
Railroad Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Distance, End Use and Region, 2025-2033
Railroad Market Size and Share:
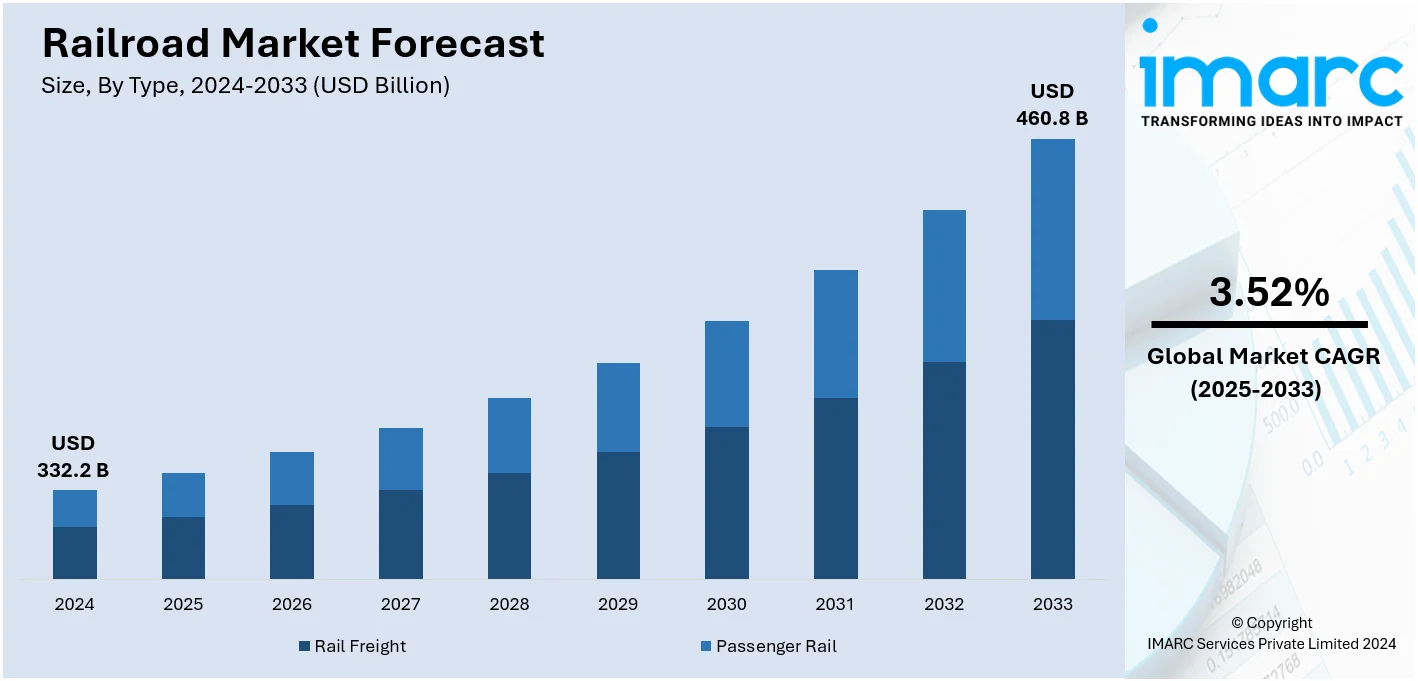
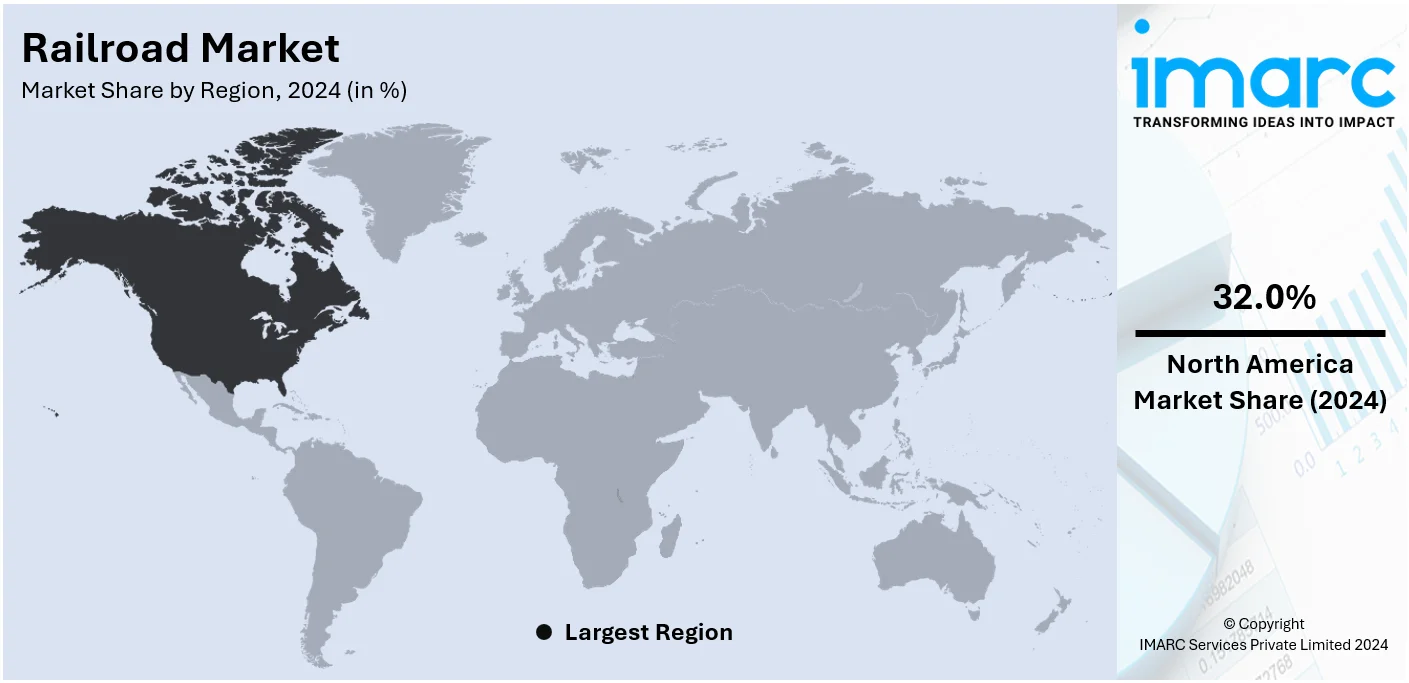
The railroad market size was valued at USD 332.2 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 460.8 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.52% from 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market in 2024. The market growth is driven by the rising awareness among individuals about environmental sustainability, favorable government initiatives, and innovations like automated train operation, intelligent signaling systems, and real-time monitoring tools.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 332.2 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 460.8 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 3.52% |
The railroad market growth is increasing due to the development of infrastructure, where both governments and private entities are committing significant resources toward the expansion and upgrading of rail lines. This includes the new rail line construction, upgrades of existing tracks, and building high-speed rail systems that would enhance connectivity and efficiency for both passengers and freight. Moreover, environmental concerns also promote the implementation of rail transport as trains have fewer emissions per ton-mile than trucks or airplanes. Thus, in this regard, rail is the most sustainable option. This will be very vital during the increasing campaigns to fight against climate change and reduce urban congestion. Another major factor is the rise of urbanization, where more people are moving into cities, thus increasing the demand for mass transit options such as commuter rails and subways to alleviate traffic and provide efficient mobility solutions. Technological innovations, such as automation, digital signaling systems, and energy-efficient locomotives, are transforming industry, enhancing safety, speed, and operational efficiency. Furthermore, the growth of e-commerce has created a demand for efficient freight transport solutions, with railroads being the key mover of large volumes of goods across regions, which are cost-effective and reliable.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The United States has emerged as a key regional market for railroads, driven by factors such as infrastructure investment, technological innovation, and the need for efficient freight transport. Thus, the ongoing expansion of its rail networks remains a very important focus for both the public and private sectors in terms of upgrading tracks and stations and upgrading high-speed rail systems. Infrastructural development supports the rapidly increasing demand for efficient passenger and freight services. The largest market driver for freight transport is rail, as it continues to play an important role in moving goods around the country. Railroads play a vital role in industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and energy as they offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to trucking. Technological developments in digital signaling, automation, and data analytics enhance the safety, efficiency, and capacity of rail networks. E-commerce further fuels the railroad demand for reliable freight transport, which railroads service in large volumes over long distances. Environmental regulations and the push to reduce carbon emissions are also forcing more sustainable transport options and positioning rail as an eco-friendly solution.
