
Smart Crop Monitoring Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Technology, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Smart Crop Monitoring Market Size and Share:
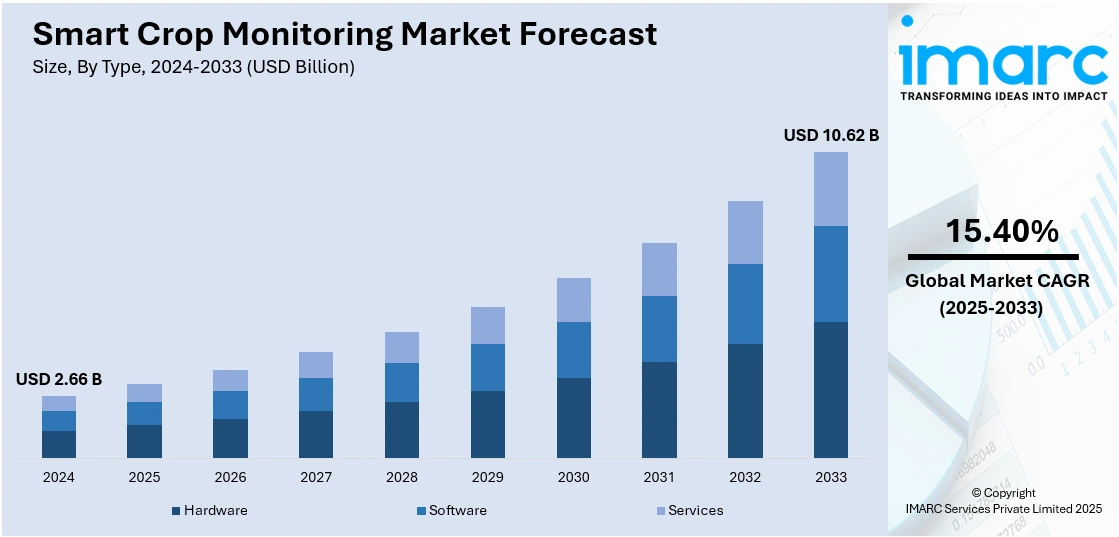
The global smart crop monitoring market size was valued at USD 2.66 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 10.62 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 15.40% from 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market, holding a market share of over 32.5% in 2024. The rising demand for precision agriculture, increasing adoption of internet of things (IoT) enabled sensors, growing concerns over crop yield optimization, expansion of smart farming technologies, and implementation of supportive government initiatives promoting agri-tech innovations are some of the key factors augmenting smart crop monitoring market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.66 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 10.62 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 15.40% |
The market is primarily driven by the increasing investments in precision farming startups, and public-private partnerships that stimulate technological uptake. Moreover, the push towards traceability in food supply chains is also compelling producers to adopt monitoring systems to ensure compliance and transparency. According to industry reports, the world's population is predicted to exceed 10 Billion by 2050, and by the end of the century, it could reach 11 Billion. This rise in global population is placing immense pressure on agricultural systems to enhance food production efficiency without proportionally expanding arable land. This demographic shift necessitates higher crop yields per unit area, thereby leading to smart crop monitoring market demand. Apart from this, regulatory emphasis on agricultural efficiency and environmental stewardship supports continued technology adoption. In addition to this, growing concerns over climate variability are intensifying the need for real-time, adaptive agricultural monitoring frameworks, thereby strengthening market prospects across both developed and emerging economies.
The market in the United States is expanding, driven by the proliferation of agritech startups, and the availability of advanced communication infrastructure. In line with this, the prevalence of high-value crops requiring intensive care is further resulting in an increased need for efficient monitoring solutions. Also, the widespread adoption of automated systems, including drones, autonomous ground vehicles, and stationary sensor arrays, enable continuous surveillance of large agricultural tracts with minimal human intervention. These technologies not only enhance the precision and frequency of crop monitoring but also contribute directly to improved profitability. A 2023 study involving 500 farms across North America found that operations with high levels of automation reported profit margins approximately 40% higher than similarly sized farms with lower automation uptake. Furthermore, the rising demand for sustainable farming practices, supported by USDA-led funding initiatives and grants, is propelling the integration of real-time monitoring technologies.
