
United States Biosimilar Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Molecule, Manufacturing Type, Indication, and Region, 2026-2034
United States Biosimilar Market Size and Share:
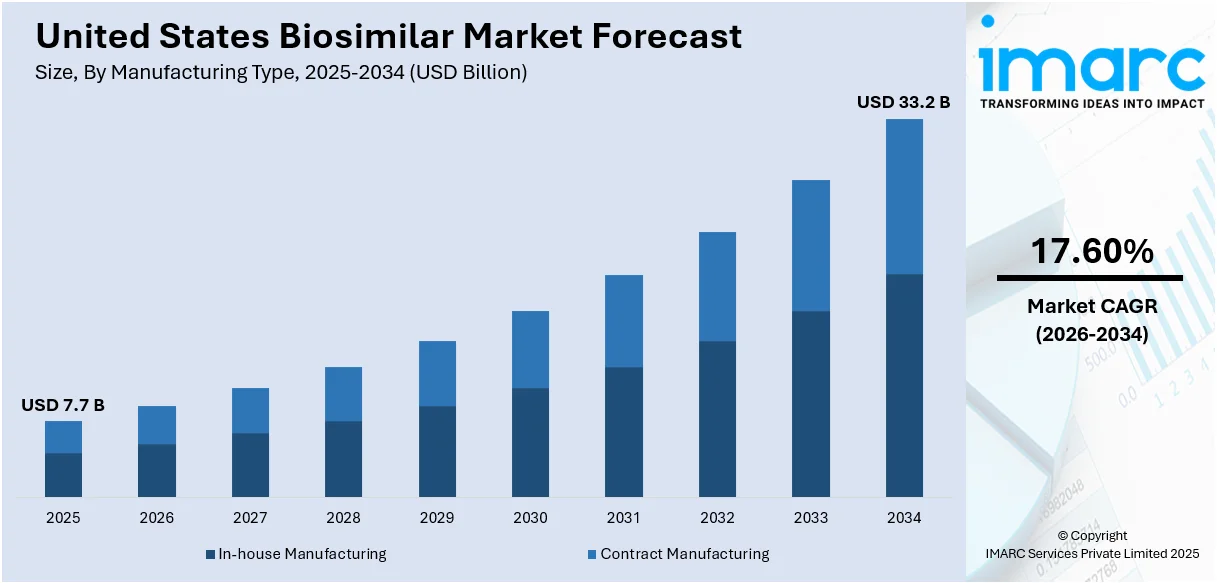
The United States biosimilar market size was valued at USD 7.7 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 33.2 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 17.60% from 2026-2034. The market is driven by the rising demand for affordable treatments for chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Additionally, the increasing number of efforts to reduce healthcare costs, the introduction of educational programs to build trust in biosimilars, and strategic collaborations among pharmaceutical companies further contribute to the United States biosimilar market share and enhance affordability, accessibility, and overall product adoption in the healthcare system.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 7.7 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 33.2 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 17.60% |
The biosimilar market in the United States is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders, which demand cost-effective biologic treatments. According to a 2024 research report by the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, about 129 million Americans have one or more major chronic conditions, of whom 42% have two or more, and 12% have five or more. Five of the top 10 leading causes of death are strongly related to preventable and treatable chronic conditions. Chronic diseases account for 90% of the annual USD 4.1 trillion U.S. health care costs, and their prevalence has been increasing steadily for the past two decades. With biosimilars offering comparable efficacy and safety to originator biologics at significantly reduced prices, they are increasingly being adopted as a cost-saving alternative in healthcare systems. The increasing number of patent expiration for several high-revenue biologics is further opening the market for biosimilar manufacturers. Additionally, policy reforms by the FDA, including the Biosimilar User Fee Act (BsUFA), are streamlining regulatory pathways, making the approval process faster and less burdensome for biosimilars.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
In addition, the growing focus on reducing healthcare expenditures in the U.S. is significantly supporting the United States biosimilar market growth. Along with this, rising healthcare costs are encouraging insurers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to prioritize affordable treatment options, fueling the adoption of biosimilars. Moreover, the implementation of educational initiatives targeting healthcare professionals and patients are also playing a vital role in improving confidence in biosimilar products. Furthermore, strategic collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and pharmaceutical companies have accelerated market entry and increased accessibility. On 3rd April 2024, Sandoz acquired CIMERLI, the ranibizumab biosimilar developed by Coherus BioSciences for USD 170 Million, thereby increasing its portfolio of ophthalmology drugs and speeding access to low-cost treatment options for retinal diseases. This transaction covers product inventory, a biologics license, proprietary software, and a retina-specific sales force. Some of the other factors, such as the presence of a supportive regulatory environment, inflating disposable income levels of individuals, and increasing public awareness are creating a positive United States biosimilar market outlook.
