
Solar-Powered Microbes Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application and Region, 2025-2033
Solar-Powered Microbes Market Size and Share:
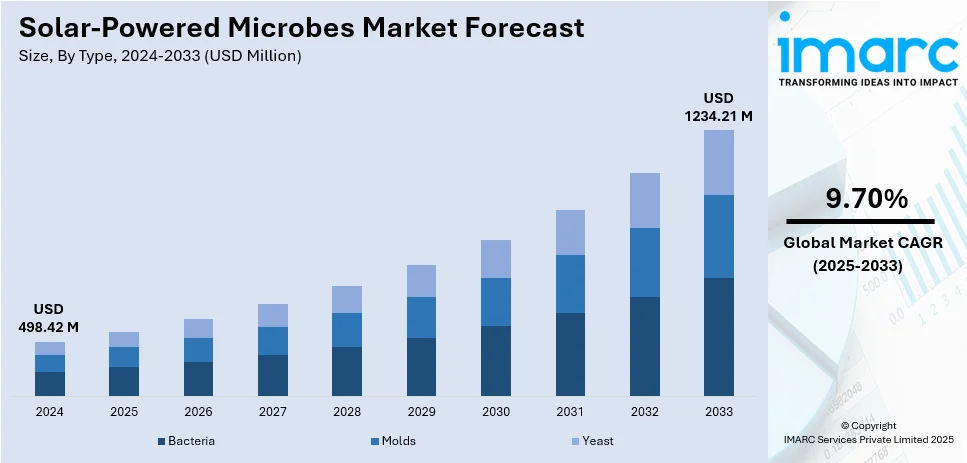
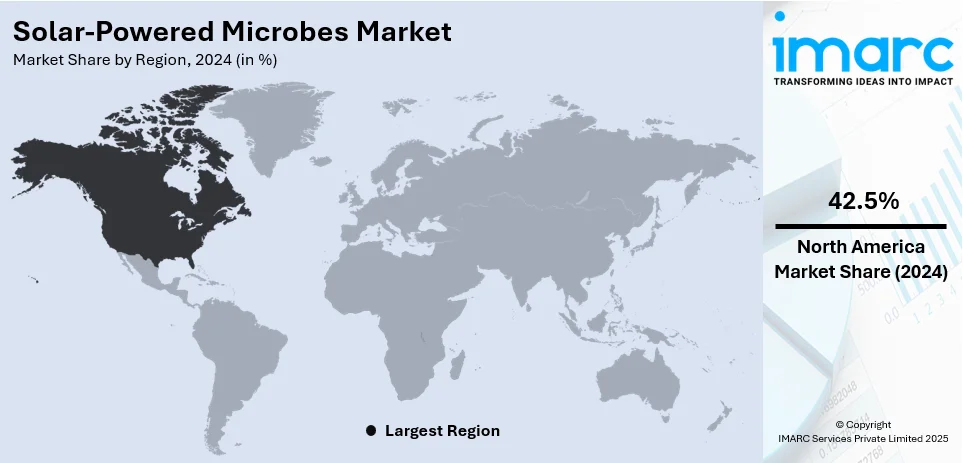
The global solar-powered microbes market size was valued at USD 498.42 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 1234.21 Million by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.70% from 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market, holding a market share of over 42.5% in 2024. The solar-powered microbes market share is driven by advancements in synthetic biology, rising demand for sustainable biofuels, and growing interest in carbon-neutral solutions. Government funding, increasing industrial applications, and innovations in microbial engineering further accelerate market growth and commercial adoption.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 498.42 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1234.21 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 9.70% |
The solar- powered microbes market growth is gaining impetus due to adding demand for sustainable and bioengineered solutions across industries. Rising interests over climate change and carbon emissions are driving interest in microbial systems that use solar energy to produce biofuels, bioplastics, and high- value chemicals. Advancements in synthetic biology and bioengineering are enabling the development of largely effective microbes that can convert sun and CO ₂ into useful composites. Governments and private investors are funding exploration initiatives to accelerate commercialization, farther boosting market growth.
