
United States Gene Therapy Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Gene Type, Vector Type, Delivery Method, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
United States Gene Therapy Market Size and Share:
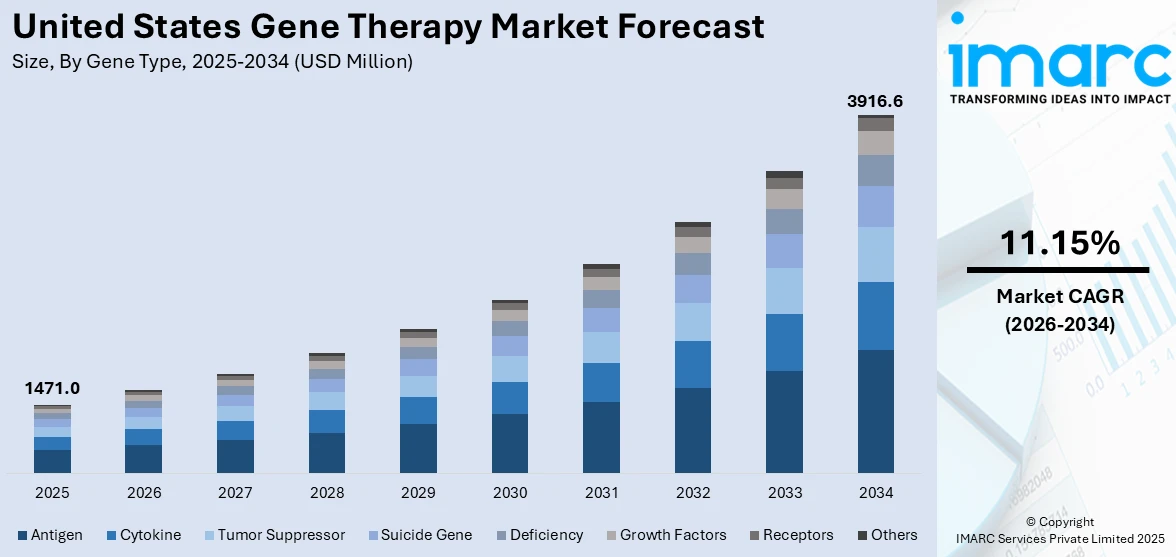
The United States gene therapy market size was valued at USD 1,471.0 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 3,916.6 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.15% from 2026-2034. The market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, rapid advancements in genetic engineering, heightened focus on strategic collaborations, imposition of supportive regulatory frameworks, and the rising investments in research and development (R&D).
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1,471.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 3,916.6 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 11.15% |
The regulatory landscape in the United States is playing an important role in speeding the development of gene treatments. Since the start of the Orphan Drug Designation program, the FDA has designated more than 1,000 medicines for uncommon diseases as orphan drugs, many of which are gene therapies. Additionally, the FDA showed its dedication to promoting the development of these medicines in 2023 by approving three novel gene therapies for conditions including spinal muscular atrophy and hemophilia. In fact, by 2023, FDA approvals for gene treatments will have more than doubled, with over 20 medications having received clearance since 2017, including Zolgensma, Hemgenix, and Onpattro. Furthermore, as of 2023, more than 100 treatments had received the FDA's regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT) designation, which speeds up the approval process for gene therapies.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Healthcare infrastructure in the U.S. has adapted to accommodate gene therapies. According to IQVIA’s tally, 114 gene therapy trials were started in the year 2023, a large majority (88 of 114, or 77%) of which were sponsored by the healthcare industry. As per the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, there are now more than 50 certified centers in the U.S. that focus on delivering gene therapies. The Gene Therapy Access Program, launched by the American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy (ASGCT), provides guidelines to ensure that gene therapies are administered safely and effectively. Moreover, insurance coverage for gene therapies is improving. In 2023, Novartis secured favorable coverage policies for Zolgensma covering about 97% of patients on commercial insurance and 86% on Medicaid. As healthcare systems evolve and support gene therapies, treatment becomes more accessible to patients, further driving the market growth.
