
Middle East Meat Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Product, Distribution Channel, and Country, 2025-2033
Middle East Meat Market Size and Share:
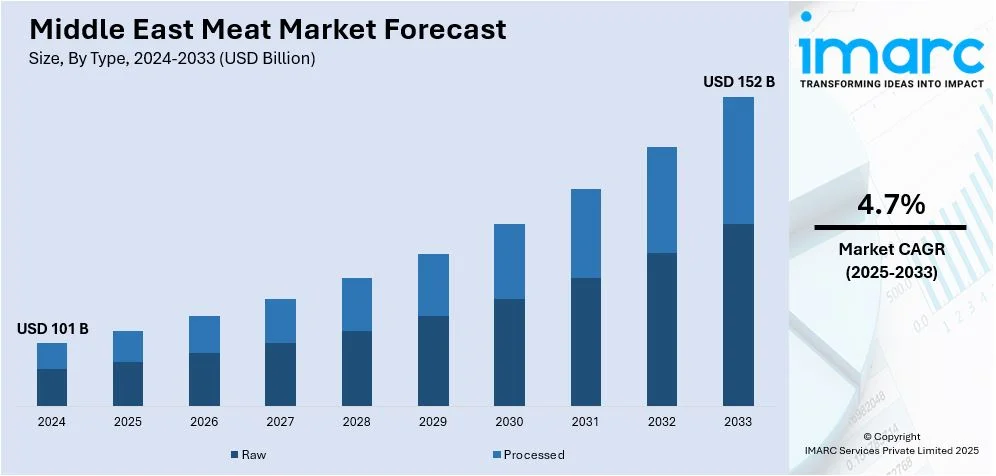
The Middle East meat market size was valued at USD 101 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 152 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.7% from 2025-2033. The market is expanding due to rising demand for protein-rich diets, a shift toward convenience-driven processed meats, and a focus on halal certification. Moreover, rising investments in local production and healthier meat options further fuel growth.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 101 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 152 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 4.7% |
The Middle East meat market is driven by high growth rate in population and urbanization which has increase the demand for proteins in various meals. Additionally, the strong emphasis on halal certification in the region shapes both production and import trends, ensuring compliance with cultural and religious requirements. Governments are also focusing on food security initiatives, investing in local meat production facilities and supply chain infrastructure to reduce dependency on imports. For instance, according to the Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Environment, Water, and Agriculture, the poultry meat production reached 558 million kilograms in early 2024, a 9% increase compared to the same period last year, driven by biosecurity measures, modern technologies, financing support, and initiatives aligned with Vision 2030 to achieve poultry self-sufficiency.
There are other key demand drivers, mainly health-consciousness among consumers to have organic, lean, and high-quality meat options. Improved technology in processing and packaging increases the availability of products and the shelf life thereof, catering to the changing demands of urbanization. E-commerce platforms and new retail formats continue to make premium meat products available, thus fuelling growth in the market. Furthermore, substantial investments are being directed toward expanding businesses, including the establishment of new processing plants and distribution centers, ensuring wider market reach and increased production capacities. For instance, in July 2024, JBS, a global food company, invested USD 50 million in a new Jeddah plant, quadrupling production capacity, focusing on chicken nuggets and expanding its business of poultry operations in Saudi Arabia. This aligns with Saudi Vision 2030’s goals of boosting investments, generating employment, and promoting sustainable, locally-focused economic development in the food production sector.
Middle East Meat Market Trends:
Rising Demand for Processed and Frozen Meat Products
The Middle East meat market is witnessing a growing shift toward processed and frozen meat products, driven by changing consumer lifestyles and urbanization. With more individuals seeking convenient meal solutions, products such as ready-to-cook meat and pre-marinated options are gaining popularity. Advances in cold chain logistics and packaging technologies ensure product freshness, boosting consumer confidence in frozen options. Furthermore, retailers are expanding their offerings in modern supermarkets and hypermarkets to cater to this demand, making such products widely available. For example, in April 2024, Organic Meat Company Limited (TOMCL) won a contract worth USD 4 million with First Quality Food Stuff LLC to export frozen boneless beef to the United Arab Emirates (UAE), which is one of the examples of increasing demand for frozen meat products.
