
Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Model Type, Transportation Mode, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Summary:
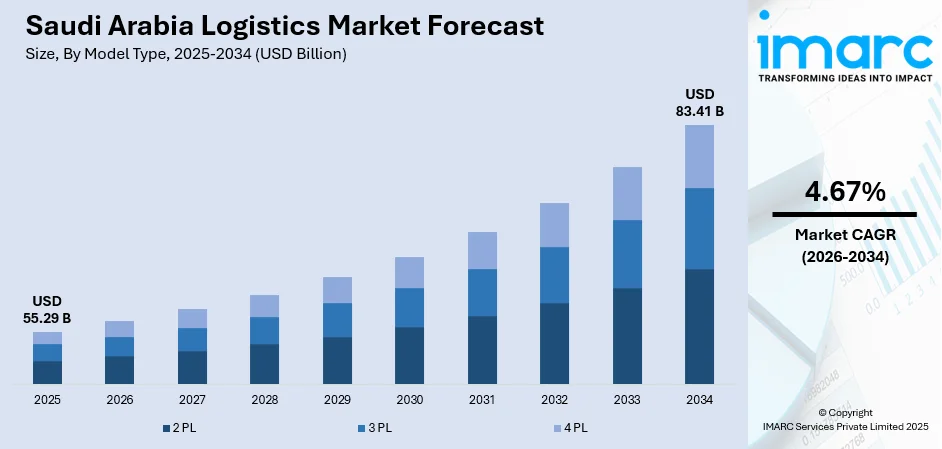
The Saudi Arabia logistics market size was valued at USD 55.29 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 83.41 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 4.67% from 2026-2034.
The Saudi Arabia logistics market is experiencing robust expansion, as the Kingdom accelerates its Vision 2030 economic diversification initiatives. Strategic infrastructure investments, spanning ports, airports, railways, and road networks, are establishing the country as a pivotal global trade corridor connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa. Growing e-commerce penetration, rising manufacturing activities, and expanding cross-border trade partnerships are creating sustained demand for comprehensive logistics solutions. The proliferation of specialized logistics zones and free trade areas is attracting multinational operators and fostering competitive service standards that continue to strengthen the market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Model Type: 3 PL dominates the market with a share of 46.12% in 2025, driven by the increasing preference for outsourcing supply chain operations as businesses focus on core competencies while leveraging specialized expertise for transportation, warehousing, and distribution management.
-
By Transportation Mode: Roadways lead the market with a share of 59.08% in 2025, owing to the extensive highway network that enables flexible door-to-door delivery services across urban centers and industrial hubs.
-
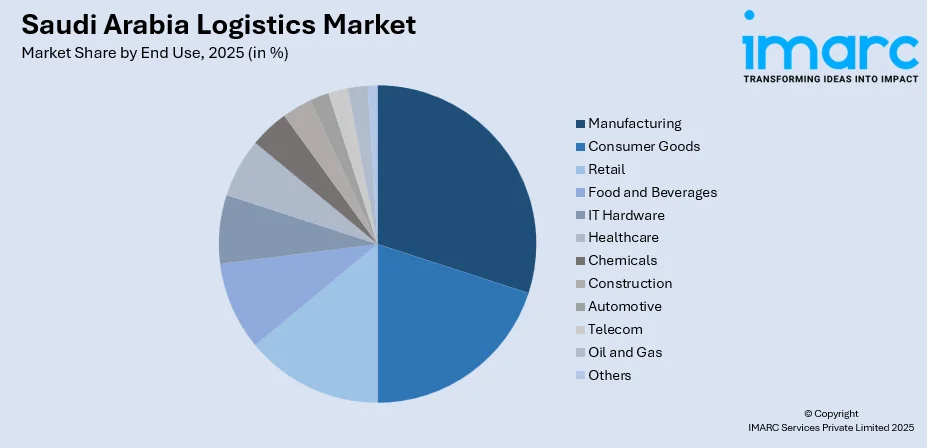
By End Use: Manufacturing represents the largest segment with a market share of 18.07% in 2025, reflecting the Kingdom's industrial diversification strategy supporting petrochemical, automotive, and electronics production facilities requiring integrated logistics solutions.