United States Biosimilar Market Trends:
Expansion of Biosimilar Treatment Categories
Biosimilar manufacturers are diversifying their portfolios to target a broader range of therapeutic areas. Beyond oncology and autoimmune diseases, biosimilars are being developed for rare diseases, ophthalmology, and hormonal therapies, expanding their presence across various medical fields. This shift reflects growing confidence in biosimilar efficacy and safety, encouraging manufacturers to explore United States biosimilar market trends. Additionally, technological advancements in biosimilar production have enabled companies to develop more complex molecules, opening doors to treatments for highly specific conditions. As a result, biosimilars are becoming increasingly versatile and integrated into more areas of healthcare, catering to the growing need for specialized and cost-efficient treatment options. On 28th May 2024, the FDA approved the first interchangeable biosimilar in Bkemv (eculizumab-aeeb) for the therapy of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). This product, which is manufactured by Amgen, may provide an affordable option in these life-saving treatments and promote further competition within the marketplace.
Increasing Focus on Biosimilar Substitution Policies
Many states in the U.S. are adopting laws and guidelines to allow pharmacy-level substitution of biosimilars for reference biologics. This trend reflects growing policy-level support aimed at improving biosimilar accessibility and affordability for patients. As biosimilars gain regulatory approval, healthcare systems are emphasizing automatic substitution protocols to reduce reliance on costly branded biologics. Moreover, insurers are revising their formularies to promote biosimilar use, aligning with broader cost-containment strategies which is also increasing United States biosimilar market demand. This shift toward substitution policies helps normalize biosimilars in the marketplace, fostering a competitive environment that encourages innovation, reduces healthcare expenses, and strengthens patient access to effective therapies. A Harvard study predicts that the Inflation Reduction Act will push Medicare coverage from brand-name biologics to lower-cost biosimilars by 2025. The findings are in line with reports that biosimilars are gaining traction in the commercial market.
Strategic Partnerships and Co-Development Initiatives
Collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and established pharmaceutical companies are becoming increasingly prevalent. These partnerships enable smaller biosimilar firms to leverage the expertise, distribution networks, and resources of larger companies, accelerating market entry and product commercialization. On 10th January 2025, Samsung Bioepis and Teva have formed a collaboration to develop, seek regulatory approval, and commercialize EPYSQLI (eculizumab-aagh), a biosimilar of Soliris, in the U.S. It was approved by the FDA in 2024. EPYSQLI is used for the treatment of rare diseases, including PNH, aHUS, and gMG. The alliance will make available more affordable treatments for patients who have limited choices. In addition, co-development collaborations assist firms in sharing the costs of research, reducing the risks, and improving manufacturing efficiency. Such cooperation is especially valuable in the complicated biosimilar manufacturing and regulatory arena. Through collaborative efforts, companies can bring forth high-quality biosimilars more rapidly and effectively, allowing them to gain a competitive advantage in a marketplace that requires innovation and affordability.
United States Biosimilar Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States biosimilar market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on molecule, manufacturing type, and indication.
Analysis by Molecule:
- Infliximab
- Insulin Glargine
- Epoetin Alfa
- Etanercept
- Filgrastim
- Somatropin
- Rituximab
- Follitropin Alfa
- Adalimumab
- Pegfilgrastim
- Trastuzumab
- Bevacizumab
- Others
One major market contributor is the infliximab segment, with its usage across a wide scope of autoimmune disease treatment, including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, being one of the major market drivers. With a similar therapeutic efficacy as reference biologics, yet being cost-effective, biosimilars for infliximab have been gaining steady acceptance and adoption. More patients are affected by autoimmune diseases, and in response, this market is projected to continue seeing growth as providers increase their infliximab biosimilar usage.
Insulin glargine biosimilars is playing an important role in the management of the increasing diabetes population in the United States. The biosimilars become a relatively more affordable option to long-acting insulins in diabetic patients compared to the branded products, thereby making it accessible for the diabetic population. Rising healthcare expenditure and a growing diabetic population are the reasons for this growth of the market for insulin glargine biosimilars. Further, the progress in the production of biosimilars and a positive regulatory framework are supporting the growth of this segment.
Epoetin alfa biosimilars have been used in the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease, cancer, and other medical conditions. Their popularity among healthcare service providers has been based on cost-effectiveness combined with therapeutic equivalence to branded erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. An increasing awareness of managing anemia and the availability of biosimilars is further growing the segment. Ongoing efforts in bringing down the cost of treatment while improving patient outcomes propel further growth in the segment of epoetin alfa.
Analysis by Manufacturing Type:
- In-house Manufacturing
- Contract Manufacturing
In-house manufacturing is an important part of the market since it allows companies to have better control over quality, costs, and timelines. The model ensures strict regulatory requirements are followed and the development of complex biologics. Companies that have sufficient infrastructure and experience prefer in-house manufacturing as a means of ensuring intellectual property security and simplifying operations. Although capital-intensive, the approach ensures that companies can track each step of a product's production firsthand, leading to consistency, innovation, and competitiveness in the biosimilar market.