Railroad Market Trends:
Favorable government initiatives
Governing authorities of many countries are investing in rail infrastructure through public funding and long-term infrastructure development plans. According to the India Brand Equity Foundation, India will spend around USD 1,727.05 Billion on infrastructure in seven fiscal years till 2030. Rail is a solution suitable to several societal challenges, such as reducing traffic congestion, enhancing economic connectivity, and promoting sustainable growth. Along with policies, the governments initiate funding projects for high-speed rail, improvement of existing rail lines, and new network development. The governing bodies are also enhancing policies to encourage industries to shift from road to rail transport by initiating subsidies and incentives for those industries that rely on rail logistics.
Environmental concerns and sustainability
Increased awareness about being environmentally sustainable from individuals' perspectives are highly influencing the railroad market trend. Rail transport is the least ecologically harmful of all means among air and road travel, with its comparison showing lower amounts of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions per passenger or metric ton of freight. For example, global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions increased by 51% from 1990 to 2021. To meet climate targets, governing agencies of different countries are imposing severe environmental regulations to encourage the use of environmentally friendly transportation methods. Specifically, electrified rail systems help in decarbonization efforts by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Investments in rail infrastructure, including electrification projects and the development of hydrogen-powered or electric trains, support global climate objectives. The increasing emphasis on improved passenger comfort is also driving growth in the railroad market.
Technological advancements
Automated train operation, smart signaling systems, and real-time monitoring tools improve the safety, efficiency, and reliability of rail transport. With more autonomous trains on the way, it reduces the involvement of manual interference and human errors while increasing efficiency in operation. Smart rail systems that include the Internet of Things (IoT) enable predictive maintenance, route optimization, and enhanced energy efficiency. This increases the railroad market share. Digitalization also transforms passenger experience through mobile ticketing, real-time updates, and better user service platforms. These developments, coupled with the adoption of green technologies like electrified and hydrogen-powered trains, make rail transport more sustainable and attractive.
Railroad Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the railroad market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type, distance, and end use.
Analysis by Type:
.webp)
- Rail Freight
- Passenger Rail
Passenger rail is the leading segment. This is attributed to the growing demand for eco-friendly, cost-effective, and efficient modes of transportation in urban and suburban areas. Passenger rail systems play an important role in reducing traffic and are a more sustainable alternative to road and air travel as urban populations continue to grow. High-speed rail networks, too, have become very popular for long-distance traveling, as they travel considerably faster and with greater reliability than cars and airplanes. It is also environmentally friendly, as trains produce a much lower volume of greenhouse gas emissions per passenger compared to any other form of transportation. All governments around the world are investing in expanding and modernizing their rail networks as a means of catering to ever-increasing commuting needs, increasing efficiency in service provision, and reducing congestion. The shift toward more sustainable transportation solutions further supports the dominance of passenger rail in the market, making it the leading segment in the global railroad industry.
Analysis by Distance:
- Long Distance
- Short Distance
The long distance category can offer both freight and passenger services in a very cost-effective manner for large distances over vast geographical areas. Rail has a comparative cost advantage over road or air transport for the transportation of bulk products such as coal, iron ore, steel, and agricultural products. This segment also derives benefit from rail's capability of carrying massive amounts of freight all at one go, an appropriate choice for large industries, for example, mining and agriculture, where one needs the delivery of volumes as a result. In addition to freight, long-distance passenger rail services are also increasingly used, such as high-speed trains, where transportation is quicker and cheaper with a relatively lower pollution impact than travel by air or by road. These services ease congestion on highways and offer a more sustainable transportation solution. On the other hand, the short-distance rail segment, while vital for urban commuting and regional freight, does not command the same economic scale as long-distance services. Short-distance rail deals mainly with commuter transport in metropolitan areas that reduces traffic and provides a greener alternative to vehicles however, has a more limited impact compared to long-distance rail.