The United States has emerged as a key regional market for solar- powered microbes driven by advancements in synthetic biology, adding demand for sustainable energy, and rising interest in bio-based manufacturing. Researchers and biotech enterprises are using genetically framed microbes that use solar energy to produce biofuels, bioplastics, and high- value chemicals, offering an eco-friendly choice to traditional fossil energy- based production. Government support and backing for renewable energy initiatives further propel the market. Agencies like the Department of Energy (DOE) are investing in innovative bioengineering results to reduce carbon outflows and enhance energy effectiveness. Also, growing concerns over climate change and commercial sustainability goals are pushing industries to borrow green biotechnologies.
Solar-Powered Microbes Market Trends:
Demand for sustainable bio-manufacturing
The shift toward sustainable production methods is a major solar- powered microbes market trend. Industries similar as medicinals, agriculture, and biofuels are seeking options to fossil energy- based manufacturing, and solar- powered microbial systems offer a promising result. These microbes use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide into precious products like biofuels, bioplastics, and high- value chemicals. Unlike conventional fermentation, which relies on sugar or other organic feedstocks, solar- powered microbes reduce dependence on agrarian resources and minimize carbon outflows. As companies aim for carbon neutrality and resource effectiveness, the embracement of these biotechnologies is anticipated to accelerate, driving market growth. For instance, as published by Ceres Roadmap 2030, The World Green Buildings Council's Net Zero Carbon Building (NZCB) Commitment has been signed by JLL, a real estate services company. By making investments in energy efficiency and purchasing renewable energy, JLL will endeavor to decarbonize its worldwide office network of 460 buildings in accordance with the commitment's framework.
Advancements in biotechnology
Breakthroughs in synthetic biology are expanding the capabilities of solar-powered microbes, making them more efficient and commercially viable. As per ScienceDirect, recent innovations in this area include the creation of heme in an impossible burger and the ability of Escherichia coli to grow on CO2 and produce fuels with no carbon emissions. In the coming years, synthetic biology combined with newly created artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities can significantly advance the fourth industrial revolution's (industry 4.0) goal of smart production. Genetic modifications allow microbes to capture solar energy more effectively and convert it into targeted biochemicals with higher yields. Researchers are also engineering microbes to thrive in diverse environments, reducing operational constraints. The integration of artificial intelligence and computational biology further enhances strain optimization, enabling precise metabolic engineering. These innovations are making solar-powered microbial systems more scalable, cost-effective, and competitive with traditional production methods, attracting investment from biotech firms and research institutions worldwide.
Supportive policies and funding
Government initiatives and funding programs are playing a crucial role in escalating solar-powered microbial market demand. Countries are increasingly promoting bio-based economies through grants, subsidies, and regulatory support for sustainable biomanufacturing. In the U.S., agencies like the Department of Energy (DOE) and National Science Foundation (NSF) are investing in research to improve microbial photosynthesis and industrial applications. The European Union’s Green Deal and China’s focus on bio-innovation are also fostering market growth. Additionally, corporations are partnering with research institutions to develop scalable solar microbial platforms. These supportive policies and funding mechanisms are accelerating commercialization, making solar-powered microbes a key component of the future bioeconomy.
Solar-Powered Microbes Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global solar-powered microbes market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type and application.
Analysis by Type:
- Bacteria
- Molds
- Yeast
Bacteria leads the market with 44.5% share due to their rapid growth, adaptability, and efficiency in bio-production. Engineered bacterial strains like cyanobacteria are widely used to convert solar energy into biofuels, bioplastics, and specialty chemicals. Their simple genetic makeup allows for precise modifications, optimizing metabolic pathways for higher yields. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and wastewater treatment benefit from bacterial-based solar biomanufacturing. Continuous research in synthetic biology and photosynthetic engineering further strengthens their role in advancing sustainable microbial technologies.
Molds play a crucial role in the solar-powered microbes market, particularly in bioenzyme production, bioremediation, and pharmaceutical applications. Their complex metabolic capabilities allow them to produce valuable compounds such as antibiotics, organic acids, and bioactive proteins. Scientists are exploring ways to enhance mold photosynthesis through genetic engineering, making them more efficient in converting solar energy. With increasing demand for natural bio-based solutions in industries like healthcare and agriculture, molds are emerging as an important segment in solar microbial technology.
