
Solar PV Inverter Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Voltage, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Solar PV Inverter Market Size and Share:
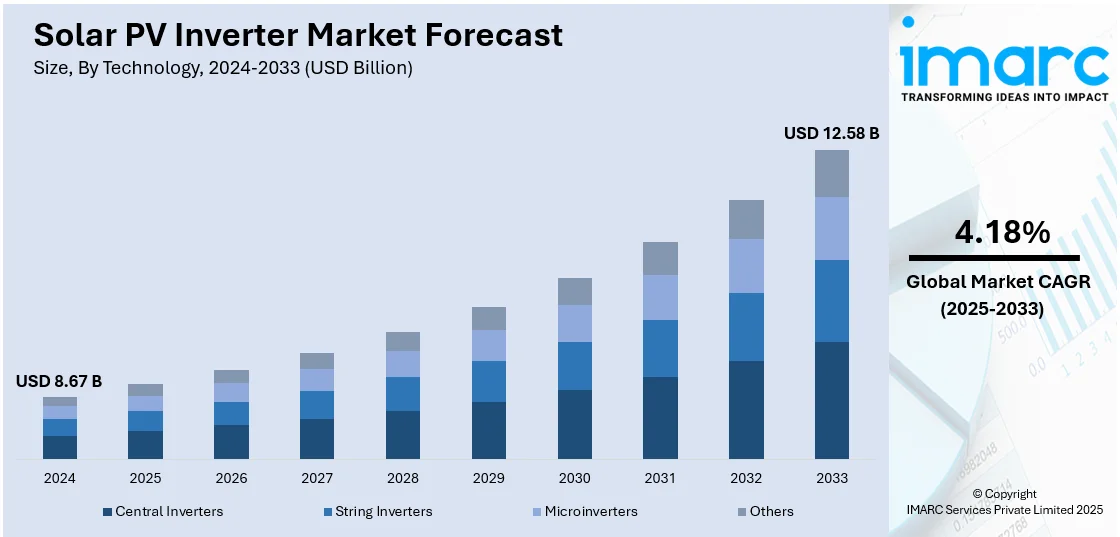
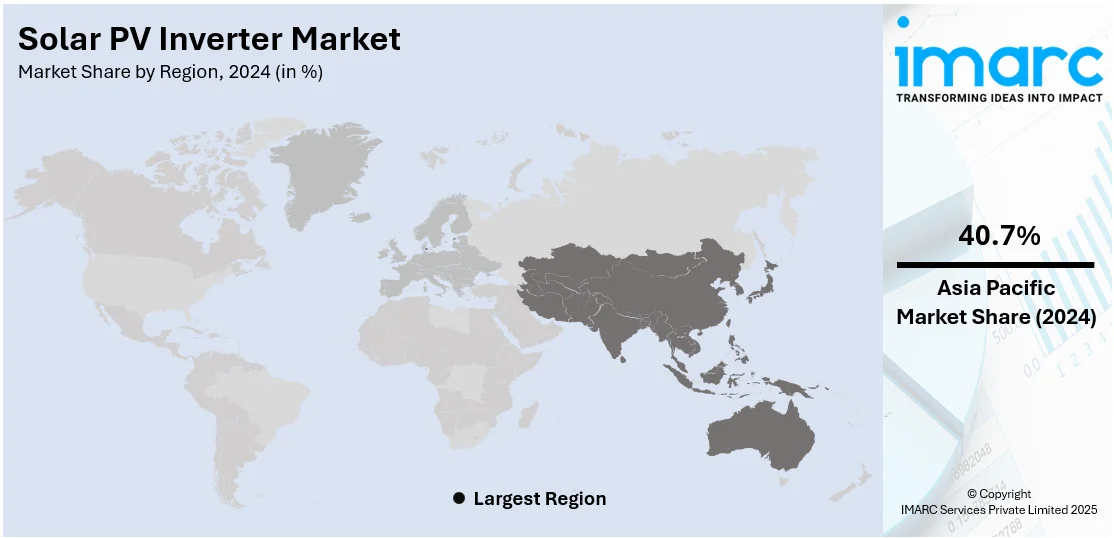
The global solar PV inverter market size was valued at USD 8.67 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 12.58 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.18% during 2025-2033. Asia-Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of over 40.7% in 2024. The region leads the market owing to extensive solar installations in China and India, robust policy support, growing manufacturing capacity, and fast-paced urban development. Its emphasis on energy independence and transition to clean energy continues to drive widespread adoption.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 8.67 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 12.58 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 4.18% |
The global solar PV inverter market is driven by the shift toward decentralized energy systems and the growing need for efficient power conversion technologies. For instance, in May 2024, GP Eco Solutions India Limited (GPES) announced plans to raise ₹30-35 crore through an IPO on NSE Emerge to fund its expansion and subsidiary operations. The company allocated ₹12.45 crore for working capital and expansion, and ₹7.6 crore to establish a new solar inverter assembly facility in Noida. GPES aims to enhance its manufacturing capabilities, contribute significantly to India's clean energy transition, and support decentralised and scalable energy generation. Rising electricity costs and heightened awareness of carbon emissions are accelerating solar adoption across residential, commercial, and utility segments. The proliferation of digital monitoring and control features within inverters is enhancing system performance and user engagement. Moreover, the rapid expansion of microgrids and off-grid installations in remote regions is boosting demand for flexible inverter solutions. Increasing investments in renewable infrastructure by both public and private sectors, coupled with the scaling of utility-scale solar projects, further reinforce the market's momentum, particularly in emerging economies focused on expanding energy access and grid stability.
In the United States, the solar PV inverter market is advancing due to aggressive federal tax incentives, state-level renewable portfolio standards (RPS), and net metering policies that encourage solar integration. The widespread electrification of buildings and transportation sectors is increasing demand for intelligent inverter technologies capable of grid interaction and load balancing. Growing interest in residential and community solar programs, particularly in states like California, Texas, and Florida, is contributing to segment diversification. Additionally, the country’s emphasis on enhancing grid resilience against climate-related disruptions is fueling adoption of hybrid inverters with storage compatibility. U.S.