
Low GWP Refrigerant Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Low GWP Refrigerant Market Size and Share:
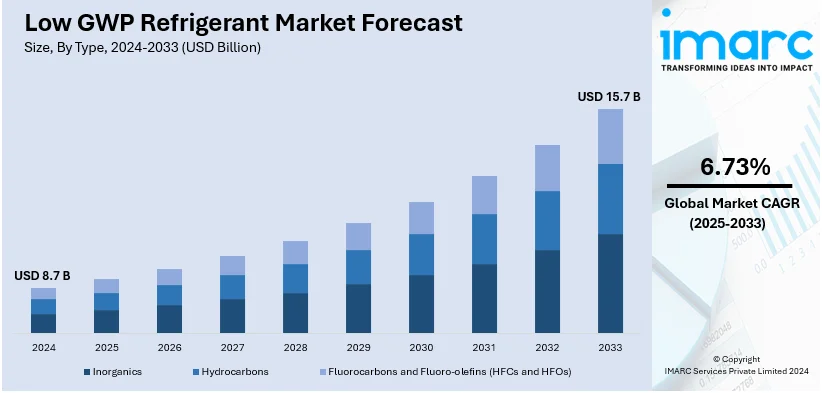
The global Low GWP Refrigerant market size was valued at USD 8.7 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 15.7 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.73% during 2025-2033. Asia-Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of over 34.7% in 2024. This region is leading due to rapid industrialization, stringent environmental regulations, and high demand for sustainable cooling solutions across various industries and applications.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033 |
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 8.7 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 15.7 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 6.73% |
The demand for low-GWP refrigerants is accelerating through industries, as they favor energy-efficient solutions to comply with sustainability goals and manage operational costs. These options, superior in thermodynamics, provide better efficiency through lower energy consumption. Alternatives that increase system efficiency and contribute to long-run cost savings are being pursued by end-users in various sectors of commercial, residential, and industrial applications. For example, in 2024, Honeywell announced that its Solstice 454B low-GWP refrigerant will be used in Bosch's Florida Heat Pump series, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 78%. The collaboration also includes technician training and is in line with Honeywell's focus on energy transition and sustainable heating solutions. Coupled with development in refrigerant technology, this shift toward energy-efficient solutions is playing a pivotal role in driving the market since businesses are looking to find ways to align with new global energy efficiency standards as well as environmentally responsible practices.
The United States is leading the low-GWP refrigerant market through progressive environmental policies and significant investments in sustainable technologies. The AIM Act, which phases down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), aligns with global commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Federal incentives and state-level mandates, particularly in California, are accelerating the transition to low-GWP alternatives. The U.S. also supports innovation by backing the development of advanced refrigerant technologies. For example, in 2024, Honeywell and Bosch collaborated to integrate Honeywell’s low-GWP Solstice® 454B refrigerant into Bosch’s Florida Heat Pump series, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 78% compared to traditional refrigerants. Honeywell has invested over $1 billion in Solstice technology, preventing the release of 326 million metric tons of CO2-equivalent emissions. This partnership aligns with U.S. regulatory trends, supporting sustainable energy solutions and reducing environmental impact in heating and cooling. Consequently, major HVAC and automotive manufacturers are embracing this approach in order to meet legislation requirements as well as strong demand from consumers for "green" and energy-saving solutions.
Low GWP Refrigerant Market Trends:
Introduction of new eco-friendly low GWP refrigerants
Inclusions of new ecologically-friendly products are shifting the perspective of the market in terms of low-GWP refrigerant. When the environment is facing immense pressure worldwide, industries prefer alternative and environmentally friendly rather than traditional high-GWP refrigerants. The availability and subsequent launch of advanced low-GWP refrigerant will encourage people to follow this and help reduce GHG and move towards achieving a sustainable future. These types of eco-friendly refrigerants comply more with statutory and people's preferences than products that are friendly to the environment. Industries in commercial, industrial, and residential fields are looking forward to adopting these green options to strengthen their corporate social responsibility efforts and thereby minimize their carbon footprint. For instance, the introduction of sustainable cooling solutions, as highlighted in the World Bank report, presents a USD 1.6 trillion investment opportunity for India by 2040, addressing rising cooling demands, reducing emissions by 213 Metric tons annually, and supporting sustainable development initiatives. These refrigerants fuel technological advancements and inspire further research and development to create even more efficient and effective solutions. With governments and organizations prioritizing emission reductions, the new eco-friendly low-GWP refrigerants shape purchasing decisions, accelerate market growth, and reinforce the broader commitment to combat climate change.