Analysis by End Use:
- Mining
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Others
The mining industry is one of the biggest contributors to rail transport demand as the raw materials, such as coal, iron ore, and minerals, need the most efficient and cost-effective logistics for moving. Rail becomes the preferred choice for long-haulage of these bulky commodities as the volume can be transported over enormous distances at costs much lower compared to trucks. In addition, rail has fewer carbon emissions per ton-mile, so it is another option for mines that are facing environmental regulations. The construction industry is another major end-user of rail in transporting bulk construction materials such as cement, steel, aggregates, and machinery. Construction goods are high volume and weight. Thus, it is suitable for massive infrastructure projects as the rail ensures that construction sites get timely delivery of materials with minimum costs. Agriculture uses much of the railway for transporting crops, grains, livestock, and fertilizers. It provides an efficient method for shipping agricultural products over long distances to connect rural farming regions with urban markets. Its capacity to move high volumes of agricultural products across long distances ensures an efficient throughput of products from farms to processing plants or export centers, thus, it is an integral part of the agricultural supply chain. Each of these end-use sectors relies on rail for its capacity to move high volumes of goods in a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable manner.
Analysis by Region:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
North America leads this market due to extensive rail networks developed there and huge demand for both efficient freight as well as transportation of passengers in the region. The United States, for its part, sports one of the largest and best rail systems that cover a substantial part of the rural and urban areas. Bulk freight is critical for North America due to its bulk commodity requirements like coal, agriculture, and manufactured products, hence becoming the primary driver for rail freight. Other industrial drivers like mining, agriculture, and manufacturing provide a robust source of economic needs, thus also demanding more usage of rail transportation. The importance of sustainability on environmental issues, like reducing carbon emissions, is currently one of the significant factors. Rail transport, compared to road and air, presents a more environmentally friendly way of transportation. The North American region takes the lead in environmentally friendly logistics. Besides that, North America is highly investing in upgrading its rail infrastructure and developing high-speed rail services with efficiency improvement for freight operations so that the continent continues to hold a dominant position in the railroad market of the world.
The Asia Pacific market growth is due to fast-paced urbanization and population increase. Countries in the region like China, India, and Japan have been undertaking rail infrastructure with massive investments in high-speed rail networks and freight systems that increase demand in the passenger as well as freight markets. For instance, the extensive rail network in China is its key logistics sector. In Japan and South Korea, high-speed trains are propelling the growth of passenger railways. The focus on sustainable transport solutions in the region bodes well for rail as a greener alternative.
Europe's railroad market is driven by the region's robust rail infrastructure, sustainability goals, and technological advancements. The European Union's policies are centered around carbon emissions, and rail transport is a strategic component of attaining the carbon target. Countries such as France, Germany, and Spain possess high-speed rail networks that, along with their freight systems, help move people and goods across borders. There is also an emerging demand for commuter rail and smart rail in urban areas due to cities' increased focus on using environmentally friendly modes of transportation as a way of combating congestion and environmental degradation.
Latin America sees opportunities in railroad-based freight and efficient urban transport, and some revival of the network is visible through investments in revamping rail systems by countries such as Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico. However, most such improvements are largely oriented toward handling commodities like soybeans, minerals, and farm produce. Increasing infrastructural development investments and public-private collaborations are on an upward growth path for freight services. The other one is the urban rail system. They are coming up to try to solve the traffic congestion in major cities such as Sao Paulo, Buenos Aires, and Mexico City with high demand for commuter rail services.
The railroad market is growing in the Middle East and Africa due to large investments in rail infrastructure led by government efforts and economic diversification. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are building high-speed rail systems for passenger travel, while other countries are developing freight rail to support industries such as oil, mining, and agriculture. The region's thrust toward sustainable infrastructure and reducing dependency on road transport fuels the demand for rail. Key projects such as the Saudi Arabian North-South Railway and Morocco's rail modernization are crucial drivers of market growth.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Railroad Market Analysis
Investments in infrastructure are increasing to improve connectivity between urban and rural areas, which is driving the growth of expanding rail networks. According to the U.S. Department of the Treasury, two years ago, President Biden's USD 1.2 Trillion Bipartisan Infrastructure Law was signed, fueling significant railroad improvements through state-allocated funds that boost efficiency and support economic growth in U.S. transportation infrastructure. Modernization of existing lines and new routes leads to streamlined freight transport and reduced transit times. Industrial hubs and logistics corridors are being developed to integrate rail as the primary mode of transportation, reducing reliance on road freight. Advanced technologies such as electrification and signaling upgrades improve operational efficiency and promote sustainability. Intermodal facilities, which connect rail with other transport modes, help ensure smooth cargo movement. The modernization of passenger rail networks is also leading to higher speeds and improved ease of commuting for passengers. In addition, expanding suburban rail systems provide regional connectivity to growing metropolitan populations. The use of renewable energy in rail transport is also making the transport option greener.
