
South Korea Aerospace & Defense Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Industry, Type, and Region, 2026-2034
South Korea Aerospace & Defense Market Size and Share:
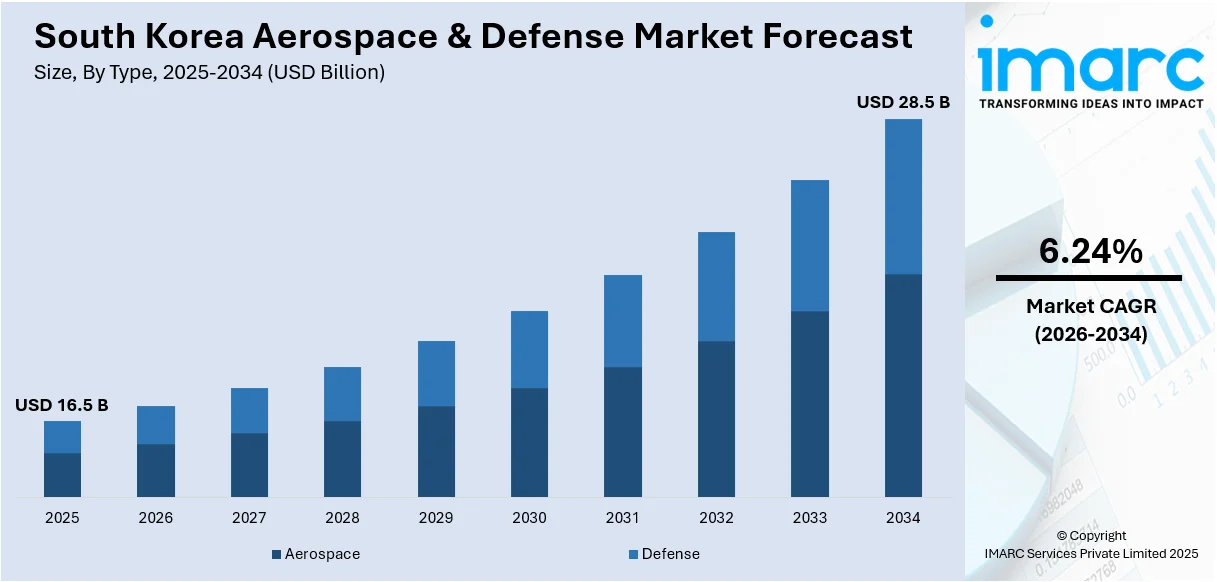
The South Korea aerospace & defense market size was valued at USD 16.5 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 28.5 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.24% during 2026-2034. The growing number of space exploration activities, increasing focus on modernizing military forces with advanced technologies, and rising need for cybersecurity to protect critical military infrastructure and data from cyber threats represent some of the key factors driving the South Korea aerospace & defense market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 16.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 28.5 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 6.24% |
South Korea is steadily advancing its military capabilities through structured modernization initiatives. The focus is on upgrading existing platforms and introducing new, high-performance systems to improve defense readiness. This approach is not only improving domestic defense resilience but also expanding opportunities in international markets. In 2024, the government committed USD 4 Billion toward defense upgrades, including USD 2.35 Billion for building advanced Ulsan-class frigates and USD 1.1 Billion to develop long-range air-to-air missiles for the KF-21 fighter aircraft. These developments are positioning South Korea as a major player in next-generation defense solutions across both land and air domains.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
As cyber threats intensify, protecting military infrastructure has become a top priority in South Korea’s defense strategy. The rise in hostile cyber activity has increased investments in digital security systems and secure communication networks. In 2023, daily cyberattack attempts reached 1.62 Million, with the majority linked to North Korean sources. Parallel to this, the country is investing in the aerospace sector with a long-term vision for space exploration. Targets include moon and Mars missions by 2032 and 2045, backed by a space budget exceeding KRW 1.5 trillion. This dual focus is driving South Korea aerospace & defense market growth as the nation builds a more tech-driven and resilient defense ecosystem.