Smart Crop Monitoring Market Trends:
Adoption of Smart Farming Technologies
The rapid integration of smart farming technologies into mainstream agricultural operations is significantly contributing to the smart crop monitoring market growth. Tools such as automated weather stations, soil sensors, AI-powered decision support systems, and drone-based imaging platforms are widely implemented to collect granular data on field conditions. In contrast to traditional farming, where farmers must regularly visit fields throughout the crop life cycle to assess plant health, smart farming enables up to 80% of monitoring activities to be performed remotely. This allows more time to be dedicated to interpreting crop conditions and planning interventions rather than physically inspecting and managing crops on-site. These systems provide real-time insights into variables such as nutrient levels, pest activity, and water stress, enabling site-specific responses that enhance efficiency and reduce waste. The compatibility of these technologies with mobile platforms ensures accessibility, even across dispersed farming zones, while aligning with broader sustainability and resource optimization goals.
Development of Crop-Specific Monitoring Algorithms and Models
The growing emphasis on creating crop-specific monitoring systems tailored to the physiological and phenological characteristics of individual crops, is positively impacting the smart crop monitoring market outlook. Generalized remote sensing tools are increasingly replaced by algorithms trained on crop-specific spectral, thermal, and morphological data. These models consider parameters like ideal growth stages, stress thresholds, and disease susceptibility patterns unique to each crop. For instance, on March 21, 2025, Penn State researchers introduced a machine vision system employing an AI-driven image segmentation model to monitor bok choy growth in greenhouse environments. This system facilitates continuous, non-invasive tracking of individual plant development, enhancing data accuracy and yield predictions in controlled environment agriculture. The recursive, one-shot segmentation model efficiently identifies overlapping plants without extensive training data, streamlining the monitoring process. In addition to this, the availability of annotated agronomic datasets and advances in supervised learning are enabling higher model accuracy for both disease prediction and yield forecasting. Tailored solutions are also more compatible with regional agronomic practices and climatic conditions, which makes them valuable for localized deployment across diverse agricultural zones.
Growing Adoption of Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing Technologies
The growing adoption of satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies is an emerging smart crop monitoring market trend. These tools are becoming central to large-scale agricultural operations and government-backed surveillance programs aimed at improving crop productivity and sustainability. According to an industry report, satellite images, and remote sensing in agriculture can boost crop yields by as much as 20% with precise management of resources. Moreover, these technologies also allow stakeholders to continuously track crop health, vegetation patterns, and growth stages across expansive areas, offering critical insights throughout the crop cycle. The emergence of commercial satellite providers offering near real-time, cloud-free radar and nighttime imagery is further extending the reach and reliability of such systems, especially in challenging weather conditions or during key nocturnal growth periods. The fusion of satellite imagery with AI, IoT sensors, and predictive analytics is positioning smart agriculture as a data-rich ecosystem capable of transforming decision-making in farming.
Smart Crop Monitoring Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global smart crop monitoring market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type, technology, and application.
Analysis by Type:
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
Hardware leads the market with around 56.8% of market share in 2024. Hardware consists of devices like sensors, GPS modules, drones, weather stations, and probes that collect parameters such as temperature, humidity, moisture, pH, and crop health. These components serve as the foundation for generating actionable insights and sending data into software platforms or cloud-based systems for processing. Reliable and precise hardware guarantees the stability of monitoring, which is vital for timely intervention, maximizing the usage of input, and improving yield. Further, the implementation of internet of things (IoT) based hardware is broadening remote monitoring possibilities, enabling farmers to handle crops effectively over large or dispersed land holdings. As the demand for precision agriculture rises, the hardware segment is further experiencing innovation, especially in autonomous monitoring equipment and multi-parameter sensors, to remain a crucial factor in smart farming strategies.