Europe Railroad Market Analysis
The agricultural sector's need for efficient transportation dictates the adoption of rail to deliver produce and commodities on time. Rail systems support the transportation of grains, fruits, and other perishables in bulk so that wastage during transit is minimal. For example, the GCF of the Indian agriculture sector grew at the rate of 19.04 percent in 2022-23. Cold chain logistics development integrated with rail enhances the movement of temperature-sensitive goods. Investments in dedicated rail corridors for agricultural exports improve access to ports and reduce logistics costs. Regional rail connectivity enables farmers in remote areas to gain access to national and international markets. New-generation freight wagons for agriculture are improving the load capacity and efficiency of handling. Rural area infrastructure development helps meet the growing demand of rising agricultural production with better rail accessibility. Besides, rail systems have been pivotal in facilitating cooperative farming and agro-industrial complexes by ensuring that farmers reach wider markets effectively.
Asia Pacific Railroad Market Analysis
Increasing tourism is developing passenger rail systems to serve travelers who prefer a more efficient and scenic journey. For example, in 2024, the region expects an increase of 23% in tourist volumes, and Northern Europe will grow faster than Southern Europe, with 12% versus 10%, indicating healthy growth across all European subregions. High-speed rail options connecting major cities and cultural landmarks enhance accessibility. Heritage routes with iconic landscapes and historical sites attract tourists, offering unique travel experiences. Investments in luxury and panoramic trains are creating niche travel opportunities, appealing to premium market segments. Enhanced onboard amenities, such as Wi-Fi and dining options, improve passenger satisfaction and convenience. Seasonal routes tailored to festivals, winter sports, and coastal getaways are gaining popularity. Rail's lower environmental footprint compared to other transport modes aligns with sustainable tourism trends, appealing to eco-conscious travelers. Ticketing systems are integrated across transport modes to ensure that tourists traveling to multiple destinations can travel seamlessly. Rail hubs located near major airports and hotels further enhance accessibility for international visitors.
Latin America Railroad Market Analysis
Mining activities rely on railroads to efficiently transport extracted minerals from remote sites to processing plants and export terminals. For example, in 2023, Latin America was the destination of almost half (45.9%) of the world's copper exploration budget, and Chile was the leader, as copper represented an impressive 82% of its mining sector investments. Robust freight wagons designed for heavy loads ensure safe and efficient transportation of bulk minerals. Dedicated rail lines connecting mining regions to industrial zones enhance supply chain efficiency. Investments in track durability and safety measures support the long-term reliability of mining rail networks. Electrification of rail operations reduces energy costs, contributing to sustainable mineral transportation. These advancements are crucial to meeting the increasing global demand for raw materials while supporting regional economic development.