Growth of Halal and Organic Meat Markets
Halal-certified meat remains a cornerstone of the Middle East market, with increasing global interest in halal products further fueling demand. Alongside this, organic and healthier meat options are gaining traction as health-conscious consumers seek products free from additives and antibiotics. Moreover, producers are responding by introducing organic-certified and free-range meat, often coupled with halal certification to cater to dual demands. For instance, in June 2024, AGWA and Believer Meats collaborated to develop cultivated meat capabilities in Abu Dhabi, focusing on market expansion, manufacturing, and R&D. The partnership addresses food security, promotes alternative proteins, and establishes halal certification standards for cultivated meat in the MENA region. This trend is also supported by rising awareness of animal welfare and sustainable farming practices, prompting both local and international suppliers to prioritize eco-friendly and ethical production methods.
Expansion of E-Commerce and Modern Retail Formats
The growth of e-commerce platforms and the proliferation of modern retail outlets are transforming how meat products are marketed and sold in the Middle East. Online platforms now offer fresh, frozen, and specialty meat products, delivering convenience to tech-savvy consumers, further supporting the meat market growth. For instance, in August 2024, Meat House Gourmet, a premium meat provider in the UAE, launched an online butcher shop offering specialty meats like Wagyu beef and beef Wellington, with free delivery over 250 AED, same-day delivery in Dubai, and personalized customer service. In line with this, modern retail formats, including large-scale supermarkets and hypermarkets, provide a broader range of meat options under one roof, enhancing accessibility. These channels often include value-added services such as pre-cut, packaged, and marinated meat to cater to consumer preferences.
Middle East Meat Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Middle East meat market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type, product, and distribution channel.
Analysis by Type:
- Raw
- Processed
Raw meat remains a prominent segment in the Middle East meat market, with high demand for fresh cuts of beef, chicken, and mutton. This segment caters to traditional cooking methods, where consumers prefer to purchase meat in its natural form for preparation at home. Raw meat is sold primarily in supermarkets, hypermarkets, specialty stores, and butcher shops, offering a wide range of cuts tailored to local culinary preferences. Furthermore, the demand for raw meat is supported by cultural practices, with a strong emphasis on halal certification and quality. Local production and imports continue to meet this segment's growing needs.
Processed meat is gaining traction in the Middle East due to increasing consumer convenience, longer shelf life, and evolving dietary preferences. This segment includes a variety of products such as sausages, cold cuts, ready-to-eat meals, and frozen meat items. Processed meats are often favored by busy consumers, expatriates, and those seeking quick meal solutions. The market for processed meat continues to expand, driven by innovations in packaging, flavoring, and health-conscious options such as reduced-sodium or organic products. Moreover, as consumer lifestyles become more fast-paced, processed meats are expected to play a growing role in the region's meat industry.
Analysis by Product:
- Chicken
- Beef
- Mutton
- Others
Chicken is the one of the most consumed meat in the Middle East, driven by its versatility, affordability, and cultural significance. It is a staple in both home cooking and foodservice, widely available in fresh, frozen, and processed forms. The demand for chicken is bolstered by the region’s preference for halal-certified products, with chicken being a primary choice for consumers seeking value and convenience. As the population grows and consumer preferences shift toward healthier options, the chicken segment continues to expand, with innovations in value-added products and sustainable farming practices shaping its future growth.
Beef holds a significant share in the Middle East meat market, particularly in countries where traditional dishes feature red meat. The demand for beef is driven by factors such as the region's growing middle class, higher disposable incomes, and cultural consumption patterns. Beef is typically available in various cuts, catering to diverse culinary preferences, from stews and grills to steaks. While the Middle East still relies on imports to meet domestic beef demand, local production initiatives are rising, supported by government efforts to boost food security and self-sufficiency in the region’s beef industry.