-
By Region: Northern and Central Region comprises the largest region with 38% share in 2025, driven by Riyadh's position as the economic hub hosting major distribution centers, manufacturing clusters, and the expanding Special Integrated Logistics Zone (SILZ) infrastructure.
-
Key Players: Key players drive the Saudi Arabia logistics market by expanding service portfolios, deploying advanced automation technologies, and strengthening nationwide distribution networks. Their investments in digital platforms, sustainable fleet operations, and strategic partnerships with global operators enhance supply chain efficiency and accelerate market penetration.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Saudi Arabia logistics market is advancing rapidly, as government-backed infrastructure investments and regulatory reforms create a favorable operating environment for logistics providers. The market growth is supported by strategic initiatives under Vision 2030, which aim to transform the Kingdom into a regional logistics hub connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa. Expansion of ports, airports, and road networks is improving cargo handling efficiency and reducing transit times, while regulatory reforms simplify licensing, customs procedures, and cross-border trade. In November 2024, Alstom signed an SAR 300 Million agreement with Saudi Railway Company to enhance the east-west freight corridor, demonstrating continued commitment to strengthening transport connectivity. Increasing demand from the e-commerce, retail, and industrial sectors is driving investments in warehousing, fulfillment centers, and last-mile delivery solutions. Together, these developments are enabling logistics providers to scale operations, enhance service quality, and meet rising domestic and international transportation needs across Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Trends:
Digital Transformation and Technology Integration
The Saudi Arabia logistics market is witnessing accelerated adoption of digital technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and blockchain-based tracking systems. As per IMARC Group, the Saudi Arabia AI market size was valued at USD 1,242.5 Million in 2025. Logistics providers are implementing warehouse management systems with real-time inventory visibility and automated sortation capabilities to enhance operational efficiency. Companies are deploying AI-driven route optimization and predictive analytics to improve delivery accuracy while reducing operational costs across last-mile networks.
Broadening of Free Trade Zones and Special Economic Areas
The proliferation of specialized logistics zones is reshaping the Saudi Arabia logistics market landscape as the Kingdom develops integrated facilities offering streamlined customs procedures and tax incentives. The SILZ near Riyadh's King Khalid International Airport provides a 50-year tax holiday and a system built for 4-hour customs clearance, attracting global operators. These specialized zones enhance supply chain efficiency by enabling faster import-export operations and reducing operational costs for businesses. As a result, they are drawing increased investments from multinational logistics providers and manufacturing companies seeking strategic regional distribution hubs.
Sustainability Initiatives and Green Logistics Adoption
Environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly central to the Saudi Arabia logistics market as operators align with the Kingdom's net-zero emissions targets by 2060. Companies are integrating electric delivery vehicles, solar-powered warehouses, and carbon-neutral fleet operations into their service offerings. The Saudi Green Initiative is driving investments in green logistics solutions across the value chain as regulatory frameworks are increasingly mandating environmental compliance for transport and storage operations.
How Vision 2030 is Transforming the Saudi Arabia Logistics Market:
Vision 2030 is fundamentally transforming the Saudi Arabia logistics market by positioning the Kingdom as a global trade and transport hub connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa. Large-scale investments in ports, airports, rail networks, and logistics zones are improving cargo handling capacity, transit efficiency, and multimodal connectivity. Regulatory reforms are encouraging private sector participation, foreign investment, and competition across logistics services. Digitalization initiatives are streamlining customs clearance, warehouse management, and last-mile delivery through smart platforms and automation. The growth of e-commerce, industrial clusters, and special economic zones is further boosting demand for advanced logistics solutions. Together, these developments are enhancing supply chain resilience, reducing turnaround times, and elevating Saudi Arabia’s competitiveness in regional and global logistics networks.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Saudi Arabia logistics market is positioned for sustained expansion, as Vision 2030 initiatives continue to drive infrastructure development and service modernization. The market generated a revenue of USD 55.29 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 83.41 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 4.67% from 2026-2034. E-commerce growth, manufacturing sector expansion, and rising cross-border trade volumes will sustain demand for integrated logistics solutions. The upcoming FIFA World Cup 2034 and Expo 2030 will accelerate infrastructure buildout while attracting global logistics operators seeking regional expansion opportunities. Strategic positioning at the crossroads of three continents, combined with liberalized foreign ownership regulations, ensures continued foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows that strengthen competitive dynamics across the sector.
Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Model Type | 3 PL | 46.12% |
| Transportation Mode | Roadways | 59.08% |
| End Use | Manufacturing | 18.07% |
| Region | Northern and Central Region | 38% |
Model Type Insights:
- 2 PL
- 3 PL
- 4 PL
3 PL dominates with a market share of 46.12% of the total Saudi Arabia logistics market in 2025.
The 3 PL segment leads the Saudi Arabia logistics market, as businesses increasingly outsource transportation, warehousing, and distribution operations to specialized providers. The segment's growth reflects rising demand for comprehensive supply chain solutions that enable companies to focus on core business activities while accessing advanced logistics capabilities. The Saudi Arabia 3 PL market reached USD 14.5 Billion in 2025, driven by e-commerce expansion and manufacturing sector growth requiring efficient inventory management and last-mile delivery services across the Kingdom.
International logistics providers are expanding their presence through strategic acquisitions and partnerships with local operators to capture market opportunities. Government initiatives supporting foreign investment and regulatory liberalization have enabled global companies to establish integrated operations combining transportation, warehousing, and value-added services. The increasing complexity of supply chains and rising consumer expectations for faster, more reliable deliveries further bolster demand for 3PL services. Advanced technologies, including AI-driven route optimization, warehouse automation, and real-time tracking, are enhancing service efficiency and reinforcing the segment’s leadership in the market.
Transportation Mode Insights:
- Roadways
- Seaways
- Railways
- Airways
Roadways lead with a share of 59.08% of the total Saudi Arabia logistics market in 2025.
Roadways command the largest share of the Saudi Arabia logistics market owing to the extensive road network spanning 73,000 kilometers connecting major urban centers, industrial zones, and border crossings. The segment's dominance reflects the flexibility of trucking services for door-to-door delivery, time-sensitive shipments, and last-mile distribution across diverse geographic regions. Road transport also offers adaptability for varying shipment sizes and routes, making it a preferred option for both domestic and regional logistics operations.
Infrastructure modernization programs are enhancing road transport efficiency through projects, such as the Eastern Expressway connecting Riyadh to Dammam, improving connectivity between industrial centers and seaports. Fleet operators are adopting telematics systems, fuel-efficient vehicles, and digital freight-matching platforms to optimize asset utilization and reduce operational costs. Additionally, upgraded highways, bypasses, and logistics hubs are reducing transit times and congestion, supporting faster, more reliable road-based supply chain operations across the Kingdom.
End Use Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Manufacturing
- Consumer Goods
- Retail
- Food and Beverages
- IT Hardware
- Healthcare
- Chemicals
- Construction
- Automotive
- Telecom
- Oil and Gas
- Others
Manufacturing exhibits a clear dominance with an 18.07% share of the total Saudi Arabia logistics market in 2025.
The manufacturing sector drives logistics demand through expanding petrochemical complexes, automotive assembly plants, and electronics production facilities requiring integrated supply chain solutions. Vision 2030 localization mandates are accelerating industrial diversification, creating sustained requirements for inbound raw material flows and outbound finished goods distribution. Automotive assembly clusters in King Abdullah Economic City and Jeddah require synchronized just-in-time parts delivery and certified freight forwarding services supporting export operations to regional markets.