Yeasts are gaining traction in the solar-powered microbes market due to their robust fermentation abilities and industrial scalability. Researchers are engineering yeast strains to utilize solar energy for bioethanol production, high-value chemicals, and sustainable food ingredients. Their ability to thrive in controlled environments makes them suitable for large-scale biomanufacturing. Solar-powered yeast systems are particularly attractive in the alternative protein and synthetic biology sectors, where precision fermentation is revolutionizing food production. With growing investments in renewable biotech, yeast-based solar microbes hold strong commercial potential.
Analysis by Application:
- Food
- Bakery & Confectionery
- Beverages
- Dairy
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Meat
- Feed
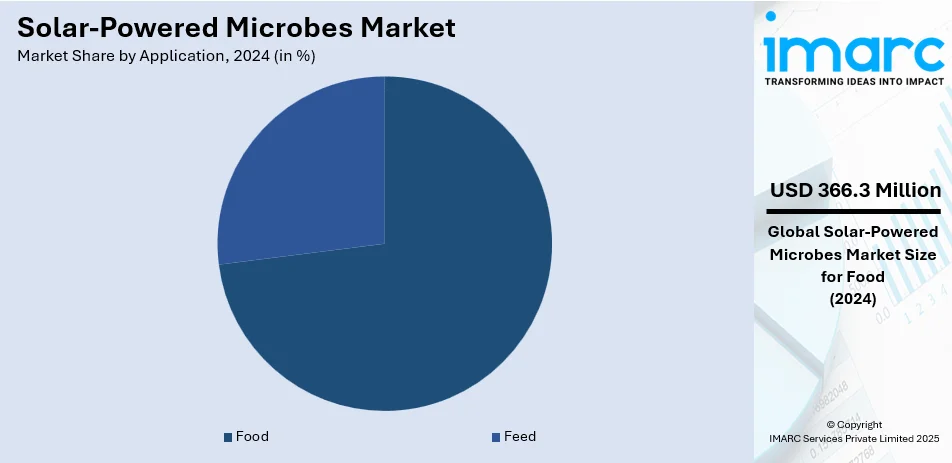
Food dominates the market with 73.5% share. Solar-powered microbes are transforming the food industry by enabling sustainable production of alternative proteins, vitamins, and essential nutrients. Microbial fermentation powered by solar energy reduces reliance on traditional agriculture, minimizing land and water use. Companies are developing lab-grown dairy, plant-based meat enhancers, and biofortified ingredients using engineered microbes. With increasing consumer demand for sustainable and cruelty-free food options, this segment is gaining traction, supported by investments in precision fermentation and regulatory approvals for novel microbial food products. In animal nutrition, solar-powered microbes offer an eco-friendly alternative for producing high-protein feed ingredients, such as single-cell proteins and omega-3 fatty acids. These microbial solutions replace traditional fishmeal and soy-based feeds, reducing deforestation and overfishing. The technology enhances feed efficiency and improves livestock health while lowering carbon emissions. As the global livestock and aquaculture industries seek sustainable feed sources, solar-powered microbial protein is emerging as a scalable and cost-effective solution for the future.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East
- Africa
North America leads the market with 42.5% share in solar-powered microbes market due to strong government funding, advanced biotechnology infrastructure, and growing sustainability initiatives. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and National Science Foundation (NSF) actively support research in microbial bio-manufacturing. Key players and startups in synthetic biology are driving innovation, while industries seek renewable solutions for biofuels and chemicals. With increasing corporate sustainability goals and favorable policies, North America remains a hub for technological advancements and commercialization of solar-powered microbial applications.
Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid market growth due to strong investments in biotechnology, rising demand for sustainable bio-manufacturing, and government-led renewable energy initiatives. China, Japan, and India are at the forefront, leveraging synthetic biology advancements to develop biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and bioplastics using solar-powered microbes. Supportive policies, such as China’s bio-economy strategy and India’s renewable energy focus, are accelerating research and commercialization. With expanding industrial applications and a growing emphasis on reducing carbon emissions, the region is poised for significant market expansion.
Europe is a key player in the solar-powered microbes market, driven by stringent environmental regulations, strong government funding, and the European Green Deal. The EU’s commitment to reducing carbon footprints is encouraging industries to adopt bio-based manufacturing solutions. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are investing in microbial research for biofuels, specialty chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. With a well-established synthetic biology ecosystem and increasing corporate interest in sustainable production, Europe continues to lead in research, innovation, and industrial adoption of solar-powered microbes.
