
South Korea LNG Bunkering Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by End User and Region, 2026-2034
South Korea LNG Bunkering Market Size and Share:
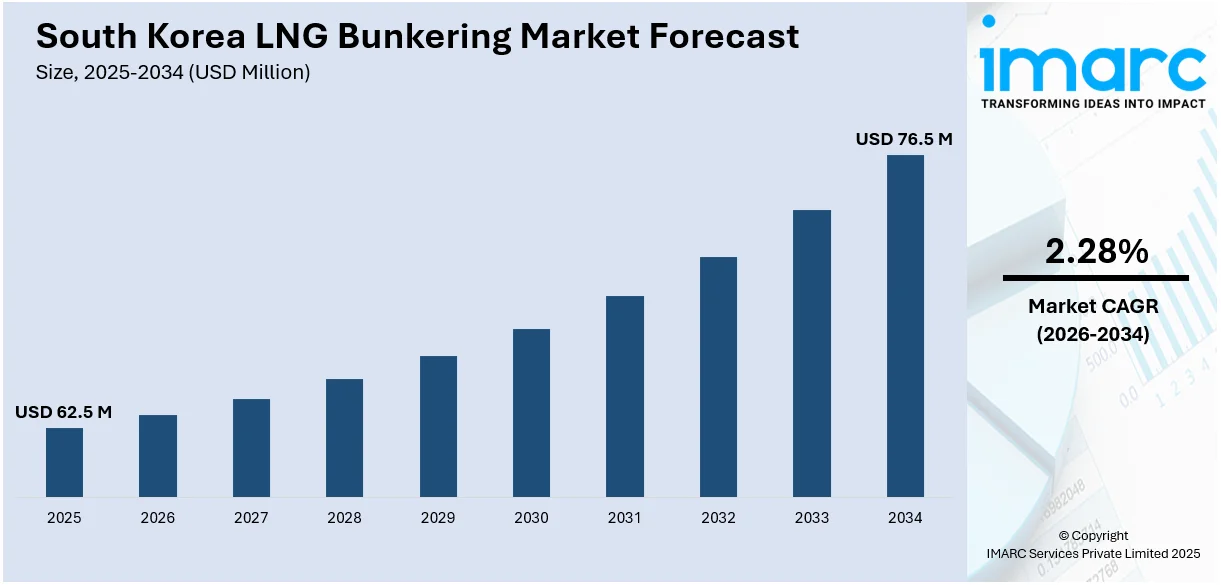
The South Korea LNG bunkering market size was valued at USD 62.5 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 76.5 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.28% from 2026-2034. The market is expanding due to stricter emissions regulations, increasing LNG-fueled vessel adoption, and port infrastructure investments. Government incentives and digital innovations enhance efficiency, positioning the country as a key LNG refueling hub for sustainable maritime operations in global shipping routes.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 62.5 Million |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 76.5 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 2.28% |
LNG bunkering industry is benefiting due to South Korea’s strong commitment to reduce carbon neutrality in association with stringent international emissions compliance requirements. South Korea’s pivotal position as an international maritime center plays a crucial role in LNG bunkering requirement, with prominent ports broadening refueling infrastructure to support the advancement of conversion strategies. For instance, in September 2024, TotalEnergies entered into a Heads of Agreement with HD Hyundai Chemical to supply 200,000 tons per year of LNG for seven years from 2027, bolstering its long-term position in South Korea's LNG market and contributing to energy transition initiatives. Besides this, shipowners are receiving advantages from government incentives which include tax relaxation and subsidies, thus pushing shipowners to invest in LNG-powered vessels, resultantly advancing maritime industry with cleaner and more sustainable industry.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Moreover, advancing technology and magnifying LNG supply system are some key drivers. Increasing developments of LNG-fueled vessels are building South Korea’s shipbuilding industry as a leading position, bolstering requirement for solid bunkering providers. In addition, South Korean ports are advancing LNG storage distribution channels in order to facilitate broader vessel traffic. For instance, in September 2024, South Korea, the world’s third-largest LNG importer, imported 3.34 Million tons of LNG, marking a 12% increase compared to September 2023. Furthermore, the implementation of advanced technology, such as digital monitoring arrangements, are notably enhancing the efficiency and security of LNG fuel. Resultantly, fleet operators are currently inclining towards the adoption of these advancements, which further strengthen their services. Besides this, increasing interest of international companies in fuel sustainably and expense management is supporting in the growth of the South Koreas’ LNG bunkering industry.