Industrial logistics complexity is increasing as manufacturers demand quality-certified handling, temperature-controlled storage for sensitive components, and real-time shipment visibility across extended supply chains. Export-oriented small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are leveraging government-backed financing programs to penetrate African and Asian markets, generating sustained demand for international freight forwarding and customs brokerage services. These evolving requirements are prompting logistics providers to invest in advanced tracking technologies, specialized storage facilities, and skilled workforce training to meet the high standards expected by manufacturers.
Regional Insights:
- Northern and Central Region
- Western Region
- Eastern Region
- Southern Region
Northern and Central Region represents the leading segment with a 38% share of the total Saudi Arabia logistics market in 2025.
Northern and Central Region dominates the Saudi Arabia logistics market, driven by Riyadh's position as the Kingdom's economic and administrative capital hosting major corporate headquarters, retail distribution centers, and expanding manufacturing operations. The capital's 2025 population was projected at 7,952,860, creating substantial consumer demand supporting e-commerce fulfillment and last-mile delivery networks. The region’s well-developed road infrastructure and strategic location enhance connectivity with other key urban centers and industrial zones.
Logistics providers are increasingly investing in advanced distribution centers, automated warehousing, and technology-driven inventory management systems to meet growing demand in Northern and Central Region. The rise of e-commerce and retail expansion is driving last-mile delivery innovations, while multinational companies and SMEs leverage these logistics networks for efficient domestic and regional distribution. This makes the region a critical hub for both commercial and industrial supply chain operations.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Growing?
Vision 2030 Infrastructure Development Programs
The logistics market in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is growing strongly, supported by large-scale infrastructure development initiatives in line with the Vision 2030 national transformation agenda. The government-led strategy has been focused on establishing integrated multimodal transport networks that build strong connectivity in air, sea, rail, and road systems. Considerable investments are being made towards the modernization of ports, expansion of airport cargo capacity, and extension of rail corridors to achieve higher efficiency in domestic distribution and international trade. The government targets increasing the transport and logistics sector's GDP contribution from 6% to 10% by 2030, creating substantial capital flows into modernization programs. The port expansion projects are enhancing the ability to handle cargo, turning around ships, and facilitating more trade. On the other hand, the development of the rail network will increase the connectivity of the industrial areas to the gateway ports, facilitating the economical transportation of cargo by rail. Overall, these projects will place Saudi Arabia in a paramount position as a logistics platform that interconnects the global trading routes of Asia, Europe, and Africa.
E-Commerce Expansion and Digital Retail Growth
The rapid expansion of e-commerce portals is creating sustained demand for warehousing, fulfillment, and last-mile delivery services across the Saudi Arabia logistics market. Online retail penetration has accelerated with 34.4 Million people using the internet by the end of 2025, driving requirements for efficient order processing and rapid delivery capabilities. Consumers are increasingly expecting same-day or next-day delivery, prompting logistics providers to establish micro-fulfillment centers, optimize distribution networks, and expand delivery fleets. Advanced technologies are being deployed to enhance efficiency and meet rising service expectations. Cross-border e-commerce is also broadening, as consumers seek a broader variety of international products, creating demand for specialized customs clearance, international shipping, and parcel management solutions. This shift is encouraging logistics operators to adopt integrated, technology-enabled supply chain models capable of handling higher volumes, tighter delivery timelines, and complex international trade requirements, reinforcing the overall growth of the market.
Strategic Geographic Positioning and Trade Facilitation
Saudi Arabia's location at the crossroads of three continents positions the Kingdom as a natural logistics hub for Asia-Europe-Africa trade flows driving sustained market expansion. The country's access to the Red Sea, Arabian Gulf, and Indian Ocean shipping lanes provides connectivity to major global markets through established port infrastructure. Government initiatives, including cabotage relaxation and streamlined customs procedures, are enhancing the Kingdom's attractiveness for transit trade and regional distribution operations. Various programs aid in attracting foreign investment across key industries, including aerospace, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and renewables, strengthening Saudi Arabia's integration into international supply chains. New shipping services connecting Saudi ports with East Asian markets, including Singapore, Shanghai, and Colombo, are expanding export competitiveness while reducing transit times for inbound cargo movements.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Saudi Arabia Logistics Market is Facing?