Mutton, a popular choice in the Middle East, is consumed widely due to its rich flavor and cultural significance in traditional dishes. It is particularly favored during festive seasons and special occasions. The demand for mutton remains strong in countries with high lamb and goat meat consumption, with both fresh and frozen varieties available. Additionally, mutton is also an essential part of the region’s halal meat market. As consumer interest in sustainable and locally sourced meat rises, mutton’s role in the market continues to expand, with investments aimed at improving production efficiency and quality.
Analysis by Distribution Channel:
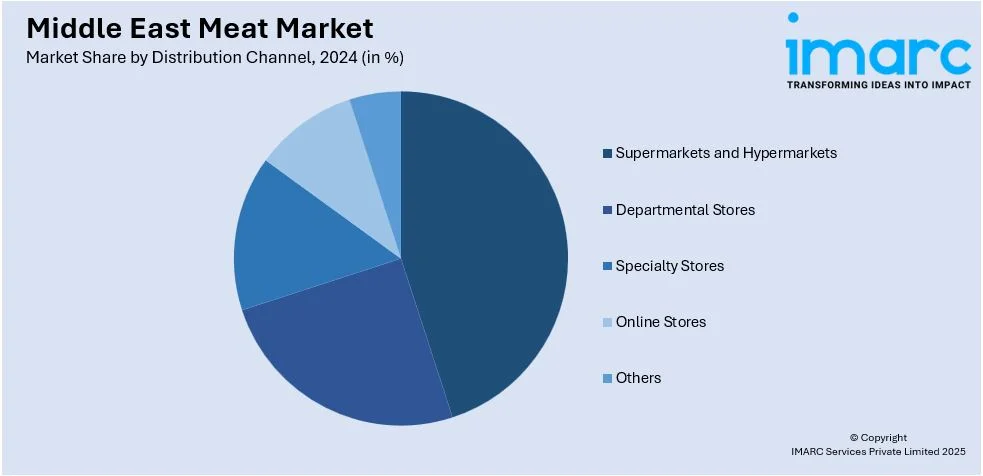
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Departmental Stores
- Specialty Stores
- Online Stores
- Others
Supermarkets and hypermarkets are key distribution channels in the Middle East meat market, catering to a broad consumer base with a wide variety of meat products. These retail outlets provide convenience, offering consumers both fresh and frozen meat, as well as packaged and processed products. With large-scale operations, supermarkets and hypermarkets benefit from economies of scale, enabling competitive pricing. They also offer a wide range of options, including halal-certified meats, making them a primary choice for many consumers. The growing urban population and increasing consumer demand for quality products further drive the expansion of this channel.
Department stores in the Middle East contribute to the meat market by offering a range of high-quality products to middle and upper-income consumers. These stores typically feature dedicated food sections where meat is sold alongside other groceries. They attract customers seeking premium or specialty meats, including organic and grass-fed options. While not as extensive in meat variety as supermarkets and hypermarkets, departmental stores appeal to consumers looking for convenience and quality. Additionally, the segment has witnessed growth due to increasing consumer purchasing power and rising demand for premium products, particularly in urban centers.
Specialty stores play a significant role in the Middle East meat market by offering curated selections of meat products tailored to specific consumer preferences. These stores focus on high-quality offerings, including gourmet cuts, organic meats, and exotic options, catering to niche markets. Additionally, they tend to focus on customer service, where they give advice on meat selection and preparation. Specialty stores cater to the consumers who prefer quality, sustainability, and other meat products, hence a growing market in the region's food retail landscape. The channel is likely to grow with increasing consumer awareness of food quality.
Online stores are increasingly popular in the Middle East meat market, providing convenience and accessibility for consumers to purchase meat products from the comfort of their homes. With a growing trend toward e-commerce, many retailers now offer fresh, frozen, and processed meats through online platforms. This distribution channel is especially appealing to busy consumers or those seeking contactless shopping options. Additionally, online stores allow for a wider selection of products, including premium and specialty meats, often accompanied by home delivery services. As digital transformation accelerates, online meat sales are expected to continue growing in the region.