Increasing product application in the residential sector
Increased usage of the Low GWP Refrigerant, particularly in residential premises has become a driver. Customers, being homebuyers or housebuilders will realize their own ecological imperatives to become ever increasingly ecological, thereby pushing higher and higher demand for carbon footprints friendly cool/and heat solutions. According to data from Our World in Data, air conditioning currently contributes around 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This is due to the widespread use of air conditioning units, which rely on energy and refrigerants that can have high environmental impacts. At present, there are approximately 2 Billion air conditioning units globally. However, the International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that this number could nearly triple to over 5.5 Billion units by 2050, driven by factors such as population growth, urbanization, and increased demand for cooling in hotter regions. Low-GWP refrigerants are one of the feasible alternatives for high-GWP options and support the residential sector's sustainability goals. Homeowners now look for energy-efficient and eco-friendly cooling systems that provide comfort and reduce their carbon footprint. The use of low-GWP refrigerants helps combat climate change and fosters a more sustainable living environment. Additionally, government policies and efforts aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions further encourage the residential sector to embrace these eco-friendly refrigerants. Rebates, incentives, and mandates for more environmentally friendly cooling solutions force the shift toward these alternatives. Increased awareness of health and safety considerations also influences this. Low-GWP refrigerants are often less toxic and flammable, which boosts residential safety standards. As the residential sector adopts low-GWP refrigerants, growth in their market is catalyzed by environmental concerns, support from regulations, and a need for eco-friendly and efficient home cooling solutions.
Rising demand for frozen food products
Growing demand for frozen food products represents another driver for market growth. With consumers increasingly busier, convenience and accessibility to frozen food have been well received. Low-GWP refrigerants help keep these frozen products fresh and safe while also reducing the negative environmental impacts of such frozen products. They help to create efficient and environmentally friendly cooling systems used in cold storage facilities, distribution centers, and retail freezers for frozen foods. For instance, the rising demand for frozen food, which reached USD 252.5 Billion in 2023, is driving innovations in low-GWP refrigerants to meet sustainability goals. Inflation-driven price rises and the shift of consumers toward value and convenience drive frozen food purchasing trends. Rising demand for frozen food products warrants parallel demand for reliable refrigeration solutions, which support the preservation of product quality and compliance with food safety standards. Additionally, sustainability in the food industry has forced manufacturers, retailers, and consumers to adopt products and processes that minimize carbon emissions. These refrigerants, therefore, are part of the sustainability efforts that enhance the environmental responsibility of the frozen food supply chain.
Low GWP Refrigerant Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global low GWP refrigerant market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been classified based on type and application.
Analysis by Type:
- Inorganics
- Hydrocarbons
- Fluorocarbons and Fluoro-olefins (HFCs and HFOs)
Hydrocarbons stand as the largest component in 2024, holding around 35.3% of the market. Their wide acceptance is because of their excellent thermodynamic properties, low environmental footprint, and compatibility with current refrigeration and HVAC equipment. Being natural refrigerants, hydrocarbons, such as propane and isobutane, represent a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to high-GWP refrigerants in alignment with global regulatory mandates. Their efficiency and scalability in commercial, industrial, and residential applications further establish them at the top, and thus hydrocarbons will remain a significant driver for growth and innovation in the low GWP refrigerant market.
