
Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Production Pathway at Smelter Level, Non-Commercialized Pathways, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Low-Carbon Aluminium Market 2024, Size Share And Trends
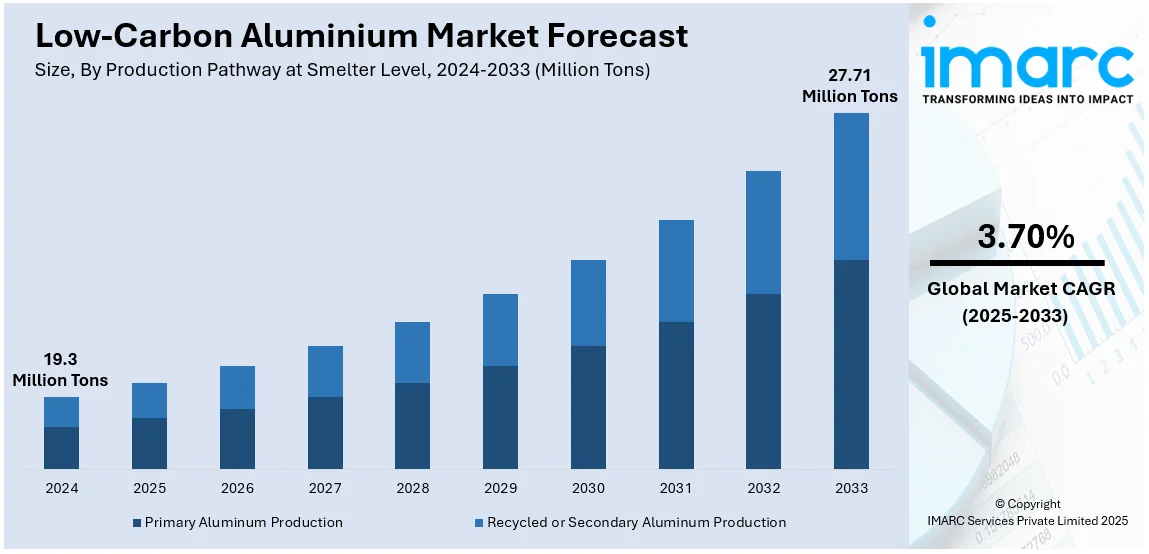
The global low-carbon aluminium market size was valued at 19.3 Million Tons in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach 27.71 Million Tons by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.70% from 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market. The market is primarily driven by the increased renewable energy integration in smelting, ongoing recycling innovations enhancing circular economy efforts, and rising low-carbon smelting technologies like hydrogen-based reduction, driving emissions reduction, cost efficiency, and sustainability while meeting global carbon neutrality and regulatory targets.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | 19.3 Million Tons |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | 27.71 Million Tons |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 3.70% |
The global market is growing due to decarbonization efforts in automotive, aerospace, and packaging, driven by net-zero goals and carbon regulations. Similarly, rising consumer demand for sustainability and advancements in electrolysis processes, including inert anode technology, are propelling the low-carbon aluminium market growth. For example, on June 28, 2024, ELYSIS granted Rio Tinto the first inert anode smelter technology license for a 100-kA demonstration plant in Québec, eliminating all direct greenhouse gas emissions from aluminum production. With a CAD 650 Million investment, this zero-carbon smelting process could cut GHG emissions by 7 million tonnes annually. Moreover, the rising adoption of recycled aluminum, corporate ESG commitments, carbon pricing mechanisms, and renewable energy integration in smelting processes are further enhancing cost competitiveness and reinforcing aluminum’s role in sustainable supply chains and circular economies.
The United States stands out as a key regional market, which is expanding driven by the federal and state emissions regulations, promoting sustainable manufacturing and clean energy adoption. In line with this, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and government incentives are driving green aluminum production by supporting renewable-powered smelting. The growing demand for sustainable infrastructure and electric vehicles (EVs) is increasing the use in lightweight components and augmenting the low-carbon aluminium market share. Moreover, favorable sustainability initiatives, carbon mandates, recycling, and hydrogen-based production are encouraging emissions reduction in construction, aerospace, and packaging. For instance, on August 16, 2024, MIT researchers developed a process to produce hydrogen from recycled aluminum cans in seawater, using gallium-indium eutectic (eGaIn) and imidazole, achieving 90% eGaIn recovery and 99% hydrogen yield in under 10 minutes, with a marine reactor in development.
Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Trends:
Increasing Integration of Renewable Energy in Aluminum Production
Low-carbon aluminium market demand continues to witness accelerating shift toward renewable energy-powered smelting. To cut their carbon footprint, manufacturers are investing in hydropower, solar, and wind energy. The majority of smelters now incorporate green hydrogen as a source of fuel instead of fossil fuel for high-temperature processes. As more infrastructure is put up for renewable energy, the production of low-carbon aluminum is becoming less costly and making manufacturers capable of achieving corporate ESG commitments and carbon reduction targets. According to the US Energy Information Administration, the capacity for wind power will grow to 153.8 GW (+6.5 GW) by the end of 2024; that of solar to 128.2 GW (+38.4 GW); and that of battery storage to 30.9 GW (+14.9 GW). The rate of attachment for residential solar will be up to 25% in 2024 from 14% in 2023. Governments support this change with clean energy subsidies and carbon credits that further push adoption in the industry. As grids turn greener, off-grid renewable power will be the route to sustainable, efficient aluminum production.
Advancements in Recycling Technologies and Circular Economy Initiatives
The market is changing with rapid advancements in recycling technologies, enabling greater recovery of post-consumer and industrial scrap. Low-carbon aluminum market trends indicate increased adoption of closed-loop recycling systems and advanced sorting technologies, enhancing secondary aluminum quality and making it a viable alternative to primary production. Automated processing and AI-driven material separation are improving recycling efficiency while lowering operational costs. Corporate commitments to circular economy principles are driving higher recycled content usage, reducing environmental impact. Strategic collaboration among automotive, aerospace, and packaging industries is strengthening closed-loop supply chains, ensuring consistent demand for recycled aluminum. As of October 9, 2024, Novelis and TSR Recycling signed a three-year agreement to supply 75,000 tonnes of presorted end-of-life aluminum for low-carbon automotive production, reinforcing circular economy efforts and targeting 75% recycled content by 2030, further advancing sustainable aluminum solutions.
Development of Low-Carbon Smelting Technologies
The low-carbon aluminum market outlook is shifting with breakthroughs in smelting technologies, significantly reducing direct greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing process efficiency. Companies are increasingly investing in hydrogen-based reduction processes, replacing carbon-intensive methods with green hydrogen to lower the industry’s footprint. Notably, on October 29, 2024, Press Metal launched GEM, a low-carbon aluminum brand, featuring P1020, PFA ingots, billets, and wire rods. Its 1.08 million mt/year smelters in Sarawak, Malaysia, run on hydropower, limiting CO₂ emissions to under 4 mt per ton. The company prioritizes carbon footprint traceability, supply chain transparency, and upstream alumina investments for raw material security. As commercial viability increases, aluminum producers will accelerate the shift to zero-emission manufacturing, aligning with global sustainability targets and ensuring competitiveness in low-carbon materials markets.
Low-Carbon Aluminium Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global low-carbon aluminium market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on production pathway at smelter level, non-commercialized pathways and application.
Analysis by Production Pathway at Smelter Level:
- Primary Aluminum Production
- Recycled or Secondary Aluminum Production
Recycled or secondary aluminum production holds the largest share in the market as it significantly reduces energy consumption and emissions, requiring up to 95% less energy than primary production. Industries like automotive, packaging, and electronics are increasing reliance on secondary aluminum to meet sustainability targets. Improved sorting, processing, and alloying technologies enhance quality, making recycled aluminum a viable alternative to virgin material. The rise of closed-loop recycling and extended producer responsibility programs ensures a stable supply while lowering costs. As the demand for eco-friendly materials grows, expanding recycling capacity strengthens market competitiveness, reduces waste, and supports a circular economy, reinforcing aluminum’s role in sustainable industrial production.