South Korea LNG Bunkering Market Trends:
Expansion of LNG Bunkering Infrastructure
South Korea is rapidly expanding its LNG bunkering infrastructure to meet rising demand from domestic and international shipping operators. Major ports, including Busan, Ulsan, and Incheon, are investing in LNG storage facilities, refueling terminals, and bunkering vessels to support fleet transitions. In line with this, the government is driving initiatives to enhance LNG supply chains, ensuring seamless fuel availability. For instance, in December 2024, South Korea’s Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries announced a 14 Trillion KRW (USD 9.78 billion) investment to upgrade the Port of Busan by 2045, aiming to achieve the world’s largest container capacity and strengthen its role as a regional logistics hub. With the country positioning itself as a key LNG bunkering hub in Asia, strategic partnerships between energy providers and shipping companies are strengthening South Korea’s role in the global shift toward sustainable maritime fuels.
Rising Adoption of LNG-Fueled Vessels
The increasing adoption of LNG-powered vessels is a significant trend in South Korea’s maritime sector. Shipowners are investing in dual-fuel engines and LNG-ready ships to comply with International Maritime Organization (IMO) emissions regulations. For instance, in February 2025, South Korea’s Hanwha Ocean procured four bi-fuel engines from Germany’s MAN Energy Solutions for two liquefied natural gas vessels. Additionally, South Korean shipbuilders are leading LNG vessel production, further accelerating demand for reliable bunkering services. As environmental policies tighten, more fleet operators are shifting to LNG to reduce sulfur and nitrogen oxide emissions. The transition is particularly strong in container shipping, bulk carriers, and offshore support vessels, reinforcing LNG’s role as a long-term fuel solution.
Integration of Digital and Smart Bunkering Solutions
Digitalization is transforming South Korea’s LNG bunkering market, improving efficiency, transparency, and fuel management. Smart bunkering solutions, including automated monitoring systems, AI-driven fuel optimization, and blockchain-based transactions, are enhancing operational accuracy. LNG suppliers and fleet operators are adopting digital platforms to streamline refueling logistics, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with environmental standards. For instance, in September 2023, HD Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) and HD Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE) obtained ABS certification for AI-based LNG technologies, which increases fuel efficiency and autonomous navigation. These technologies push the boundaries of smart gas carriers and green LNG vessel operations. Furthermore, as technological advancements continue, smart bunkering solutions are expected to play a crucial role in South Korea’s transition to cleaner and more sustainable maritime fuels.
South Korea LNG Bunkering Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the South Korea LNG bunkering market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on end user.