Analysis by Technology:
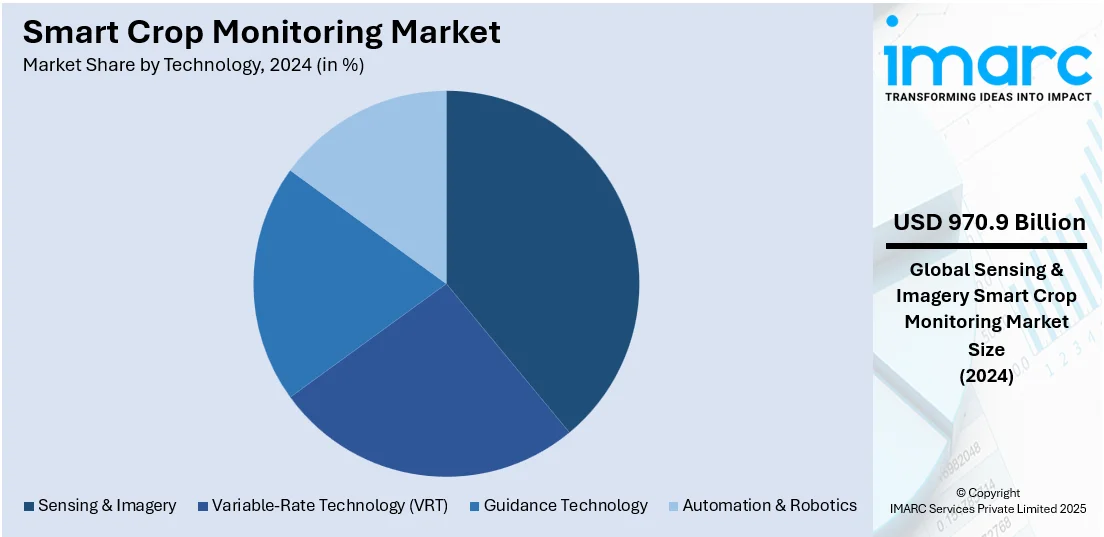
- Sensing & Imagery
- Variable-Rate Technology (VRT)
- Guidance Technology
- Automation & Robotics
Sensing & imagery leads the market with around 36.5% of market share in 2024. These technologies comprise remote sensing instruments, satellite imagery, drones with multispectral or hyperspectral cameras, and ground sensors that take precise data on crop health, soil status, and infestations. By offering high-resolution, real-time images and continuous environmental information, they enable early detection of stress factors, nutrient deficiency assessments, and observation of plant growth patterns at various stages of the crop cycle. This enhances the effectiveness of field management techniques and enables timely intervention, eventually improving yield and efficiency in the use of resources. Sensing and imagery also enable field mapping and variable-rate input application, enabling treatment to be specifically delivered to specific zones. As the uptake of precision agriculture grows, these technologies are widely integrated into farming activities across both large-scale and smallholder farm establishments.
Analysis by Application:
- Soil Monitoring
- Yield Monitoring
- Crop Protection
- Others
Crop protection leads the market with around 31.7% of market share in 2024. This segment emphasizes early recognition and management of pests, diseases, and weeds. Farmers benefit from technologies such as sensor networks, drone-based aerial imagery, and AI-driven analysis that track crop health in real-time and flag affected zones accurately. This enables the precise application of pesticides and fungicides while lowering chemical utilization overall and causing less harm to the environment. Smart crop monitoring systems enable predictive analysis by tracing patterns of weather and environmental conditions responsible for infestations, enabling preventive measures prior to the spread of outbreaks. With increasing pressure from regulatory bodies and consumers toward sustainable agriculture practices, the value of crop protection in smart monitoring is also rising, providing an essential edge toward optimizing input consumption while sustaining productivity and crop quality.