Analysis by Application:
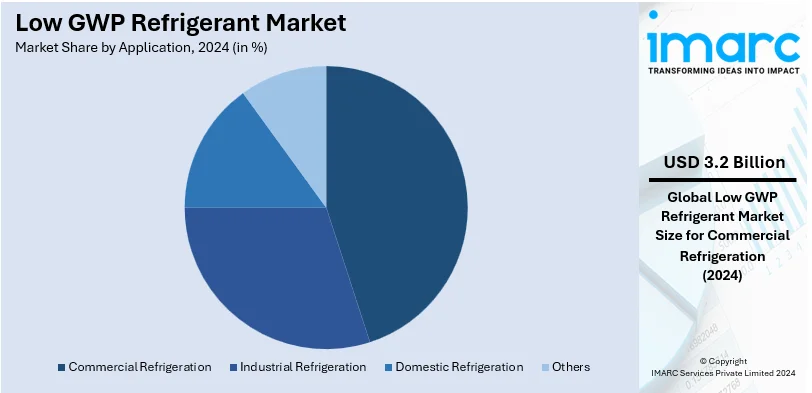
- Commercial Refrigeration
- Industrial Refrigeration
- Domestic Refrigeration
- Others
Commercial refrigeration leads the market with around 36.8% of market share in 2024. This dominance is catalyzed by the requirement for energy-efficient and more sustainable cooling solutions in many industries such as retailing, food storage, and cold chain logistics. More importantly, regulatory compliance by the business with global environmental mandating of low GWP refrigerants propels it in this segment. For businesses looking to meet consumer expectations for a more sustainable and efficient delivery of services, commercial refrigeration stands out as the most significant application area.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
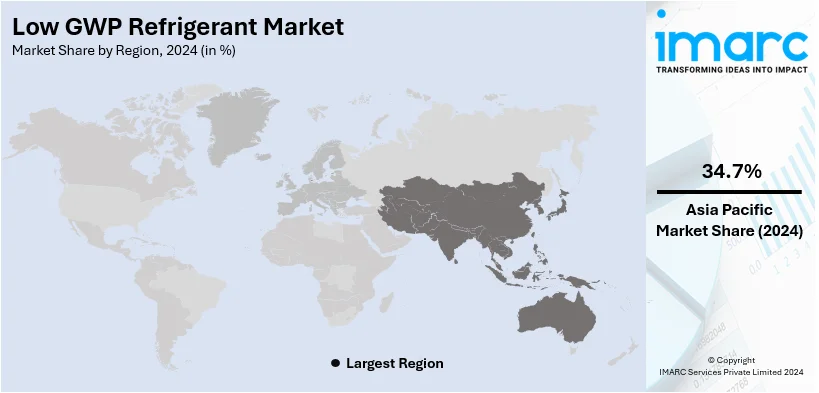
In 2024, Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market share of over 34.7%. This growth is led by rapidly industrializing and expanding the urbanization rate and strong demand for energy-efficient coolants in commercial, residential, and industrial spaces. Strict government regulations mandating the reduction of greenhouse gases and banning or phasing out high GWP refrigerants enhance this adoption in the region as well. China, India, and Japan are actively driving this transition, buoyed by heavy investments in sustainable technologies and infrastructure. The robust manufacturing base and growing consumer awareness of environmental sustainability in the region reinforce market leadership.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Low GWP Refrigerant Market Analysis
US accounts for 83.1% share of the market in North America. The adoption of low-GWP refrigerants in the US is spurred by stringent regulatory measures such as the AIM Act, which mandates the phasedown of HFCs. These regulatory environments foster innovation and accelerate the adoption of alternatives like hydrofluoroolefins and natural refrigerants to reduce environmental impact. A key driver in the US market is its robust research and development capabilities, backed by government incentives for green technologies. Companies including Honeywell and Chemours are capitalizing on this momentum by introducing energy-efficient products, ensuring compliance, and maintaining market competitiveness. The growing adoption of low-GWP refrigerants in commercial and residential HVAC systems supports energy efficiency mandates, exemplified by supermarkets transitioning to CO₂ refrigeration systems. For instance, the adoption of low GWP refrigerants is accelerating in the residential sector, with U.S. homes contributing 6% of the nation's electricity use via air conditioning, costing USD 29 Billion annually and emitting 117 Million Metric Tons of CO₂. Transitioning to environmentally safer alternatives is key to reducing the carbon footprint of these systems. This market growth is further fueled by the increasing demand for eco-friendly cooling solutions across industries such as automotive and industrial refrigeration, reinforcing a future-proof approach.