Middle East and Africa Railroad Market Analysis
The booming construction industry relies on rail networks for the smooth transportation of raw materials like cement, steel, and aggregates to urban and infrastructure projects. For example, Saudi Arabia's construction industry is booming, with more than 5,200 projects currently underway, worth USD 819 Billion, reflecting the rapid growth in infrastructure development and economic activities. Railways ensure mass movement that reduces road congestion and avoids logjam delays. Advanced freight services are specialized in the construction industry for on-time delivery and cost-effectiveness. Rail infrastructures are developing links to quarries and industrial locations, making material supply chains easier. More advanced rail technologies are developed for carrying high-capacity loads, fulfilling the requirements of large-sized infrastructure development projects. All these can prove to be crucial for driving both urbanization and the modernization processes underlying different regions.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players are aiming at enhancing infrastructure, improving efficiency, and promoting sustainability. A significant focus is placed on expanding and modernizing rail networks, particularly high-speed rail and freight systems, to meet the growing demand for both passenger and cargo transport. Investments in digital technologies such as automation, predictive maintenance, and real-time tracking systems are helping improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance service reliability. Besides that, most key participants are now concentrating on environmental sustainability while promoting rail over road and air transport. Their efforts in achieving this goal will include the process of electrification of the systems and lowering the carbon footprint per ton mile. Public-private partnerships with government support on funding also assist in promoting larger infrastructure projects for developing regions or urban cities in traffic congestion conditions. With urbanization and industrialization increasing, rail systems are being incorporated into larger transportation networks to promote economic development while offering an eco-friendly solution for long-distance freight and urban commuter needs.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the railroad market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Bnsf Railway Company
- Canadian National Railway Company
- CPKC
- Japan Freight Railway Company
- Norfolk Southern Corp.
- PKP Cargo International
- SBB Cargo International AG
- SNCF Group
- Union Pacific
Latest News and Developments:
- January 2025: China Railway says that by 2030, it will expand the high-speed rail network to 60,000 km from 48,000 km in 2024. The total railway network is expected to increase from 162,000 km in 2024 to 180,000 km by 2030. This ambitious plan shows China's commitment to improving its transport infrastructure. The expansion supports economic growth and connectivity across the country.
- December 2024: China’s high-speed rail network has grown to 47,000 kilometers, significantly enhancing transportation efficiency, tourism, and economic growth. This expansion underscores China’s commitment to infrastructure modernization and development. The milestone reflects the strategic role of railways in the nation’s progress. The achievement was reported by a leading railway transport news portal.
- December 2024: India's first bullet train, the Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR), is a 508-kilometer stretch that will be using advanced Shinkansen technology from Japan. Indian Railways has achieved key milestones, completing over 331 kilometers of pier structures and progressing on a 21-kilometer undersea tunnel, a national first. The project aligns with the "Make in India" initiative, emphasizing technology transfer and innovation.
- December 2024: A $5 million regional New South Wales investment is strengthening the country's rail systems. A new facility being built by Brimble at Dungog, on the site of an old timber mill, will play a critical role in rail resurfacing. Strategically placed near key corridors, the facility supports infrastructure improvements across the nation. This is just one of Brimble's efforts to continue modernizing and sustaining Australia's rail networks.
- October 2024: The US Department of Transportation's Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) has committed more than $2.4 Billion to support 122 rail improvement projects across the country through the CRISI Program. Covering 41 states and Washington, D.C., this initiative will further improve rail safety, efficiency, and reliability while saving shipping dollars, reducing emissions, and bolstering supply chain resilience. Funds come from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
Railroad Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Rail Freight, Passenger Rail |
| Distances Covered | Long Distance, Short Distance |
| End Uses Covered | Mining, Construction, Agriculture, and Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Bnsf Railway Company, Canadian National Railway Company, CPKC, Japan Freight Railway Company, Norfolk Southern Corp., PKP Cargo International, SBB Cargo International AG, SNCF Group, Union Pacific, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the railroad market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global railroad market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the railroad industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
A railroad is a type of transportation of people and goods that moves on tracks that are used by trains. The mode of transportation is reliable and energy-efficient, particularly in long-distance travel and freight transport, which makes them very important for various industries such as logistics, manufacturing, and also passenger travel.
The railroad market was valued at USD 332.2 Billion in 2024.
IMARC estimates the railroad market to exhibit a CAGR of 3.52% during 2025-2033.
The market growth is driven by the rising awareness among individuals about environmental sustainability, favorable government initiatives, and innovations like automated train operation, intelligent signaling systems, and real-time monitoring tools.
In 2024, passenger rail represented the largest segment by type, driven by the growing demand for eco-friendly, cost-effective, and efficient modes of transportation in urban and suburban areas.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa, wherein North America currently dominates the global market.
Some of the major players in the global railroad market include Bnsf Railway Company, Canadian National Railway Company, CPKC, Japan Freight Railway Company, Norfolk Southern Corp., PKP Cargo International, SBB Cargo International AG, SNCF Group, Union Pacific, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