-based R&D initiatives and domestic manufacturing support under clean energy legislation also play a key role in strengthening inverter supply chains. For instance, in July 2024, SolarEdge expanded its U.S. manufacturing operations by opening a second facility in Seminole, Florida, following its first in Austin, Texas. The company now produces 50,000 Home Hub Inverters and 20,000 domestic content Power Optimizers per quarter, aiming for 2 million units when fully ramped. This supports domestic inverter manufacturing, benefiting from the Inflation Reduction Act incentives.
Solar PV Inverter Market Trends
The implementation of government initiatives and policies
Government initiatives and policies are instrumental in fostering the market growth. Governments across the globe have recognized the imminent threat owing to climate change and the need to transition towards clean, renewable energy sources, such as solar power. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy announced that India's renewable energy capacity exceeded 200 GW in October 2024, with a target of 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. Solar leads at 92.12 GW, followed by wind (47.72 GW) and hydro (46.93 GW). India aims for net-zero emissions by 2070, strengthening its position as a global clean energy leader. To incentivize this transition, they have introduced an array of support mechanisms, such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and direct subsidies, which reduces the financial burden on homeowners and businesses for installing solar panels. Along with this, numerous countries have also enacted aggressive renewable energy targets backed by supportive legislation, which is further driving the demand for solar PV inverters. These policies not only lower the upfront costs of solar installations but also enhance their economic viability over the long term. Such decisive actions from governments signal a robust commitment to renewable energy, thereby instilling confidence among consumers and investors and driving the market growth.
The rapid decline in product costs
The declining cost of solar PV inverters is another significant driver of market growth. According to industry reports, solar photovoltaic costs have dropped 90% in the last decade, decreasing 20% each time global capacity doubles. Over four decades, solar developed from one of the most expensive to the cheapest electricity source in many countries. As technology advances, the efficiencies of manufacturing processes improve, contributing to a reduction in the cost of raw materials and components. The rise of automation in manufacturing has also reduced labor costs and minimized human error, enhancing product reliability. Furthermore, the expanding scale of production due to increasing demand leads to economies of scale, which reduces the per-unit cost of solar PV inverters. Moreover, solar energy is now becoming increasingly affordable for a wide array of consumers, from homeowners wanting to offset their electricity bills to businesses aiming to achieve sustainability goals. Lower costs are driving the widespread adoption of solar power systems and, by extension, the demand for solar PV inverters.