Asia Pacific Low GWP Refrigerant Market Analysis
Asia-Pacific is adopting low GWP refrigerants driven by rapid urbanization and the demand for sustainable cooling solutions. Several regional governments are integrating international protocols like the Kigali Amendment to reduce environmental damage from HFC emissions. For instance, China's adoption of the Kigali Amendment and policies targeting low GWP refrigerants for motor air conditioning can reduce over 20 Million Tons of CO₂-equivalent emissions annually, primarily from HFC-134a. This helps achieve the worldwide goal to cut GHG emission and assist China in fulfilling its intention of peaking carbon emissions in 2030 and neutrality in 2060. The region's strength lies in its expansive manufacturing base, enabling large-scale production of cost-effective refrigerants such as ammonia and propane. Innovations such as hydrocarbon-based air conditioners in India showcase the region’s potential to combine efficiency with affordability. For example, Japan's focus on advanced CO₂-based refrigeration technology for convenience stores demonstrates leadership in cutting-edge applications. Growing consumer awareness about climate impact and rising energy costs are further accelerating the adoption of these solutions in residential and commercial spaces, ensuring a balanced approach to sustainability and economic viability.
Europe Low GWP Refrigerant Market Analysis
European countries are leading the global transition to low GWP refrigerants owing to its stringent directives like the F-Gas Regulation and the Green Deal initiatives. These favorable policies encourage the shift from high GWP refrigerants to options like HFO blends and natural refrigerants. The region's market is further being propelled by its robust infrastructure for research and policy implementation, which fosters industry-wide collaboration. European manufacturers, such as Danfoss and Emerson, are innovating with cutting-edge solutions to meet growing demand in retail and industrial refrigeration. For instance, the global refrigerants market witnessed significant shifts last year, with European air-conditioning sales reaching 11.9 Million units, primarily using high-GWP R410A. With regulations like the EU's 79% HFC reduction target by 2030 and emerging alternatives like R32, CO₂, and R290, the transition to low-GWP refrigerants is critical for mitigating climate impact. CO₂ transcritical systems are becoming a standard in supermarket chains, showcasing Europe’s leadership in sustainable technologies. Additionally, incentives for adopting energy-efficient refrigerants in public and private sectors are driving market transformation. As consumer demand aligns with regulatory frameworks, Europe is setting benchmarks for eco-friendly refrigeration systems, providing a replicable model for global adoption.
Latin America Low GWP Refrigerant Market Analysis
In Latin America, the shift to low GWP refrigerants is fuelled by increasing awareness of environmental sustainability and international commitments like the Kigali Amendment. The region benefits from its growing industrial sector and expanding refrigeration needs in agriculture and retail. Brazil and Mexico are leading the adoption of natural refrigerants like ammonia in food processing and cold storage facilities, reflecting their adaptability to industrial-scale applications. For instance, Emergent Cold LatAm's new Guarulhos facility, the largest temperature-controlled warehouse in Latin America, increases Brazil's storage capacity by 20%, offering 51,000 pallet spaces across 347,000 Cubic Meters. Such expansions present opportunities for low GWP refrigerants by enhancing energy-efficient, strategically located storage for sustainable food logistics. A key strength is the region's alignment with global best practices, supported by collaborations with international organizations. For instance, retrofitting older refrigeration systems with low GWP alternatives is gaining traction, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining economic efficiency. This shift not only reduces environmental impact but also supports long-term energy cost reductions in critical industries.
Middle East and Africa Low GWP Refrigerant Market Analysis
The Middle East and Africa are transitioning to low GWP refrigerants to address rising cooling demands in extreme climatic conditions while reducing environmental harm. Governments and industries are emphasizing natural refrigerants like propane and CO₂, given their suitability for high ambient temperatures. A significant strength is the region's focus on large-scale deployment in sectors like cold chain logistics and hospitality, ensuring consistent progress. For instance, Saudi Arabia's expansive transportation network, spanning 73,000 km of roads, 29 airports, and 4,500 km of rail, is pivotal to supporting low GWP refrigerant adoption. Enhanced intermodal connectivity and digitized freight systems align with Vision 2030, fostering energy-efficient logistics crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Countries such as the UAE are adopting advanced technologies in district cooling systems, integrating energy-efficient refrigerants into urban infrastructure. Additionally, international partnerships are fostering the adoption of eco-friendly refrigeration solutions across industrial and commercial applications. For example, initiatives to deploy sustainable cold storage systems for agricultural exports highlight practical progress while aligning with global climate goals.