United States Gene Therapy Market Trends:
Rising Prevalence of Genetic Disorders and Chronic Diseases
The growing incidence of cancer and genetic disorders is one of the primary factors of the gene therapy market. Cancer is a growing cause of mortality worldwide, with millions of cases diagnosed each year. It is expected that in 2024, there would be around 2,001,140 new instances of cancer diagnosed in the United States, with 611,720 individuals dying from the same. This growing load raises the need for better treatment options such as gene therapy. It is a key component of cancer treatment because it can precisely research and target malignant cells to prevent further damage. Additionally, the expanding geriatric population contributes to this need, as the risk of cancer grows with age. The number of Americans aged 65 and older is expected to increase from 58 million in 2022 to 82 million by 2050, which is a 47% increase. This increase is creating a need among pharmaceutical companies, research institutes, and government agencies to form partnerships in order to accelerate the development and deployment of gene therapy solutions.
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Improvements
Genetic mutations linked to a number of diseases are becoming easier to find and fix because of recent improvements in genetic engineering and biotechnology, such as clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) and other gene-editing tools. Research and development (R&D) expenditures by academic institutions and biotech companies are also speeding up the clinical trial process. For instance, in October 2023, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) awarded Yale School of Medicine almost USD 40 million to help develop a phase 2 CRISPR-based gene therapy platform that could specifically target genetic brain diseases like H1-4 (HIST1H1E) syndrome and Angelman syndrome.
Increasing Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
Another important factor pushing the gene therapy industry in the United States is the increasing cooperation between biotechnology companies, pharmaceutical firms, and university research institutes. These collaborations pool the funds and knowledge required to address the challenges associated with creating and promoting gene treatments. In January 2023, for example, Spark Therapeutics and Neurochase established an exclusive agreement to develop Neurochase's unique delivery technology for use with specific gene treatments for uncommon central nervous system (CNS) illnesses. Through this partnership, Spark's top adeno-associated virus (AAV) platform will benefit from Neurochase's extensive experience in direct drug delivery technology.
United States Gene Therapy Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States gene therapy market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on gene type, vector type, delivery method, and application.
Analysis by Gene Type:
- Antigen
- Cytokine
- Tumor Suppressor
- Suicide Gene
- Deficiency
- Growth Factors
- Receptors
- Others
The gene therapy segment on antigen genes concentrates on boosting the immune system's capacity to identify and fight off illnesses, including cancer. These genes produce antigens which assist in immunotherapy techniques by helping the immune system in accurately recognizing and pursuing tumor cells. Additionally, the market is expanding because to the growing use of antigen-based gene therapies for better treatment results for different kinds of cancer.
By encouraging the synthesis of cytokines, which are signaling proteins that aid in controlling inflammation and immunological responses, cytokine genes play a critical role in modifying immune responses. This segment is crucial for therapies that try to boost immune system function, particularly for cancer and long-term inflammatory conditions. Additionally, the increasing utilization of cytokine genes in therapy due to their potential to improve the body’s defense mechanisms against malignancies is fueling the market growth.
The tumor suppressor gene segment involves gene therapies that introduce or restore genes that naturally prevent uncontrolled cell growth. These therapies target genetic mutations that inactivate tumor-suppressing functions. Moreover, the rising focus on reintroducing functional copies of these genes to inhibit tumor development and progression is favoring the market growth.
Suicide gene therapy is designed to induce cell death selectively in targeted cells, typically cancer cells. This method involves introducing genes that, when activated, produce toxic products to kill the cells in question. Moreover, the rising application of suicide gene therapy in solid tumors and recurrent malignancies, where precision-targeted cell destruction can provide effective treatment with minimal harm to surrounding healthy tissues, is stimulating the market growth.
The deficiency gene segment focuses on correcting genetic disorders that arise from missing or malfunctioning genes. These therapies involve inserting functional versions of deficient genes to restore proper biological processes, addressing inherited conditions like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and muscular dystrophy. Along with this, the rising advancements in research, as it offers hope for long-term solutions to previously incurable genetic diseases, are enhancing the market growth.
Genes that support cell development, regeneration, and healing are introduced as part of growth factor gene therapy. Conditions like degenerative disorders or serious traumas that call for tissue repair or recovery are managed with these treatments. Growth factor gene therapy's increasing ability to promote tissue regeneration by igniting the body's inherent healing mechanisms is driving its market expansion.
In order to improve cells' ability to react to outside stimuli, the receptor gene segment involves changing or adding genes that code for receptors. This type of therapy is applied in targeting cancer cells by modifying immune cells to express specific receptors that help them better identify and attack malignant cells.
