydrogen production technologies, mainly green hydrogen, and by the push toward decarbonization across industries. The companies are improving efficiency and lowering costs, and government incentives and investments in hydrogen infrastructure are fueling expansion in the market. Industry players and research institutions are also encouraging innovation through partnerships and collaborations. Increased demand for hydrogen in industrial, transportation, and energy sectors has increased competition and accelerated developments in production, storage, and distribution technologies.
Latest News and Developments:
- July 18, 2024: Gold H2, a Houston-based company, has developed the Black 2 Gold Technology (B2G) to upgrade crude oil into clean, affordable Gold Hydrogen. They have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with a major oil and gas company to conduct pilot demonstrations over the next 12 months. This technology aims to produce cheaper, cleaner hydrogen and transform non-productive oil wells into hydrogen-producing assets, reshaping the traditional oil and gas industry.
- December 22, 2023: The U.S. Department of the Treasury and IRS have released the proposed regulations for the Clean Hydrogen Production Credit, which aims to incentivize the production of clean hydrogen to reduce emissions in industries like heavy transportation and manufacturing.
U.S. Hydrogen Generation Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Coal Gasification, Steam Methane Reforming, Others |
| Applications Covered | Methanol Production, Ammonia Production, Petroleum Refinery, Transportation, Power Generation, Others |
| System Types Covered | Merchant, Captive |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the U.S. hydrogen generation market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the U.S. hydrogen generation market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the U.S. hydrogen generation industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Hydrogen generation involves producing hydrogen through methods such as electrolysis, steam methane reforming (SMR), and renewable energy-based processes. Hydrogen is primarily used in refining, industrial manufacturing, transportation fuel cells, and energy storage. Its applications focus on reducing carbon emissions, supporting clean energy transitions, and enhancing energy security across various sectors.
The U.S. hydrogen generation market was valued at USD 40.3 Billion in 2024.
IMARC estimates the U.S. hydrogen generation market to exhibit a CAGR of 3.9% during 2025-2033.
The market is majorly driven by the escalating demand for clean energy solutions, growing government investments in hydrogen infrastructure, ongoing advancements in cost-effective production technologies such as electrolysis, expansion of hydrogen fuel cell applications in transportation, and an enhanced emphasis on energy security and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