Country Analysis:
- Saudi Arabia
- Turkey
- Israel
- United Arab Emirates
- Iran
- Iraq
- Qatar
- Kuwait
- Oman
- Jordan
- Bahrain
- Others
Saudi Arabia is a prominent market in the Middle East meat industry, driven by high demand for halal-certified meat products. As a key player in the region’s food security strategy, the country is focused on increasing domestic production through investments in local poultry, beef, and lamb. Government initiatives, such as Vision 2030, emphasize sustainable food production and diversification, spurring growth in the meat sector. Additionally, the nation’s large expatriate population contributes to the demand for various types of meat, further bolstering market dynamics.
Turkey holds a significant position in the Middle East meat market due to its advanced production facilities and strategic location bridging Europe and the Middle East. The country is a major producer and exporter of both red meat and poultry, with robust domestic demand driven by cultural preferences. Local consumption is supplemented by exports to neighboring countries, making Turkey a key regional player. Additionally, the government’s support for agriculture and meat production has helped the sector thrive, with increasing investments in modernizing processing facilities and enhancing quality standards.
Israel’s meat market is characterized by a highly efficient supply chain, driven by technological advancements in agriculture and food production. The country has a strong focus on innovation, including the use of alternative proteins and lab-grown meat, positioning it as a leader in the sustainable meat sector. Moreover, local consumption is complemented by growing demand for kosher-certified products, which are exported to various international markets. Despite its small size, Israel’s meat market is highly developed and competitive, with a strong emphasis on quality and food safety.
The UAE is a prominent contributor to the Middle East's meat market, providing much of the diverse meat products required by the multicultural population in a growing industrial relationship. Heavily dependent on imports for poultry and red meat, the country focuses on enhancing local production through technological innovations and sustainable practices. Besides the retail and foodservice industry in the UAE, it has established itself on high-quality, halal-certified meat products. Growth will likely arise from the emphasis government policies place on food security in the country.
Meat market of Iran is huge and rapidly growing due to its large population that demands beef, lamb, and poultry. The market remains one of the biggest consumers of meat in the region, despite the fact that the country is heavily affected by economic sanctions. The government has focused on boosting local meat production to reduce dependency on imports, particularly by supporting domestic livestock farming. Additionally, Iran’s meat sector faces challenges in terms of supply chain management and quality control yet continues to grow due to increasing consumer demand and efforts to improve production efficiency.
The Iraq meat market enlarges as the country develops its agricultural sector and increases domestic production. With this growing population and rising demand for beef, lamb, and poultry, Iraq becomes a potential future market for meat producers. Local production is slowly increasing, fostering the market growth.. Obstacles for market development still include political instability and infrastructure problems; however, continuous efforts toward better agriculture systems and improving the local supply chain would, in turn, strengthen this sector and increase its resilience over the years.
The meat market within Qatar has a strong demand for locally produced and imported meat, specifically poultry and lamb. The country's population in addition to a larger expatriate community encourages different consumption patterns, and one of the major attractions would be the halal products. Qatar is working towards food security and sustainability, with investments in local production and raising local livestock and poultry. Furthermore, as a part of Vision 2030, Qatar reduce imports and further encouraging the growth in home meat industry and enhance efficiency in overall supply chains.
The Kuwait meat market has predominantly high demand for imported meat products, especially the poultry and lamb. There is little domestic production in this country; thus, most of the products come from neighboring countries. With an increasing population and growing taste of consumers for quality meat products that are certified halal, there are prospects for market growth. As the government invests in food security and improves agricultural practices, it is expected that local production will increase, even though importation will remain an important source of demand-satisfaction.