Analysis by Vector Type:
- Viral Vector
- Adenoviruses
- Lentiviruses
- Retroviruses
- Adeno-Associated Virus
- Herpes Simplex Virus
- Poxvirus
- nia ViruVaccis
- Others
- Non-Viral Techniques
- Naked and Plasmid Vectors
- Gene Gun
- Electroporation
- Lipofection
- Others
Viral vectors are widely used in gene therapy due to their efficiency in delivering genetic material into target cells. It is available in various types, such as adenoviruses, lentiviruses, and adeno-associated viruses (AAV). The high transduction rates and stable gene expression make it essential for therapies that target a variety of diseases, including inherited disorders and certain cancers.
Non-viral techniques involve methods such as electroporation, liposomes, and nanoparticle-based delivery to introduce genetic material into cells without using viral agents. Along with this, the lower risk of immune reactions and greater flexibility in modifying genetic payloads are boosting the market growth. Furthermore, their potential to overcome some of the limitations associated with viral vectors, such as high immunogenicity and production costs, is favoring the market growth.
Analysis by Delivery Method:
- In-Vivo Gene Therapy
- Ex-Vivo Gene Therapy
By delivering genetic material directly into a patient's body, in-vivo gene therapy allows target cells to absorb it and create the desired therapeutic effect. Additionally, this method uses vectors, such as viral particles, to transport the gene to certain tissues or organs and is supplied by injection or infusion.
In ex-vivo gene therapy, a patient's cells are taken out, altered outside of the body by adding the necessary genetic information, and then the altered cells are reintroduced into the patient. Because of the great level of control provided by this gene therapy technique, the altered cells are thoroughly tested and validated prior to implantation, making it a popular choice.
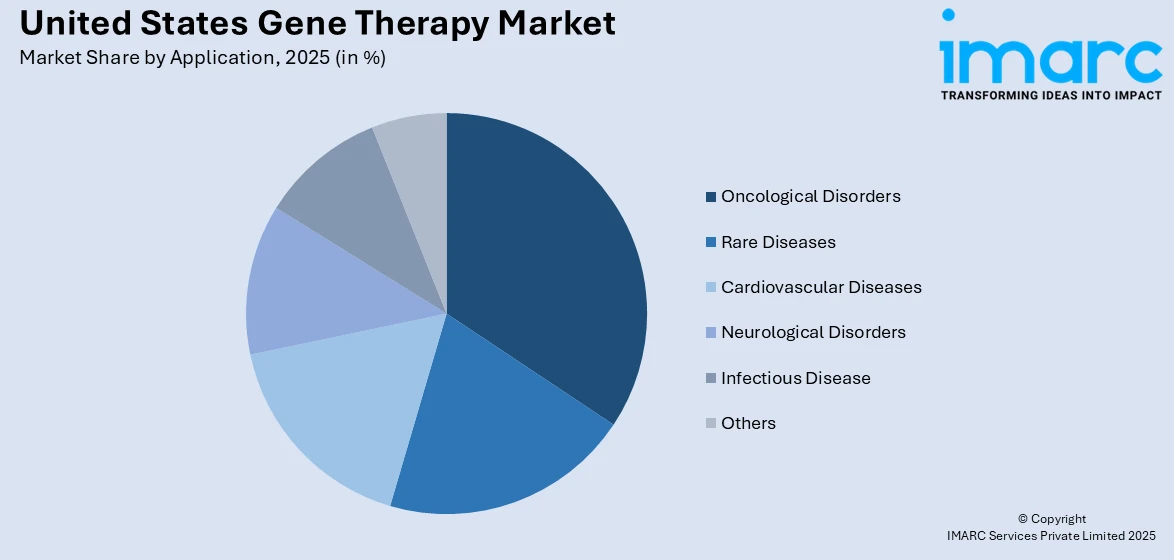
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Oncological Disorders
- Rare Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Neurological Disorders
- Infectious Disease
- Others
The need for novel therapies for different forms of cancer is motivating the use of gene therapy in oncological disorders. I this, the goal of gene treatments is to target and eliminate tumors by altering or manipulating the genes found in immune or cancer cells. It involves techniques like adding genes that improve the immune system's capacity to identify and combat cancer cells or introducing genes that cause cancer cells to die.
In the treatment of rare genetic diseases, a group of illnesses for which there are no reliable conventional therapies, gene therapy is crucial. Certain illnesses, including hemophilia, spinal muscular atrophy, and other forms of hereditary metabolic problems, have clear genetic roots, making them perfect prospects for gene therapy.