The increasing energy demand across the globe
The energy demand across the globe is surging due to rapid industrialization and urbanization activities. According to the United Nations Population Fund, over half of the global population currently resides in cities and towns, and by 2030, this figure is expected to rise to approximately 5 billion. Traditional energy sources are limited and environmentally damaging, making it essential to find sustainable alternatives. Solar power, facilitated by solar PV inverters, provides a viable solution. Solar energy harnesses the sun's power, an abundant and renewable resource, to generate electricity. With the global shift towards electrification in sectors such as transport, heating, and cooling, the demand for electricity is set to grow exponentially. Solar power systems using PV inverters can meet this increased demand in a sustainable manner. From residential rooftops to commercial installations and utility-scale solar farms, the application of solar energy is expanding across the board. Thus, rising global energy demand is a key driver propelling the growth of the solar PV inverter market.
Solar PV Inverter Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global solar PV inverter market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on technology, voltage, and application.
Analysis by Technology:
- Central Inverters
- String Inverters
- Microinverters
- Others
String inverters stand as the largest technology in 2024, holding around 44.3% of the market. String inverters are currently dominating the market as they have been the standard in the solar industry for many years, and their long-standing presence in the market has led to wide acceptance and trust in their technology. Furthermore, they offer a significant cost advantage over other types of inverters, such as microinverters and power optimizers. String inverters also have lower upfront costs, making them an attractive option for cost-conscious consumers. Apart from this, string inverters are incredibly efficient for larger, unshaded installations. They perform exceptionally well in conditions where solar panels receive uniform sunlight, making them a preferred choice for large residential, commercial, or utility-scale installations. Additionally, the recent development of multi-string inverters, which provide more flexibility and efficiency, is contributing to the market growth.
Analysis by Voltage:
- < 1,000 V
- 1,000 – 1,499 V
- > 1,500 V
>1500V leads the market with around 50.2% of market share in 2024. The >1500V segment is dominating the market as it allows more solar modules to be connected in series in a string, reducing the number of strings needed. This reduction leads to fewer combiner boxes, fewer cables, and fewer connections, thereby resulting in significant balance of system (BOS) cost savings. Furthermore, it results in a lower current for the same power output, which reduces resistive losses in the system, leading to an overall increase in system efficiency. Additionally, the recent technological advancements in components, such as inverters, transformers, and switchgears, have made it safer and more reliable to operate at these higher voltages, such as > 1500. For instance, in September 2024, GE Vernova launched a 6 MVA, 2000 Vdc (>1500) utility-scale solar inverter aimed at lowering solar energy costs and improving scalability. The new FLEXINVERTER 2000 Vdc will be deployed in a multi-megawatt pilot solar park in North America, expected to be operational by Q1 2025. It boosts power output by 30% in the same footprint and achieves record efficiency levels of 99.4%, reducing project costs and improving performance. GE Vernova is collaborating with Shoals Technologies and a PV module supplier for the project.
Analysis by Application:
- Utility Scale
- Residential Scale
- Small Commercial Scale
- Large Commercial Scale
- Industrial Scale
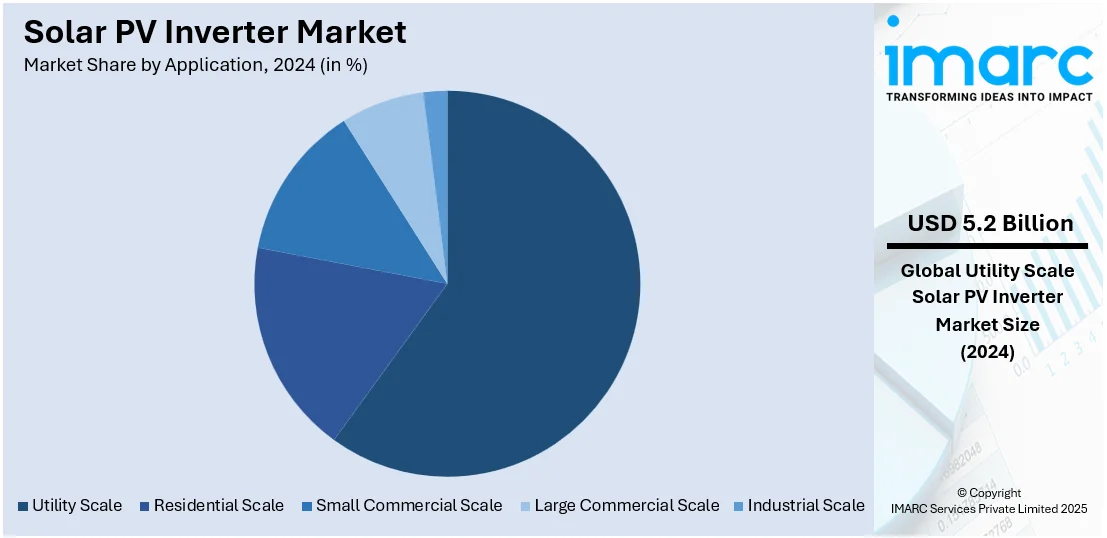