Oman’s meat market is expanding as the country’s population grows and demand for meat products increases. While the nation produces some local meat, particularly poultry, it relies heavily on imports to meet the demand for beef and lamb. The government has invested in modernizing local farming and meat processing industries to boost self-sufficiency and ensure sustainable practices. Oman’s focus on food security and sustainability, coupled with growing consumer interest in quality, halal-certified products, is expected to shape the future of its meat market, driving both local production and imports.
The Jordanian meat market is reliant on homegrown production as well as imports. Beef, lamb and poultry are the most consumed varieties of meat. However, strategically located Jordan with its increasing population is considered an important market. The government of the country is currently focused on developing food security by enhancing agricultural productivity and improving local production. With the increase in consumer demand for higher quality and more halal-certified meat, the Jordanian market will grow at the same time that it will still significantly depend on imports while domestic initiatives to grow the sector continue to expand.
Bahrain's meat marketplace is small but burgeoning with varied calls for poultry, beef, and lamb by its expatriate populace and local consumers. Besides meeting poultry needs, most meat resources are imported into the board. Bahrain's government is currently engaged in programs focusing on improvements in local meat production aimed to enhance food security and sustainability. The meat business therefore has a strong retail and off-take food markets and is projected with the rising preference for consumption among local customers of halal and high-quality products to exhibit a growth trend in the future, with an almost equal balance between local and imported meat sources.
Competitive Landscape:
The Middle East meat market becomes highly competitive due to the high growth rate in population and urbanization which has increased the demand for proteins in various meals. Key players focus on innovation, supply chain efficiency, and pricing to capture market share. In addition, rising health consciousness has spurred growth in value-added and organic meat products, intensifying competition. Moreover, government initiatives promoting local production and self-sufficiency have reshaped dynamics, encouraging investments in advanced facilities and strategic acquisitions. These moves enable companies to expand capabilities, strengthen market presence, and meet growing demand while addressing sustainability and cost-effectiveness to cater to diverse consumer preferences in the region. For instance, in October 2024, BRF Arabia Holding Company announced an agreement to acquire 26% of Addoha Poultry Company for SAR316.2 million. This investment strengthens BRF’s Middle East operations, enhances synergies, and supports Saudi Arabia’s food security goals, subject to regulatory approvals and conditions precedent.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Middle East meat market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Al Ain Farms
- Al-Watania Poultry
- BRF S.A.
- Herfy Food Services Co.
- Kibsons International LLC
(Please note that this is only a partial list of the key players, and the complete list is provided in the report.)
Latest News and Developments:
-
In December 2024, Al Ghurair Foods launched a new integrated poultry facility in Khalifa Economic Zones of Abu Dhabi (KEZAD), featuring a hatchery, processing plant, rendering facility, and effluent treatment, supporting the company’s role in UAE's 2051 food security strategy.
Middle East Meat Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Raw, Processed |
| Products Covered | Chicken, Beef, Mutton, Others |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Departmental Stores, Specialty Stores, Online Stores, Others |
| Countries Covered | Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Iran, Iraq, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Jordan, Bahrain, Others |
| Companies Covered | Al Ain Farms, Al-Watania Poultry, BRF S.A., Herfy Food Services Co., Kibsons International LLC, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Middle East meat market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Middle East meat market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Middle East meat industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Meat refers to the edible flesh of animals, primarily consumed as a source of protein and essential nutrients. It includes various types such as beef, poultry, pork, and lamb. In the food industry, meat plays a central role in global diets, contributing to cultural cuisines, nutrition, and the economy.
The Middle East meat market was valued at USD 101 Billion in 2024.
IMARC estimates the Middle East meat market to exhibit a CAGR of 4.7% during 2025-2033.
The meat market is driven by factors such as population growth, rising disposable incomes, increasing demand for halal products, and evolving consumer preferences for convenience and quality. Additionally, investments in local meat production, along with government initiatives to enhance food security, are fueling market growth and diversification.
Some of the major players in the Middle East meat market include Al Ain Farms, Al-Watania Poultry, BRF S.A., Herfy Food Services Co., Kibsons International LLC, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