Latin America is emerging as a promising market for solar-powered microbes due to its abundant natural resources, growing bioeconomy, and increasing investments in renewable energy. Brazil, a leader in biofuels, is exploring microbial technologies to enhance sustainable ethanol production. Argentina and Mexico are also investing in synthetic biology research. Government incentives and collaborations with international biotech firms are fostering innovation. As industries seek cost-effective and eco-friendly manufacturing alternatives, Latin America presents significant growth opportunities for solar-powered microbial applications.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) market for solar-powered microbes is growing steadily, driven by increasing interest in renewable biotechnology and resource-efficient production. The region's high solar energy potential makes it ideal for solar-powered microbial systems. Countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing in bio-manufacturing as part of their economic diversification strategies. South Africa is also emerging as a biotechnology hub. Although still in its early stages, the MEA market is expected to expand as research investments and sustainable initiatives gain momentum.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Solar-Powered Microbes Market Analysis
In 2024, the United States accounted for over 88.60% of the solar-powered microbes market in North America. The United States is a leading market for solar-powered microbes, driven by strong government support, advanced biotechnology research, and a well-established renewable energy sector. Federal agencies like the Department of Energy (DOE) and National Science Foundation (NSF) provide significant funding for microbial bio-manufacturing projects, fostering innovation in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. The presence of top-tier research institutions and biotech firms accelerates commercialization. Additionally, the push for sustainable industrial practices and carbon-neutral production is encouraging companies to adopt solar-powered microbial systems for biofuels, bioplastics, and specialty chemicals. With rising carbon emissions, a favorable regulatory environment and increasing corporate investments in green technologies, the U.S. market is poised for steady growth. As per United States Environmental Protection Agency, the biggest source of CO2 emissions in 2022 was the burning of fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel to move people and products; this accounted for 35% of all U.S. CO2 emissions and 28% of all U.S.
Europe Solar-Powered Microbes Market Analysis
Europe is at the forefront of sustainable biotechnology, making it a key region for the solar-powered microbes market. Industries are being pushed into renewable alternatives by the European Union's Green Deal and stringent environmental rules. The revised Ambient Air Quality Directive, as announced by the European Commission, more than halved the annual limit value for PM2.5, the main air pollutant. The revised Ambient Air Quality Directive lowers the permitted levels for 12 air pollutants: particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) ozone (O3), carbon monoxide, benzene, benzo(a)pyrene, cadmium, nickel, arsenic, and lead. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and France have strong research ecosystems focused on synthetic biology and microbial engineering. The emphasis on circular economies and bio-based production fuels the adoption of solar-powered microbial systems for applications such as biofuels, biodegradable plastics, and carbon capture. Additionally, EU funding for renewable biomanufacturing projects and strategic partnerships between research institutions and biotech companies are accelerating market growth.
Asia Pacific Solar-Powered Microbes Market Analysis
Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid growth in the solar-powered microbes market due to increasing industrialization, government initiatives supporting bio-based economies, and rising demand for sustainable solutions. China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in synthetic biology and renewable energy, fostering technological advancements in microbial applications. As published in Carbon Brief, clean-energy investment increased 40% year on year to 6.3 Trillion Yuan USD 890 Billion, accounting for all of the investment growth in the Chinese economy in 2023. China’s commitment to carbon neutrality by 2060 and significant funding for biotech innovation make it a key player in this space. Additionally, growing consumer awareness and corporate sustainability goals are driving demand for bio-based chemicals and fuels. The region’s strong agricultural and pharmaceutical industries further contribute to market expansion.
Latin America Solar-Powered Microbes Market Analysis
Latin America is emerging as a promising market for solar-powered microbes, primarily due to its abundant natural resources, strong agricultural sector, and increasing investments in renewable energy. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are leading the region’s bio-economy efforts, with government incentives promoting sustainable production methods. As per Climate Investment Funds, Brazil will become the second country to benefit from the Climate Investment Funds' Renewable Energy Integration (REI) program in June 2023. Brazil will get USD 70 Million in highly concessional capital to fund clean energy integration solutions, speeding the country's ambitious green energy transition. As part of the strategy, the country aims to increase renewable energy capacity, cut emissions by at least 57 Million Tons of CO2 equivalent, expedite large-scale hydrogen production, and provide clean energy access to millions of people. The demand for biofuels and biodegradable plastics is rising, encouraging the adoption of microbial-based solutions. Additionally, Latin America’s ample sunlight and favorable climate conditions make solar-powered microbial systems highly viable. Collaborations between local research institutions and global biotech firms are further driving innovation and commercialization in the region.