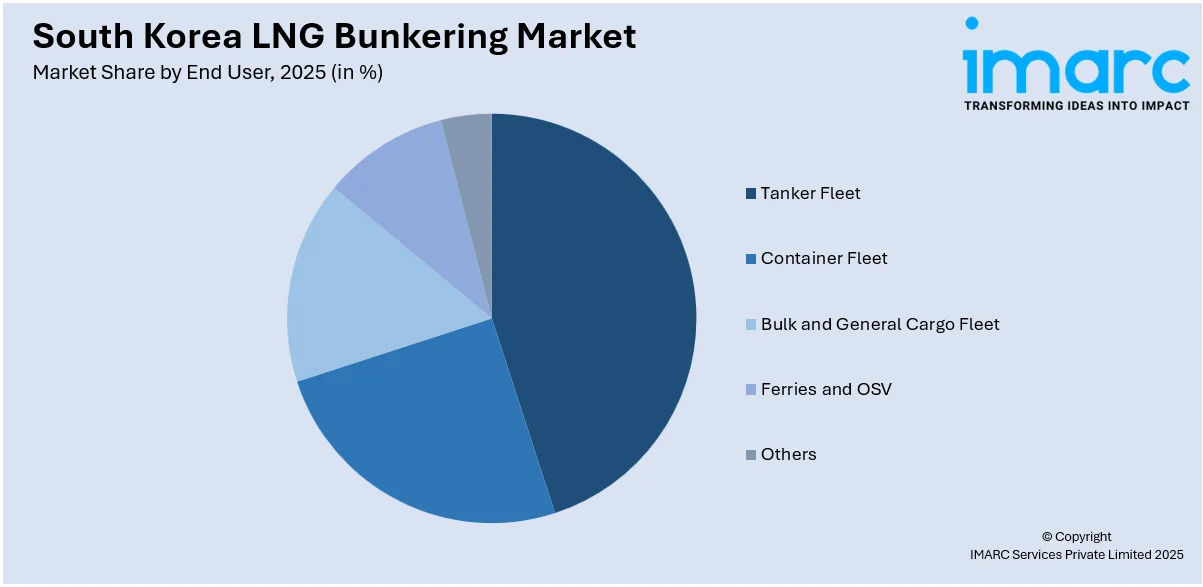
Analysis by End User:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Tanker Fleet
- Container Fleet
- Bulk and General Cargo Fleet
- Ferries and OSV
- Others
The tanker fleet is a major adopter of LNG bunkering in South Korea as shipping companies transition to cleaner fuels to meet international emission standards. LNG-fueled tankers reduce sulfur oxide and nitrogen oxide emissions, aligning with global environmental regulations. Crude oil, chemical, and LNG carriers operating in South Korea’s industrial ports, such as Ulsan and Busan, are increasingly utilizing LNG bunkering infrastructure. As demand for low-emission maritime transport grows, tanker fleet operators are investing in LNG-ready vessels to enhance fuel efficiency and regulatory compliance.
South Korea’s container fleet is rapidly shifting toward LNG bunkering as global shipping lines prioritize sustainability and fuel cost efficiency. With Busan being one of the world’s largest transshipment hubs, LNG bunkering services are expanding to accommodate large container vessels operating on international trade routes. LNG-fueled container ships offer significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions while improving operational efficiency. As South Korea strengthens its position in the global logistics market, investment in LNG infrastructure is ensuring reliable and cost-effective bunkering solutions for container fleet operators.
The bulk and general cargo fleet in South Korea relies on LNG bunkering to reduce environmental impact while maintaining cost-effective long-haul operations. Bulk carriers transporting raw materials such as coal, iron ore, and agricultural products are integrating LNG solutions to meet emissions regulations. Ports like Gwangyang and Incheon are enhancing LNG refueling capabilities to serve bulk carriers efficiently. As shipowners seek fuel alternatives to comply with evolving maritime standards, LNG bunkering is becoming a preferred choice for improving fuel efficiency and reducing operational emissions in bulk cargo transport.
Ferries and offshore support vessels (OSVs) in South Korea are adopting LNG bunkering to improve air quality in coastal regions and enhance operational efficiency. LNG-powered ferries operating between major ports, including Incheon and Jeju, benefit from lower emissions and fuel cost savings. OSVs supporting offshore energy projects utilize LNG to comply with environmental regulations while maintaining reliable performance. The government’s push for cleaner maritime transport is driving investments in LNG refueling infrastructure, ensuring that ferries and OSVs have access to sustainable and cost-effective bunkering options.