Utility scale leads the market with around 59.8% of market share in 2024. Utility-scale solar projects are dominating the market as they outsize residential and commercial installations in terms of power generation capacity. Furthermore, many countries are aggressively expanding their renewable energy capacity to meet climate goals by establishing utility-scale solar farms, which is further boosting the market growth. Apart from this, utility-scale projects offer economies of scale, as the per-unit cost of components, including solar PV inverters, decreases significantly with the scale of the project. This cost advantage makes utility-scale projects more financially attractive, thereby driving their prevalence. Moreover, recent advancements in technology have resulted in more efficient and reliable solar PV inverters that can handle the high-power output of utility-scale projects. For instance, in June 2024, Gamesa Electric secured a contract to supply 245 MW of utility-scale Proteus PV inverters and plant controllers to Repsol for large solar installations in Spain. The order includes 64 Proteus inverters, each capable of delivering up to 9.4 MVA, making them well-suited for high-capacity, grid-connected projects. Designed as compact plug-and-play units, they help reduce on-site installation time, equipment footprint, and associated costs. With a peak efficiency of 99.4% and total harmonic distortion below 0.7%, the inverters significantly enhance energy output and reduce system losses, contributing to lower levelized costs of electricity (LCoE) in utility-scale solar deployments.
Regional Analysis:
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- North America
- Middle East and Africa
- Latin America
In 2024, Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market share of over 40.7%. The Asia Pacific region continues to lead the solar PV inverter market, driven by aggressive renewable energy goals, rising electricity demand, and increased focus on rural electrification. Recent developments underscore this trend. In March 2025, Adani Enterprises established Adani New Industries One Limited (ANIOL) to manufacture and supply solar panels, inverters, and related equipment, supporting large-scale solar deployments across India. Meanwhile, Infineon’s partnership with CDIL Semiconductors in March 2025 aims to localize production of power chips used in solar inverters, strengthening domestic supply chains and aligning with the Make in India initiative. These efforts highlight how regional players are scaling infrastructure, addressing off-grid needs, and capitalizing on favorable solar conditions to expand clean energy access across diverse geographies.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Solar PV Inverter Market Analysis
In 2024, United States holds 83.8% of the market share in North America. The United States solar PV inverter market is growing rapidly, driven by renewable energy investments, federal incentives, and declining solar costs. According to reports, as of 2023, the U.S. solar industry has attracted USD 60 Billion in private investment. Over the past decade, solar installation costs have fallen by 40%, fueling market expansion and widespread adoption of solar PV systems. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is further accelerating solar inverter adoption, providing tax credits and financial incentives for both residential and utility-scale installations. Similarly, the rapid expansion of energy storage systems (ESS) is supporting demand for hybrid inverters, which integrate solar and battery storage for enhanced grid resilience. Meanwhile, the ongoing push for smart grid modernization is increasing demand for advanced grid-forming inverters, improving frequency regulation and voltage stability. Moreover, rising electricity prices and energy independence goals are encouraging homeowners and businesses to install high-efficiency solar PV inverters. Additionally, EV charging stations powered by solar energy are fostering demand for bidirectional inverters, enabling grid flexibility and decentralized energy generation, further strengthening the market demand.