South Korea Aerospace & Defense Market Trends:
Rising Focus on Cross-Border Defense Partnerships
South Korea aerospace & defense market is increasingly shaped by international partnerships, especially those aimed at co-production and technology transfers. These collaborations reflect a shift from traditional export models to joint ventures that build mutual capacity and secure long-term market presence abroad. South Korean firms are aligning with foreign defense players to broaden their strategic influence and contribute to allied nations’ defense readiness. This approach also diversifies production bases, allowing faster delivery and localized adaptation of weapon systems. In April 2025, Hanwha Aerospace and Poland’s WB Electronics signed an agreement to form a joint venture for producing CGR-080-guided missiles in Poland. These missiles are used with the K239 Chunmoo rocket artillery system already purchased by Poland. The collaboration marked a step forward in transferring missile manufacturing technology to Europe and strengthening NATO-aligned defense capacities. It signaled Poland’s intent to localize advanced weapon production while positioning Hanwha Aerospace as a reliable technology partner. This model of cross-border cooperation is now a major driver in South Korea’s defense strategy, fostering economic ties, raising export volumes, and building a reputation for high-trust, defense-grade industrial cooperation that directly benefits national security and aerospace sector growth.
Strengthening Domestic MRO and Modernization Capabilities
Another notable trend in South Korea aerospace & defense market is the emphasis on upgrading and maintaining existing military assets through localized MRO and platform modernization. This strategy enhances operational reliability and reduces foreign dependence for system upgrades. The growing focus on in-country development of digital avionics, integrated maintenance frameworks, and force-readiness support structures is aimed at improving the lifecycle performance of existing assets. South Korea is using its industrial base and decades of experience to take on complex upgrade programs that blend digital transformation with defense capability enhancements. In April 2025, Korean Air was selected as the preferred bidder for the KRW 961.3 Billion UH-60 helicopter upgrade project. The scope includes updating 36 Black Hawk helicopters with digital cockpits, improved engines, communication suites, survivability systems, and integrated depot maintenance. Korean Air had previously supported UH-60s through licensed production and partial upgrades, with over 130 units delivered between 1991 and 1999. Their role in this new project affirms the country’s technical maturity and growing confidence in handling high-value modernization programs internally. This trend of building strong, self-reliant upgrade capacity is now a critical growth driver, solidifying South Korea’s position as a capable defense modernizer with scalable, export-ready MRO solutions.
Expanding Defense Tech and Cybersecurity Focus
South Korea aerospace and defense market is growing rapidly due to stronger investment in cybersecurity, military modernization, and space ambitions. The country has become increasingly dependent on cybersecurity to shield vital defense infrastructure from escalating cyber threats. In 2023, the National Intelligence Service recorded 1.62 Million daily cyberattack attempts on public institutions, with around 80% traced to North Korean sources. This surge has reinforced the urgency for digital defense capabilities. Rising regional tensions have also led to greater demand for sophisticated defense technologies. In response, the South Korean government approved a USD 4 Billion defense upgrade plan in 2024. The package includes USD 583 Million for SM-3 interceptor missiles through 2030, USD 2.35 Billion for four Ulsan-class frigates by 2032, and USD 1.1 Billion to develop long-range air-to-air missiles for the KF-21 fighter program. These efforts align with the broader push to modernize armed forces and create avenues for defense exports. In parallel, South Korea is boosting its presence in the space sector, with targets set for the moon and Mars landings by 2032 and 2045. The government plans to raise the space budget to over KRW 1.5 Trillion and expand funding to encourage public-private participation in aerospace ventures. These developments reflect a strong South Korean aerospace & defense market outlook driven by integrated policy support, advanced R&D, and international collaboration.
South Korea Aerospace & Defense Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the South Korea aerospace & defense market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on industry and type.
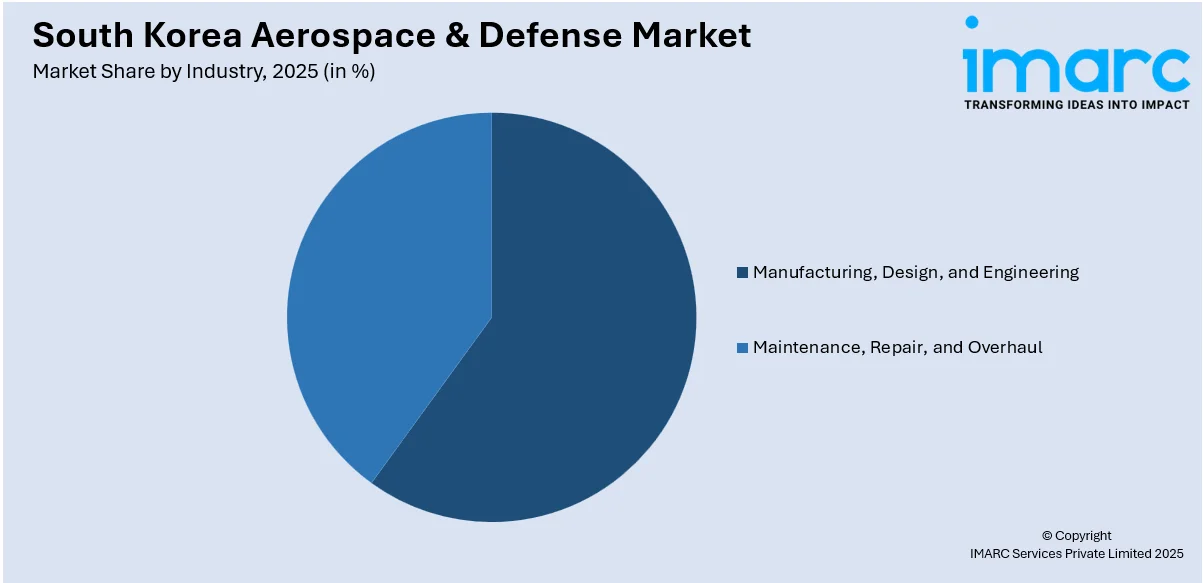
Analysis by Industry:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Manufacturing, Design, and Engineering