Regional Analysis:
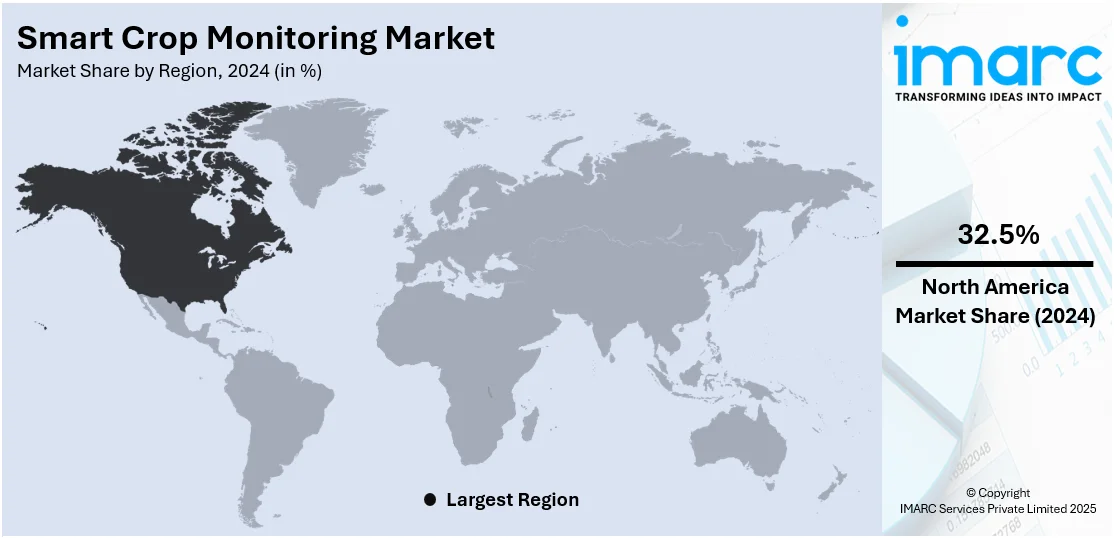
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East
- Africa
In 2024, North America accounted for the largest market share of over 32.5% due its highly developed agricultural infrastructure, high rate of adoption of precision farming methods, and high levels of investment in agri-tech technologies. The region boasts commercial-scale farms that increasingly use IoT devices to monitor, drones for aerial monitoring, and satellite-based monitoring systems to boost crop yields and optimize resource usage. Moreover, implementation of favorable policy initiatives of the government, research expenditure, and partnerships among agri-tech companies and research organizations further drive the use of IoT in agriculture. The United States is particularly at the forefront in adopting data-driven agriculture solutions, due to extensive internet penetration and access to trained technical labor. Rising concerns for climate variability and labor scarcity have also prompted the need for automation and distant monitoring. As farmers aim to maximize output and lower operational expenses, North America remains at the forefront of leveraging technology in agriculture.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Smart Crop Monitoring Market Analysis
The United States holds a substantial share of the North America smart crop monitoring market with 82.60% in 2024. The market in the United States is expanding with growing investments in precision agriculture and digital farming solutions. Also, large-scale farming operations are increasingly integrating advanced technologies into their practices. According to an industry report, yield maps, yield monitors, and soil maps were utilized on 68% of large-scale crop-producing farms in 2023. High-tech adoption by these farms, combined with a thriving ecosystem of agritech innovators, is accelerating the deployment of drones, soil sensors, satellite imagery, and AI-powered platforms across key agricultural regions. Moreover, regulatory encouragement for sustainable farming and water conservation is also pushing the demand for intelligent irrigation management systems. In addition to this, major players are forming partnerships with farming cooperatives to offer subscription-based models, thereby making tech solutions more accessible. Furthermore, government support through grants and pilot programs encourages research and development (R&D) activities in crop analytics and automation, especially in states like California, Iowa, and Nebraska. Additionally, the integration of 5G networks and cloud computing is enhancing the scalability of remote sensing tools.