Contract manufacturing is growing to more levels since many of the biosimilar manufacturers outsource production to third-party manufacturers that specialize in these products. It does not need much infrastructure investment and helps cut costs while the company can continue its research, development, and commercialization process. As contract manufacturers, they present larger-scale experience in biologic drugs, regulatory compliance, and advanced technologies that result in faster time-to-market. This model is the most attractive for small and medium-sized biosimilar companies, for it reduces their operational risks with high-quality manufacturing capabilities and flexibility in scaling up with the growing demand.
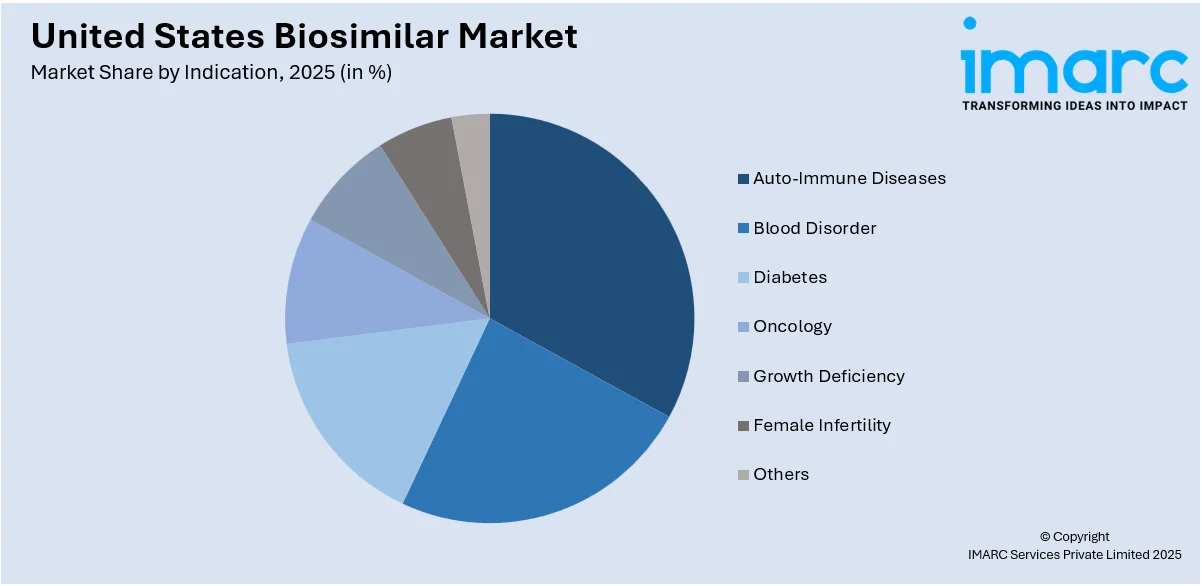
Analysis by Indication:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Auto-Immune Diseases
- Blood Disorder
- Diabetes
- Oncology
- Growth Deficiency
- Female Infertility
- Others
Auto-immune diseases hold a major share of the market. The costs have plummeted with biosimilars that target biologics including infliximab and adalimumab because these illnesses, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn's disease, have been rising at a terrific speed. Greater awareness among both patients and healthcare physicians with the option of low-cost solutions is fueling further progress. More growth is contributed by increasing research and approval of new products in the pipeline for auto-immune diseases.
Biosimilars such as epoetin alfa and filgrastim for blood disorders are revolutionizing treatments for anemia and neutropenia. As biosimilars have increasingly been applied in the management of chronic kidney disease or chemotherapy-related anemia, they have become popular and cost-effective alternatives for treatments. The segment is experiencing growth due to advancements in biosimilar technology and rising demand for hematological treatments. Increasing focus on reducing treatment costs for patients with critical conditions further supports market expansion in this category.
The diabetes segment has seen rapid growth as biosimilars for insulin glargine and other analogs gain market acceptance. With diabetes rates rising across the U.S., these biosimilars provide a cost-effective alternative for long-term management. Patient awareness campaigns, physician education programs, and improved biosimilar accessibility are driving adoption. Regulatory initiatives to ensure competitive pricing and expand biosimilar use in diabetes care continue to strengthen this segment, enhancing affordability and patient outcomes in diabetes management.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
The Northeast region leads in biosimilar adoption due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high concentration of specialized medical facilities. With a well-established pharmaceutical industry and research institutions, the region supports biosimilar development and usage. Additionally, strong awareness among healthcare professionals and patients, along with policy-driven cost-control measures, has driven the market growth in states including New York and Massachusetts.