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul
Strong domestic manufacturing and engineering capabilities propel South Korea’s aerospace and defense market. The country invests in advanced R&D to design high-precision systems, including aircraft components, guided weapons, and satellite technologies. Local firms like Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) and Hanwha are leading innovation through homegrown programs such as the KF-21 fighter jet. Government-backed projects, tax incentives, and academic partnerships are also encouraging innovation in aerospace design and systems engineering. These developments reduce dependency on foreign suppliers and enhance export potential, positioning South Korea as a competitive hub for high-value aerospace manufacturing and design services in Asia.
Growth in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) services is a key driver for South Korea’s aerospace sector. As the number of military and commercial aircraft increases, so does the demand for local MRO capabilities. Korean Air and KAI have expanded their facilities to offer lifecycle services, modernizations, and system upgrades for aircraft like the UH-60 and F-16. The government’s push to localize defense logistics and reduce external reliance further boosts this segment. MRO investments also contribute to job creation, technical skill development, and exportable services, establishing South Korea as a trusted partner in Asia-Pacific aircraft sustainment and defense readiness.
Analysis by Type:
- Aerospace
- Space
- Civil Aviation
- Defense
- Army
- Navy
- Airforce
The aerospace industry in South Korea is advancing due to strategic investments in domestic aircraft development, satellite programs, and space exploration. Programs like the KF-21 fighter and small satellite launch vehicle (SSLV) are positioning the country as an emerging aerospace leader. Government-led initiatives are targeting dual-use (military and commercial) aerospace systems to enhance global competitiveness. Additionally, participation in international collaborations and technology-sharing frameworks bolsters innovation and accelerates timelines. The combination of strong R&D, public sector funding, and private innovation makes aerospace a high-growth pillar in South Korea’s broader defense technology ecosystem, with increasing emphasis on self-reliance and global reach.
South Korea’s defense industry is driven by heightened regional threats and a national strategy focused on military modernization. The country continues to invest in advanced technologies such as missile systems, unmanned platforms, and integrated battlefield solutions. Rising exports to countries like Poland and the UAE underline its growing credibility. Defense companies are encouraged through procurement localization policies and government-led innovation funds. Military upgrades across land, air, and naval platforms support domestic resilience while creating export opportunities. With a clear focus on operational readiness, technological edge, and global competitiveness, the defense sector remains a strategic driver of South Korea’s security and economic strength.
Regional Analysis:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
As the administrative and industrial heart of South Korea, the Seoul Capital Area drives aerospace and defense activities through proximity to government agencies, R&D institutes, and corporate headquarters. The region hosts major aerospace companies and defense-related think tanks, enabling close coordination between industry, academia, and policymakers. Investments in tech hubs, innovation parks, and smart manufacturing facilities further enhance defense research and production. Additionally, the presence of critical decision-makers in Seoul facilitates faster regulatory approvals and strategic alignments. This regional advantage plays a central role in accelerating national-level projects and supporting both the domestic and export-oriented growth of the sector. These factors are expected to heavily influence the South Korea aerospace & defense market forecast, as the region remains the nucleus of policy execution, innovation, and production scale-up for future defense initiatives.
Yeongnam is a key industrial zone supporting South Korea’s defense production through its strong manufacturing base in cities like Busan, Ulsan, and Daegu. The region is known for heavy industries and shipbuilding, which contribute to naval defense development, including submarines and destroyers. Proximity to major ports also enables efficient logistics for military exports. Aerospace components and precision machinery manufacturers in this region benefit from defense procurement contracts, helping to build domestic capacity. Local universities and R&D centers are actively engaged in defense material research and engineering, making Yeongnam a critical contributor to South Korea’s high-tech defense manufacturing ecosystem.