Europe Smart Crop Monitoring Market Analysis
The smart crop monitoring market in Europe is driven by strong sustainability goals under the EU's Common Agricultural Policy and the Green Deal, which prioritize climate-resilient and resource-efficient farming practices. Precision agriculture is gaining momentum in countries such as Germany, France, and the Netherlands, where smart sensors, drones, and variable rate technology are used to monitor crop health, detect pest outbreaks, and optimize fertilizer application. Additionally, cross-industry collaborations between agri-input companies and tech firms are helping develop real-time monitoring systems with advanced imaging capabilities. Besides this, government incentives and targeted innovation programs are positively impacting the market expansion. On November 8, 2024, the European Commission reported key advancements from the AgriBIT project, which is focused on integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into precision agriculture. The initiative successfully developed eight precision agriculture, enabling real-time crop monitoring and predictive analytics for crops such as tomatoes, vineyards, and peaches. A 20-month pilot phase demonstrated the scalability of these tools across diverse agricultural environments, proving their potential to improve yields while reducing environmental impact. These developments are reinforcing farmer confidence in smart technologies and encouraging wider adoption across both high-tech and traditional farming segments.
Asia Pacific Smart Crop Monitoring Market Analysis
The Asia Pacific smart crop monitoring market is expanding, propelled by rising food demand, climate variability, and government-led agricultural modernization efforts. In countries like China and India, adoption varies widely by region and farm size. In Japan and South Korea, aging farmer populations are driving demand for autonomous and remote farming systems. Notably, in India, the government is investing in sensor-based monitoring, the Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled farm automation, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven analytics as a top priority as it increases productivity and resource efficiency. For instance, on September 17, 2024, the Indian government announced an INR 6,000 Crore (about USD 690 Million) investment to promote precision farming using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), drones, and data analytics. This initiative, under the Mission for Integrated Horticulture Development (MIDH), aims to enhance crop yields by covering 15,000 acres and benefiting 60,000 farmers over five years. In addition to this, regional collaborations with universities and agri-tech startups are generating locally adapted crop monitoring solutions.
Latin America Smart Crop Monitoring Market Analysis
The expansion of high-value crops like soybeans, coffee, and sugarcane drives the smart crop monitoring market in Latin America. Brazil and Argentina are leading the way with precision farming practices, supported by large-scale commercial farms that invest in satellite imaging, drones, and IoT-based crop health monitoring systems. According to industry reports, in Pará State, Brazil, satellite crop monitoring has raised agricultural output by as much as 30% in certain places. Also, challenges such as climate variability and water scarcity are pushing growers to adopt predictive tools and variable rate technologies to boost productivity. Governments are promoting digital agriculture through training programs and tax incentives for tech equipment. Moreover, collaborations with global tech providers are improving access to cloud-based monitoring solutions that offer remote diagnostics and soil analysis. In smaller markets such as Chile and Colombia, agritech startups are targeting fruit and vegetable growers with app-based analytics and localized decision support tools. In addition to this, the growing trend toward climate-smart agriculture and sustainable farming is encouraging broader investment in digital crop monitoring platforms across the region.
Middle East and Africa Smart Crop Monitoring Market Analysis
The smart crop monitoring market in the Middle East and Africa is growing steadily, supported by a strong need to improve agricultural output in arid and semi-arid regions. Water scarcity remains a critical concern for the Middle East, directly influencing the region's approach to agriculture. According to industry reports, about 14 of the thirty-three countries that are expected to face the severe water stress by 2040 are in this region. This projection underscores the urgency of adopting technologies that support water conservation and maximize resource efficiency. As a result, there is a growing reliance on smart crop monitoring systems equipped with sensor-based irrigation control, remote field monitoring, and real-time weather tracking. These tools are helping farmers manage limited water supplies more effectively while maintaining crop productivity. In countries like Israel and the UAE, high-tech greenhouses and precision farming methods use AI, drones, and advanced imaging to maximize yield per drop of water. Sub-Saharan Africa is showing promise, with agritech initiatives focused on smallholder farmers through affordable tools like mobile advisory apps, soil nutrient sensors, and GPS-based field mapping.