The Midwest is showing steady growth in the biosimilar market, largely because of expanded access to low-cost healthcare and growing demand for low-cost treatment. States such as Illinois and Ohio have excellent insurance coverage, which is enhanced by growing health initiatives that further the adoption of biosimilars. An increased prevalence of chronic diseases within the region along with a greater push to contain costs also spur growth in this market.
The South is one of the rapidly growing key biosimilar markets as it hosts a large and diversified population. Growing demand for biosimilars in Texas and Florida can be attributed to the increasing incidence of chronic diseases, including diabetes and autoimmune diseases. Increased efforts in making healthcare affordable and continuous education for gaining confidence in biosimilars improve adoption across the region, which is creating steady growth in the market.
The West region is a significant contributor to the market, with states such as California leading in innovation and regulatory advancements. The region benefits from its proximity to biotechnology hubs and a strong emphasis on reducing healthcare expenses. Growing patient awareness and policy-level support for biosimilar substitution have accelerated adoption in the region, making it a key player in the market’s overall growth.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players, such as strong pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers, are investing substantial amounts in R&D to make high-quality biosimilars that meet stiff regulatory standards. Many are in collaboration with other pharmaceutical firms and healthcare providers in order to quicken market entry and distribution. Besides, players are resorting to aggressive pricing strategies that can make biosimilars more affordable for customers and augment market shares. The other strategic goal includes expansion in manufacturing capabilities through the uptake of advanced technologies in a direction toward scalability and efficiency. All marketing efforts from education campaigns through physicians and patients to inculcate confidence and acceptance of biosimilars are aimed at entrenching it more in a competitive marketplace.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States biosimilar market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Sandoz International GmbH
- Pfizer Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
- Celltrion Inc.
- Biocon Biologics Ltd
- Samsung Biologics
- Amgen, Inc.
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited
- Fresenius Kabi USA
- Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Latest News and Developments:
- September 30, 2024: Fresenius Kabi and Formycon announced the FDA approval of Otulfi (ustekinumab-aauz) biosimilar for treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. Otulfi will be the company's fourth US biosimilar as it advances toward the vision for the biopharma platform presented under Vision 2026.
- May 21, 2024: Biocon Biologics received FDA approval for YESAFILI (aflibercept) to enter the U.S. ophthalmology market. The drug was earlier approved in Europe and the UK, where it was the first biosimilar aflibercept approved. It is now the first interchangeable biosimilar in the U.S. to Eylea.
- April 16, 2024: Alvotech and Teva Pharmaceuticals announced the FDA approval of SELARSDI, a biosimilar for Stelara (ustekinumab-aekn), to treat plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis for adults and children 6 years and older. SELARSDI will be used exclusively by Teva Pharmaceuticals for commercialization purposes in the United States, starting from early next year, aiming at making better access to such an important drug against inflammatory diseases.
- December 03, 2024: Accord BioPharma, a subsidiary of Intas Pharmaceuticals, entered into an agreement to purchase UDENYCA (pegfilgrastim-cbqv), a biosimilar to Neulasta, from Coherus BioSciences. UDENYCA, which generated USD 127.1 million in sales in 2023, is the only pegfilgrastim biosimilar approved in the U.S. and available in prefilled syringes, autoinjectors, and on-body injectors. The acquisition, which is expected to close in Q1 2025, will add to Accord's biosimilar portfolio and overall market presence.
United States Biosimilar Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Molecules Covered | Infliximab, Insulin Glargine, Epoetin Alfa, Etanercept, Filgrastim, Somatropin, Rituximab, Follitropin Alfa, Adalimumab, Pegfilgrastim, Trastuzumab, Bevacizumab, Others |
| Manufacturing Types Covered | In-House Manufacturing, Contract Manufacturing |
| Indications Covered | Auto-Immune Diseases, Blood Disorder, Diabetes, Oncology, Growth Deficiency, Female Infertility, Others |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the United States biosimilar market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States biosimilar market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the United States biosimilar industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The United States biosimilar market was valued at USD 7.7 Billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.60% during the forecast period of 2026-2034.
The market is driven by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Additionally, increasing efforts to reduce healthcare costs, expiration of patents for high-revenue biologics, supportive FDA policies, and growing public awareness about biosimilars are key growth drivers.
IMARC Group estimates the United States biosimilar market to reach USD 33.2 Billion by 2034.
Key opportunities in the U.S. biosimilar market include expansion into untapped therapeutic areas, advancements in biosimilar manufacturing capabilities allowing the production of complex molecules for specialized treatments, and collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and pharmaceutical companies to accelerate regulatory approval and market entry.
Some of the key players in the market include Sandoz International GmbH, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Limited, Celltrion Inc., Biocon Biologics Ltd, Samsung Biologics, Amgen, Inc., Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited, Fresenius Kabi USA, and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