Middle East and Africa Solar-Powered Microbes Market Analysis
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region is gradually entering the solar-powered microbes market, primarily driven by increasing investments in renewable energy and water-efficient biotechnology. Countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are diversifying their economies by funding sustainable industrial projects, including microbial bio-manufacturing. The region’s abundant solar resources create a natural advantage for solar-powered microbial applications. In Africa, the focus on agricultural innovation and bio-based solutions for food security and waste management is fostering market development. While challenges such as infrastructure limitations persist, international partnerships and technology transfers are expected to drive future growth in the MEA region.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading companies are heavily investing in research and development to advance solar-powered microbial technologies. They are working on enhancing the efficiency of microbial strains to optimize energy conversion processes and increase production yields. These innovations are aimed at making microbial systems more cost-effective and competitive with traditional manufacturing methods. To accelerate technological advancements and market penetration, key players are forming strategic partnerships with academic institutions, government agencies, and other companies. For example, collaborations between biotech firms and universities are leading to breakthroughs in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. By joining forces, companies can leverage expertise, resources, and funding to advance their solar-powered microbial solutions. These efforts are creating a favorable solar-powered microbes market outlook.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the solar-powered microbes market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Angel Yeast Co., Ltd
- Associated British Foods plc
- Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- DSM-Firmenich
- Dupont Nutrition & Biosciences
- E&O Laboratories Ltd
- HiMedia Laboratories
- Kemin Industries Inc
- Kerry Foods
- Lallemand Inc
- Lesaffre
- Wyeast Laboratories, Inc
Latest News and Developments:
- In January 2025, Solar Foods, the Finnish food tech pioneer responsible for the protein out of thin air, Solein, announced its improved strategy at its Capital Markets Day on December 10th. Solein is a food ingredient that grows without the need for land or agriculture, making it the world's most sustainable protein. Instead, it is created by growing a single-cell bacterium, one of the billions present in nature, with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and renewable electricity. Solar Foods has received approval to begin commercializing Solein in the United States, which has a Self-affirmed GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) classification.
- In October 2024, Lesaffre, a global fermentation leader, has undertaken a strategic acquisition of Altar, a French firm that specializes in Adaptive Laboratory Evolution (ALE). This acquisition strengthens Lesaffre's existing technology and innovation capabilities. It will significantly improve the group's fermentation and microbe research, development, and manufacturing capacities.
Solar-Powered Microbes Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Bacteria, Molds, Yeast |
| Applications Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Angel Yeast Co., Ltd, Associated British Foods plc, Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, DSM-Firmenich, Dupont Nutrition & Biosciences, E&O Laboratories Ltd, HiMedia Laboratories, Kemin Industries Inc, Kerry Foods, Lallemand Inc, Lesaffre, Wyeast Laboratories, Inc, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the solar-powered microbes market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global solar-powered microbes market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the solar-powered microbes industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The solar-powered microbes market was valued at USD 498.42 Million in 2024.
The solar-powered microbes market is estimated to exhibit a CAGR of 9.70% during 2025-2033.
The solar-powered microbes market share is driven by advancements in synthetic biology, rising demand for sustainable biofuels, and growing interest in carbon-neutral solutions. Government funding, increasing industrial applications, and innovations in microbial engineering further accelerate market growth and commercial adoption.
North America currently dominates the market due to strong government funding, advanced biotechnology infrastructure, and growing sustainability initiatives.
Some of the major players in the solar-powered microbes market include Angel Yeast Co., Ltd, Associated British Foods plc, Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, DSM-Firmenich, Dupont Nutrition & Biosciences, E&O Laboratories Ltd, HiMedia Laboratories, Kemin Industries Inc, Kerry Foods, Lallemand Inc, Lesaffre, Wyeast Laboratories, Inc, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