Competitive Landscape:
The smart crop monitoring market is characterized by a combination of mature technology vendors and new agri-tech startups providing a variety of hardware and software solutions. Competition is fueled by the capacity to provide real-time insights, compatibility with IoT and AI technologies, and versatility across farm sizes and crop types. Accuracy, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of deployment are parameters on which players compete. Collaboration with agricultural cooperatives, research organizations, and governments is a strategy for increasing reach and credibility. The market observes constant innovation in wireless connectivity, data analytics, and sensor technology to improve monitoring accuracy and decrease the need for labor. With the growing demand for sustainable agriculture and resource efficiency, businesses heavily emphasize enhancing user interfaces, providing predictive analytics, and facilitating seamless integration with the current farm management systems to remain competitive in an increasingly changing agricultural technology landscape.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the smart crop monitoring market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- AGRIV
- IBM Corporation
- KUBOTA Corporation
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- DJI
- AIRBUS
- CropX Inc.
- Semios
- Naïo Technologies
- Microsoft Corporation
- Deere & Company
- CLAAS Group
Latest News and Developments:
- On August 16, 2024, Zambia launched its National Crop Monitor in Lusaka to enhance agricultural resilience amid a severe drought crisis. The initiative leverages Earth Observation data and remote sensing technologies to provide timely and accurate crop condition assessments, aiming to support smallholder farmers and inform policy decisions. This development follows the worst mid-season dry spell in over a century, which devastated approximately one million hectares of maize.
- On March 31, 2025, Walmart announced a partnership with Cropin, an AI-driven agri-intelligence platform, to enhance forecasting and monitoring within its fresh produce supply chain. This collaboration aims to improve yield predictions, monitor crop health, and better anticipate seasonal transitions, thereby strengthening Walmart’s sourcing capabilities across the U.S. and South America. The initiative addresses challenges posed by climate change and supply chain disruptions, with Cropin's technology offering insights into crop readiness, quality forecasts, and sustainability metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions and water usage.
- On April 3, 2025, ARB IOT Group Limited introduced its Smart AI Drone technology aimed at transforming plantation management. This advanced system integrates AI-powered mapping with drone capabilities to deliver precision mapping, crop health monitoring, pest detection, and automated spraying. The technology enables early detection of diseases and nutrient deficiencies utilizing high-resolution aerial imaging and real-time analytics, thereby optimizing resource use and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Smart Crop Monitoring Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Hardware, Software, Services |
| Technologies Covered | Sensing & Imagery, Variable-Rate Technology (VRT), Guidance Technology, Automation & Robotics |
| Applications Covered | Soil Monitoring, Yield Monitoring, Crop Protection, Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East, Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | AGRIVI, IBM Corporation, KUBOTA Corporation, Robert Bosch GmbH, DJI, AIRBUS, CropX Inc., Semios, Naïo Technologies, Microsoft Corporation, Deere & Company, CLAAS Group, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the smart crop monitoring market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global smart crop monitoring market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the smart crop monitoring industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The smart crop monitoring market was valued at USD 2.66 Billion in 2024.
The smart crop monitoring market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 15.40% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 10.62 Billion by 2033.
The market is driven by the increasing adoption of precision agriculture, rising demand for real-time data on crop health, and the growing need to enhance yield efficiency. Factors such as advancements in IoT-enabled agricultural sensors, government support for modern farming practices, and climate variability prompting better monitoring solutions also contribute significantly to the growth of the market.
North America currently dominates the smart crop monitoring market, accounting for a share of 32.5% in 2024. The dominance is fueled by strong investments in agri-tech, widespread usage of GPS and remote sensing technologies, and high awareness among farmers. Supportive regulatory frameworks and early adoption of smart farming tools further reinforce the region’s leading position.
Some of the major players in the smart crop monitoring market include AGRIVI, IBM Corporation, KUBOTA Corporation, Robert Bosch GmbH, DJI, AIRBUS, CropX Inc., Semios, Naïo Technologies, Microsoft Corporation, Deere & Company, and CLAAS Group, among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