Skilled Workforce Shortage and Talent Gap
The Saudi Arabia logistics market faces significant challenges from a shortage of skilled professionals, particularly in emerging technology domains, including automation and advanced supply chain management. The rapid industry growth has created a supply-demand gap for workers qualified in warehouse management, logistics technology integration, and digital platform operations. Saudization requirements mandating domestic employment quotas add complexity to workforce planning while increasing recruitment and training costs for logistics operators.
Infrastructure Capacity Constraints and Warehousing Shortage
Despite ongoing infrastructure development, the Saudi Arabia logistics market continues to face capacity constraints as demand growth outpaces the availability of modern facilities in major urban centers. High warehouse utilization levels are placing pressure on storage availability, leading to rising rental costs and limited expansion options. This shortage creates operational challenges for importers, distributors, and e-commerce players, particularly those operating in time-sensitive delivery segments that depend on strategically located inventory and efficient fulfillment capabilities.
High Technology Integration Costs
The adoption of advanced technologies critical for competitive logistics operations remains a significant barrier, especially for SMEs. Automation, blockchain-based tracking, and advanced material handling systems require substantial upfront capital, along with recurring maintenance and skilled workforce training costs. These financial and operational burdens slow technology adoption among local players, widening the efficiency gap between large, well-capitalized operators and smaller logistics providers.
Competitive Landscape:
The Saudi Arabia logistics market exhibits a fragmented competitive structure with international integrators and regional operators contesting specialized service segments. Global players are expanding presence through strategic acquisitions, joint ventures, and infrastructure investments targeting high-growth sectors. Local companies leverage domestic market knowledge and regulatory familiarity to serve traditional industries while investing in technology upgrades to maintain competitiveness. Competition intensifies as operators deploy automation, digital platforms, and multimodal capabilities to differentiate service offerings. Strategic partnerships between international and domestic firms are becoming prevalent as companies seek to combine global expertise with local operational networks. The market is witnessing consolidation as capital-intensive requirements favor larger operators capable of investing in modern facilities and advanced technologies.
Recent Developments:
-
In November 2025, DHL Supply Chain announced a EUR 130 Million investment to establish a 78,000 square meter regional logistics hub at Saudi Arabia's SILZ in Riyadh. The facility will feature 53,000 square meters of advanced multi-user warehouse space serving the technology, retail, automotive, energy, and e-commerce sectors under a 26-year lease agreement.
-
In August 2025, DHL eCommerce completed its minority stake acquisition in AJEX Logistics Services, a leading Saudi parcel delivery company. The strategic partnership positions both companies to capitalize on anticipated double-digit growth in Saudi Arabia's e-commerce sector while expanding last-mile delivery capabilities across the Middle East region.
Saudi Arabia Logistics Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Model Types Covered | 2 PL, 3 PL, 4 PL |
| Transportation Modes Covered | Roadways, Seaways, Railways, Airways |
| End Uses Covered | Manufacturing, Consumer Goods, Retail, Food and Beverages, IT Hardware, Healthcare, Chemicals, Construction, Automotive, Telecom, Oil and Gas, Others |
| Regions Covered | Northern and Central Region, Western Region, Eastern Region, Southern Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Saudi Arabia logistics market size was valued at USD 55.29 Billion in 2025.
The Saudi Arabia logistics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.67% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 83.41 Billion by 2034.
3 PL dominated the market with a share of 46.12%, driven by increasing outsourcing of supply chain operations as businesses leverage specialized logistics expertise for transportation, warehousing, and distribution management services.
Key factors driving the Saudi Arabia logistics market include Vision 2030 infrastructure investments, e-commerce expansion, strategic geographic positioning, manufacturing sector growth, and increasing cross-border trade partnerships.
Major challenges include skilled workforce shortages, particularly in technology domains, warehousing capacity constraints in urban centers, high technology integration costs, regulatory compliance requirements, and infrastructure development keeping pace with demand growth.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