Regional Analysis:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The Seoul Capital Area, including Incheon and surrounding ports, plays a strategic role in South Korea’s LNG bunkering market. As a major hub for logistics and trade, Incheon Port is expanding LNG refueling infrastructure to support growing maritime traffic. Government policies promoting low-emission fuels are accelerating LNG adoption among shipping operators. With increasing vessel traffic and strict environmental regulations, LNG bunkering demand in the region is expected to rise, driving investments in storage, distribution, and fueling facilities for sustainable marine operations.
Yeongnam, home to major industrial ports like Busan and Ulsan, is the focal point of South Korea’s LNG bunkering market. Busan, one of the world’s busiest container ports, is investing in LNG refueling capabilities to serve international shipping routes. Ulsan, a key petrochemical and shipbuilding hub, is strengthening LNG bunkering infrastructure to support the transition to cleaner marine fuel. With rising global emissions regulations, the region’s LNG adoption is accelerating, positioning Yeongnam as a leader in South Korea’s maritime decarbonization efforts.
Honam, with its key maritime centers in Mokpo and Gwangyang, is expanding LNG bunkering infrastructure to meet the increasing demand for sustainable shipping solutions. Gwangyang Port, a critical logistics hub, is developing LNG refueling capabilities to accommodate bulk carriers and container vessels operating along South Korea’s west coast. Government-backed initiatives are driving the adoption of LNG as a marine fuel in the region, enhancing competitiveness while reducing environmental impact. As shipping activities grow, Honam is expected to play a larger role in the country’s LNG bunkering network.
Hoseo, encompassing ports in Chungcheong provinces, is emerging as a key LNG bunkering location due to its strategic connectivity and industrial expansion. Ports in the region support cargo shipping, offshore operations, and ferry services, creating demand for alternative fuel options. LNG infrastructure development is gaining momentum as South Korea strengthens its commitment to reducing maritime emissions. With increased investment in LNG supply chains and refueling stations, Hoseo is positioned to contribute to the broader adoption of LNG as a cleaner, cost-effective maritime fuel in domestic and regional shipping.
Competitive Landscape:
South Korea’s LNG bunkering market is increasingly competitive, driven by major energy providers, shipping companies, and port authorities investing in infrastructure expansion. Leading shipbuilders are developing LNG-powered vessels, fueling demand for reliable refueling services. For instance, in January 2025, HD Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering received an order for 12 LNG dual-fuel container vessels valued at 3.716 Trillion KRW from a European shipping company. Government policies promoting low-emission fuels are attracting global partnerships, strengthening South Korea’s position as a regional LNG bunkering hub. Advancements in digital bunkering solutions and supply chain optimization further intensify competition, with companies focusing on efficiency, cost reduction, and sustainability to meet growing maritime industry demands.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the South Korea LNG bunkering market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In February 2025, HD Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (HD KSOE) secured a KRW 538.3 Billion (USD 372 Million) contract to construct four 18,000 cbm LNG refueling ships for an African maritime firm.
- In February 2025, HJ Shipbuilding & Construction (HJSC) secured a KRW 127.1 Billion (USD 87.6 Million) contract to build an 18,000㎥ LNG bunkering vessel for H-Line Shipping. The 144-meter-long ship features dual-fuel propulsion, IMO-certified LNG tanks, and carbon-reducing technology for efficient LNG refueling operations.
South Korea LNG Bunkering Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| End Users Covered | Tanker Fleet, Container Fleet, Bulk and General Cargo Fleet, Ferries and OSV, Others |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the South Korea LNG bunkering market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the South Korea LNG bunkering market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the South Korea LNG bunkering industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South Korea LNG bunkering market was valued at USD 62.5 Million in 2025.
The market is driven by stricter emissions regulations, increasing adoption of LNG-fueled vessels, and government incentives. Additionally, expanding port infrastructure, technological advancements, and strategic investments in LNG supply chains further support market growth, positioning South Korea as a key regional bunkering hub.
IMARC estimates the global South Korea LNG bunkering market to reach USD 76.5 Million in 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.28% during 2026-2034.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