Europe Solar PV Inverter Market Analysis
Europe’s market growth is primarily propelled by aggressive decarbonization policies, rising energy costs, and increasing solar adoption across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. According to Europe’s 2024 Outlook, 65.5 GW of new solar capacity was installed, exceeding 2023’s 62.8 GW, bringing the EU solar fleet to 338 GW, a fourfold increase from 82 GW a decade ago. Households with solar and heat pumps saw energy bill savings of up to 84%, highlighting solar power’s economic benefits. In line with this, the European Green Deal and REPowerEU plan are accelerating solar infrastructure investments, driving demand for next-generation inverters with higher efficiency and grid-support capabilities. Furthermore, hybrid inverters are increasingly adopted to integrate battery storage solutions, enhancing energy security. Additionally, feed-in tariffs and net metering policies are making solar investments more attractive in the market. Moreover, the growth of agrivoltaics, combining agriculture with solar farms, is driving demand for central and string inverters to optimize energy generation while preserving farmland productivity, further strengthening Europe’s ecosystem.
Asia Pacific Solar PV Inverter Market Analysis
The Asia Pacific solar PV inverter market is witnessing growth attributed to rising electricity demand, government incentives, and rising solar manufacturing capabilities. An industry report states that China dominates solar manufacturing, producing 83% of the world's polysilicon, 97% of wafers, 83% of solar cells, and 72% of modules. The region's renewable energy investments are projected to reach USD 1.1 Trillion, with grid-related market demand growing to USD 700 Billion by 2032. Similarly, falling PV module prices are making solar installations more cost-effective, driving adoption across urban and rural areas. The growth of floating solar farms in Singapore, Indonesia, and South Korea is creating demand for marine-grade inverters with corrosion-resistant designs. Meanwhile, distributed solar energy adoption is accelerating the need for microinverters in the residential and commercial sectors, thereby impelling the market. Additionally, smart inverters with real-time monitoring and AI-driven energy management are gaining traction, optimizing solar performance and grid integration, reinforcing the region's leadership in solar PV technology.
Latin America Solar PV Inverter Market Analysis
The market in Latin America is expanding due to favorable policies, energy access initiatives, and rising off-grid solar adoption. According to reports, electricity access increased from 90% in 2001 to 98% in 2021, with USD 347 Million in funding for 11 renewable projects between 2014-2023, including 26 solar plants generating 2,850 GWh annually, powering 1.1 million families. Furthermore, Brazil, Mexico, and Chile have implemented solar auctions and net metering, supporting demand for string inverters in distributed solar. Hybrid inverters are gaining traction in off-grid and rural electrification, while central inverters are powering large-scale solar farms in Argentina and Colombia. Moreover, the rise of virtual power plants (VPPs) and blockchain-based solar trading is driving demand for smart inverters with grid-forming capabilities, enabling decentralized energy management.
Middle East and Africa Solar PV Inverter Market Analysis
The solar PV inverter market in the Middle East and Africa is bolstering, fueled by rapid solar deployment, energy diversification, and abundant solar resources. Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa are developing mega solar farms, increasing demand for high-capacity central inverters for grid-scale power generation. In line with this, Saudi Arabia signed PPAs for 5,500 MW of solar projects under its National Renewable Energy Program, targeting 100-130 GW capacity by 2030. Egypt and Morocco are driving smart string inverter adoption for utility-scale projects, while solar-plus-storage microgrids in Africa support the demand for hybrid and off-grid inverters. The green hydrogen sector in the Middle East is also fueling demand for high-voltage solar inverters. Meanwhile, AI-driven monitoring systems are improving solar inverter performance and efficiency, strengthening the region’s renewable energy reliability and economic viability.
Competitive Landscape:
The solar PV inverter market is characterized by intense competition driven by rapid technological advancements, price sensitivity, and evolving grid requirements. Market players compete based on efficiency, durability, software capabilities, and integration with energy storage and smart grid systems. Innovation in hybrid, string, and microinverter technologies continues to reshape product portfolios, catering to varied residential, commercial, and utility-scale needs. Companies are focusing on offering comprehensive digital platforms with remote monitoring, predictive diagnostics, and AI-based optimization features. Strategic partnerships with EPC contractors, developers, and distributors are critical for expanding market reach. Additionally, local manufacturing capabilities and compliance with regional certification standards significantly influence procurement decisions, particularly in emerging markets prioritizing domestic content and cost-effective solar deployment. For instance, In March 2025, SMA America launched the Sunny Central Storage UP-S, a 99.2% efficient grid-scale battery inverter, now available in the U.S. market. Designed for large-scale storage projects, it uses silicon carbide MOSFETs for high power conversion and robust grid-forming capabilities. The inverter supports 4,600 kVA with no derating at high temperatures, includes dynamic grid support, fault ride-through, and low harmonic emissions.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the solar PV inverter market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- ABB Ltd
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- General Electric Company
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- Delta Energy Systems Inc.