Competitive Landscape:
The low GWP refrigerant market features a competitive landscape marked by key players striving for technological innovation and market expansion. Major companies maintain dominance through extensive product offerings, global distribution networks, and strategic collaborations. These firms are heavily investing in research and development to launch eco-friendly refrigerants aligned with regulatory mandates. Emerging players are gaining traction by targeting niche markets and focusing on cost-effective, sustainable solutions. The competition is further fueled by growing consumer demand for energy-efficient and environmentally responsible alternatives. For instance, in 2024, Honeywell announced a partnership with Hisense to integrate its low-global warming potential (GWP) Solstice® 454B refrigerant into Hisense’s residential air conditioners. This collaboration aims to reduce the environmental impact of air conditioning units by using a refrigerant with lower GWP, in line with global climate change efforts.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the low GWP refrigerant market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- A-Gas International Ltd.
- Arkema
- Daikin Industries Ltd.
- Danfoss A/S
- GTS SPA
- Harp International Ltd
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Linde plc
- Messer Group
- Tazzetti S.p.A
- The Chemours Company
Latest News and Developments:
- November 2024, LANXESS introduced Everest ESR 220, a synthetic ester lubricant designed for HVAC and refrigeration systems utilizing the low-GWP refrigerant R-1234ze. Developed in collaboration with a leading OEM and supported by a Department of Energy grant, this lubricant ensures efficient performance in screw compressors, where traditional synthetic oils for HFCs have been inadequate. Everest ESR 220 is also compatible with R-515B, a non-flammable low-GWP refrigerant blend of R-1234ze and R-227ea. This innovation aligns with LANXESS's commitment to achieving climate neutrality by 2040.
- September 2024, The Chemours Company made a low GWP refrigerant retrofit solution for the aftermarkets in automotive sector. This allowed the transition in the legacy R-134a refrigerant to the environmentally friendlier Opteon™ YF (R-1234yf). In new mobile HVAC systems, it is designed to replace R-134a.
- July 2022, A-Gas International Ltd bought CRS, which is in Punta Gorda, Florida, to boost its capacity in refrigerant reclamation and management services. The acquisition further boosts the company's footprint in North America and enhances its operational capacity.
- August 2023, Daikin Industries Ltd, a global air conditioning manufacturer, introduced plans to establish a new production base. This initiative aims to meet the increasing global demand for advanced air conditioning systems. The facility will focus on energy-efficient and environmentally friendly technologies in line with market trends. By expanding its production capacity, Daikin seeks to reinforce its competitive position in the HVAC sector. The new base reflects Daikin’s strategy to align with global sustainability goals and market growth.
Low GWP Refrigerant Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Inorganics, Hydrocarbons, Fluorocarbons and Fluoro-olefins (HFCs and HFOs) |
| Applications Covered | Commercial Refrigeration, Industrial Refrigeration, Domestic Refrigeration, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | A-Gas International Ltd., Arkema, Daikin Industries Ltd., Danfoss A/S, GTS SPA, Harp International Ltd, Honeywell International Inc., Linde plc, Messer Group, Tazzetti S.p.A, The Chemours Company, etc |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, low GWP refrigerant market forecast, and dynamics of the market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global low GWP refrigerant market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the low GWP refrigerant industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The low GWP refrigerant market was valued at USD 8.7 Billion in 2024.
The low GWP refrigerant market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.73% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 15.7 Billion by 2033.
The market is primarily driven by stringent environmental regulations, growing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions, ongoing advancements in refrigerant technology, increased adoption in HVAC, automotive, and commercial refrigeration sectors, rising awareness of sustainability and incentives for transitioning to eco-friendly refrigerants.
Asia-Pacific currently dominates the low GWP refrigerant market, accounting for a share of over 34.7%, driven by its stringent environmental regulations, increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions, rapid industrialization, and expanding HVAC-R applications in emerging economies like India and China.
Some of the major players in the low GWP refrigerant market include A-Gas International Ltd., Arkema, Daikin Industries Ltd., Danfoss A/S, GTS SPA, Harp International Ltd, Honeywell International Inc., Linde plc, Messer Group, Tazzetti S.p.A, and The Chemours Company, among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