The Honam region supports South Korea’s defense growth through agriculture-based UAV research, composite material production, and defense-related academic programs. Though not as industrialized as other regions, Honam is emerging as a niche hub for lightweight aerospace structures and defense-related automation. Universities in Jeonju and Gwangju focus on developing sensors, AI systems, and materials science aligned with defense applications. Regional development initiatives are also encouraging small and medium-sized defense firms to set up facilities, supported by tax benefits and government grants. As investment increases, Honam is expected to contribute significantly to innovation in unmanned and AI-based defense platforms.
Hoseo, covering Daejeon and surrounding areas, serves as a major science and defense R&D corridor. With institutions like KAIST and ADD (Agency for Defense Development), the region is central to weapons research, missile technology, and next-gen systems like directed-energy weapons. It also houses aerospace clusters supporting satellite engineering, propulsion systems, and smart defense networks. Hoseo’s academic-industry collaborations are driving innovation in AI, electronics, and command-control systems. The region benefits from focused government funding and public-private partnerships, allowing rapid prototyping and testing of advanced technologies. Hoseo thus functions as a powerhouse for strategic research that directly feeds South Korea’s defense pipeline.
Other regions in South Korea, including Jeju and Gangwon, are contributing to aerospace and defense through specialized roles. Jeju is being explored for drone testing and maritime surveillance due to its location, while Gangwon supports military training and simulation centers. These areas benefit from decentralized defense infrastructure investments, especially in logistics, surveillance systems, and mobility technologies. Additionally, regional universities and startups are tapping into defense innovation programs, contributing to national goals of distributed defense capability and preparedness. Though less prominent individually, these regions collectively support ecosystem diversification and ensure strategic depth across South Korea’s aerospace and defense landscape.
Competitive Landscape:
South Korea aerospace and defense market is driven by strong competition among domestic players advancing in indigenous platform development, system integration, and export readiness. Government-backed procurement policies encourage local innovation and reduce foreign reliance, intensifying rivalry in next-generation air, naval, and missile systems. Expanding global defense collaborations and rising regional demand for advanced technologies push firms to invest in R&D, digital manufacturing, and autonomous systems. Competitive pressure also stems from the race to secure long-term international contracts and maintain technological edge in high-value segments, including space, UAVs, and cyber defense, reinforcing a performance-driven, innovation-focused market environment.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the South Korea aerospace & defense market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Hanwha Aerospace
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- LIG Nex1
- Hyundai Rotem
- Hyundai WIA
- Korea Aerospace Research Institute
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing
- Raytheon Technologies
- BAE Systems
- Airbus Defense and Space
Latest News and Developments:
- April 2025: South Korea and the UAE signed an MoU to hold regular bilateral Air Force meetings every six months, making the UAE the first Middle Eastern country to do so with South Korea. The agreement includes joint training, Cheongung-II system deployment support, and potential KF-21 cooperation.
- March 2025: Shield AI partnered with Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) to integrate its Hivemind Enterprise AI-powered autonomy suite into KAI's manned-unmanned teaming programs. The collaboration aims to fast-track AI pilot development for defense aircraft, enhancing autonomous combat capabilities in GPS- and comms-denied environments.
- March 2025: Hanwha Aerospace announced a USD 2.5 Billion rights offering to expand its South Korea defense and maritime production. The funds will reportedly support overseas weapons manufacturing, warship development, UAV engine research and development (R&D), and transformation of Korean facilities into R&D hubs, targeting KRW 70 Trillion in sales by 2035.
South Korea Aerospace & Defense Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Industries Covered | Manufacturing, Design, and Engineering, Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul |
| Types Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Companies Covered | Hanwha Aerospace, Korea Aerospace Industries,LIG Nex1, Hyundai Rotem, Hyundai WIA, Korea Aerospace Research Institute, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Raytheon Technologies, BAE Systems, Airbus Defense and Space, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the South Korea aerospace & defense market from 2020-2034.
- The South Korea aerospace & defense market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the regional market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the South Korea aerospace & defense industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South Korea aerospace & defense market was valued at USD 16.5 Billion in 2025.
The South Korea aerospace & defense market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.24% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 28.5 Billion by 2034.
Key factors driving the aerospace and defense market include rising geopolitical tensions, increased defense budgets, military modernization programs, growing cybersecurity needs, expansion in space exploration, and international defense collaborations, all of which boost demand for advanced technologies, equipment upgrades, and strategic security solutions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