Gene therapy is being tested as a possible treatment for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including heart failure and ischemic heart disease. This segment aims to cover genes that improve heart muscle performance, support the development of new blood arteries, or regulate genetic variables that cause cardiovascular disorders.
Neurological disorders are an important application area for gene therapy, with a focus on conditions such as Parkinson's disease, spinal muscular atrophy, and other inherited neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, the intricate nature of the central nervous system makes effective treatment particularly difficult, which makes gene therapy even more necessary since it offers targeted solutions that may replace or alter damaged genes directly in the brain or spinal cord.
A new application area that uses genetic alterations to boost the body's immune response or introduce therapeutic genes that fight off infections is the use of gene therapy for infectious disorders. Its strategies involve the insertion of genes that generate antiviral proteins or enhance the capacity of immune cells to combat infections.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
the Northeast area of the United States is important to the gene therapy industry because of its concentration of prestigious colleges, biotech hubs, and specialized research facilities. The market expansion is driven by the increased focus on supporting innovation through partnership agreements between educational institutions, pharmaceutical firms, and start-ups.
With the help of an increasing number of biotech companies and academic research facilities, the Midwest is becoming a growing player in the gene therapy industry. In addition, the market is expanding as a result of higher investments in medical sciences, a larger network of research collaborations, and a renewed focus on healthcare innovation.
The market for gene therapy is growing in the Southern area because of the rise in biotechnology firms and encouraging state-level programs that promote life sciences. The comparatively cheaper cost of living and operating enterprises in the area is also driving market expansion by drawing in new start-ups and investments.
Because of its high concentration of pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms, prestigious research institutes, and innovative culture, the West is a significant hub for the gene therapy sector. Furthermore, market expansion is encouraged by the ecosystem of the area, which is reinforced by substantial venture capital investment and innovative partnerships.
Competitive Landscape:
The major players in the market are making significant advancements in developing and expanding treatment options across various indications. Recent progress includes gaining regulatory approvals for therapies targeting muscular dystrophies, rare enzyme deficiencies, and complex neurological conditions. Moreover, they are focusing on overcoming clinical and regulatory challenges, which include ensuring patient safety and securing favorable reimbursement agreements. Besides this, leading companies are putting efforts into highlighting the dynamic and evolving landscape of gene therapy, marked by intensive research, clinical trials, and collaboration with academic and regulatory entities to bring transformative treatments to broader populations.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States gene therapy market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2024, PTC Therapeutics, Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated the approval of its gene therapy for the treatment of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency. It is known to be the first-ever gene therapy approved in the United States that is directly administered to the brain.
- In April 2024, Pfizer Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its BEQVEZ (fidanacogene elaparvovec-dzkt), an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy. It is used for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe hemophilia B who currently use factor IX (FIX) prophylaxis therapy or have current or historical life-threatening hemorrhage. It is also used for patients who have repeated and serious spontaneous bleeding episodes and do not have neutralizing antibodies to adeno-associated virus serotype Rh74var (AAVRh74var) capsid.
United States Gene Therapy Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Gene Types Covered | Antigen, Cytokine, Tumor Suppressor, Suicide Gene, Deficiency, Growth Factors, Receptors, Others |
| Vector Types Covered |
|
| Delivery Methods Covered | In-Vivo Gene Therapy, Ex-Vivo Gene Therapy |
| Applications Covered | Oncological Disorders, Rare Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, Neurological Disorders, Infectious Disease, Others |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the United States gene therapy market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States gene therapy market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the United States gene therapy industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Gene therapy is a medical approach that aims to treat or prevent diseases by modifying a person's genetic material. This innovative treatment involves introducing, removing, or altering genetic material within a patient's cells to correct or replace defective genes responsible for a disease. The goal is to restore normal function or provide new therapeutic benefits.
The United States gene therapy market was valued at USD 1,471.0 Million in 2025.
IMARC estimates the United States gene therapy market to exhibit a CAGR of 11.15% during 2026-2034.
The gene therapy market in the US is driven by favorable regulatory landscape in the country, expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising incidences of chronic and genetic disorders, rapid improvement in genetic engineering, and ongoing strategic collaborations and partnerships.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