- Enphase Energy Inc.
- SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Kstar New Energy Co. Ltd
- Sineng Electric Co. Ltd
- Sungrow Power Supply Co Ltd
- Tabuchi Electric Co. Ltd
- TBEA Sunoasis Co. Ltd
- Toshiba Corporation
Latest News and Developments:
- In March 2025, Netherlands-based Atmoce launched new combiner boxes and microinverters for solar PV systems. The M-Combiner series integrates key energy management components and supports up to 30 kW PV input and 42 kWh battery storage. The MI series microinverters accommodate PV modules up to 700 W, with outputs ranging from 400 W to 500 W and peak efficiency of 97.4%. Designed for easy installation, the products aim to enhance system integration, flexibility, and performance in both residential and commercial solar applications.
- February 2025: Daanaa Resolution introduced Zodiac, a substring-level solar PV inverter that boosts energy harvest by up to 42%, eliminates external power electronics, and simplifies installation. Virgo and Pandora modules optimize power conversion, lower O&M costs, and enhance reliability, offering higher efficiency and faster ROI for solar PV systems.
- December 2024: McLaren Applied Group's subsidiary, MA Solar Italy, acquired Italian solar inverter manufacturer FIMER amid industry challenges. The acquisition, for an undisclosed amount, helps FIMER complete its restructuring process after being in Extraordinary Administration, securing its solar PV inverter business and assets.
- July 2024: Sungrow signed an 850 MW PV inverter supply contract with Hero Future Energies (HFE) in India. The 1500V inverters, featuring IP65-rated design and smart forced air-cooling technology, will be supplied from Sungrow’s Bengaluru factory, ensuring optimized LCOE and high performance in extreme conditions.
- June 2024: SolarEdge unveiled its next-generation 20kW three-phase solar inverter and modular home battery at Intersolar 2024. Featuring Silicon Carbide (SiC) technology, it reduces size and weight, and augments efficiency, supports SolarEdge Home wireless network, and enables multi-day home backup with optimized Time of Use (ToU) energy management.
Solar PV Inverter Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Central Inverters, String Inverters, Microinverters, Others |
| Voltages Covered | < 1000 V, 1000 – 1499 V, > 1500 V |
| Applications Covered | Utility Scale, Residential Scale, Small Commercial Scale, Large Commercial Scale, Industrial Scale |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Companies Covered | ABB Ltd, Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Omron Corporation, General Electric Company, SMA Solar Technology AG, Delta Energy Systems Inc., Enphase Energy Inc., SolarEdge Technologies Inc., Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, Kstar New Energy Co. Ltd, Sineng Electric Co. Ltd, Sungrow Power Supply Co Ltd, Tabuchi Electric Co. Ltd, TBEA Sunoasis Co. Ltd., Toshiba Corporation. etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the solar PV inverter market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global solar PV inverter market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the solar PV inverter industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The solar PV inverter market was valued at USD 8.67 Billion in 2024.
The solar PV inverter market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 4.18% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 12.58 Billion by 2033.
The solar PV inverter market is driven by rising solar power adoption, supportive government incentives, grid modernization efforts, declining inverter costs, and growing demand for efficient power conversion. Increased residential and commercial solar installations, energy storage integration, and the push for decentralized energy systems are also accelerating market growth.
Asia Pacific currently dominates the solar PV inverter market, accounting for a share of 40.7% in 2024. The region leads the market due to strong policy support, rapid urbanization, rising electricity demand, and large-scale solar deployment across emerging economies.
Some of the major players in the solar PV inverter market include ABB Ltd, Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Omron Corporation, General Electric Company, SMA Solar Technology AG, Delta Energy Systems Inc., Enphase Energy Inc., SolarEdge Technologies Inc., Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, Kstar New Energy Co. Ltd, Sineng Electric Co. Ltd, Sungrow Power Supply Co Ltd, Tabuchi Electric Co. Ltd, TBEA Sunoasis Co. Ltd., Toshiba Corporation. etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