Analysis by Non-Commercialized Pathways:
- Aluminum Carbothermic Reduction
- Direct Reduction of Alumina (Hydrogen-Based Electrolysis)
- Processing Using Intermediates Derived from Alumina
Aluminum carbothermic reduction is gaining attention as a cost-effective alternative to the traditional Hall-Héroult process, with potential for lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions. This method, which uses carbon as a reductant to produce aluminum directly from alumina, can streamline production by eliminating the need for electrolytic cells. Research into optimizing reaction kinetics and controlling carbon usage is driving progress. The heightened need for low-carbon aluminum, supported by regulatory incentives and corporate decarbonization goals, is accelerating investment in commercial-scale applications. If successfully scaled, carbothermic reduction could revolutionize the aluminum industry by reducing dependence on high-energy smelting and improving economic efficiency.
The direct reduction of alumina via hydrogen-based electrolysis presents a transformative opportunity for aluminum production, replacing carbon anodes with hydrogen to eliminate CO₂ emissions. As green hydrogen costs decline due to expanding renewable energy capacity and government incentives, this technology is becoming more viable. Investments in hydrogen infrastructure, driven by net-zero targets and industrial partnerships, are accelerating research and pilot projects. Automakers, aerospace manufacturers, and packaging companies are seeking ultra-low-emission aluminum, strengthening market demand. If successfully scaled, hydrogen-based electrolysis could enable carbon-free aluminum production, reshaping supply chains and aligning with global sustainability initiatives while securing long-term competitiveness.
Processing aluminum using intermediates derived from alumina, such as aluminum chloride or aluminum sulfide, is gaining interest due to its potential for energy savings and carbon reduction. These intermediates allow for alternative processing routes that bypass the high-energy demands of conventional electrolysis. Advances in chemical refining and catalytic conversion are driving commercial viability. The rise of green chemistry applications and demand for low-carbon materials in industries like electronics and aerospace are fueling interest in these alternative methods. As aluminum producers explore diverse feedstocks, processing through alumina-derived intermediates could enhance supply chain flexibility, reduce environmental impact, and support the transition to sustainable aluminum production.
Analysis by Application:
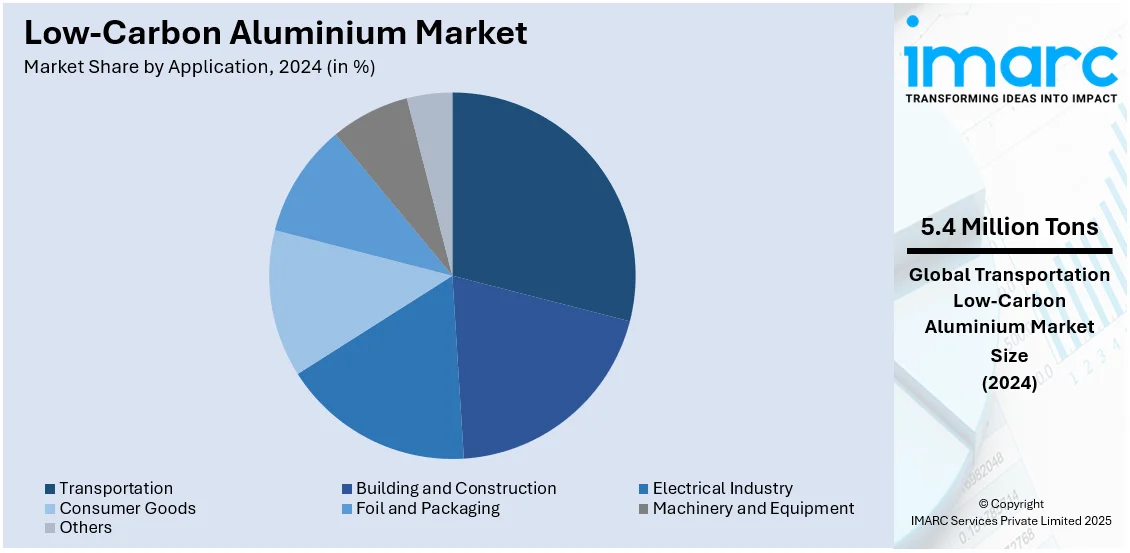
- Transportation
- Building and Construction
- Electrical Industry
- Consumer Goods
- Foil and Packaging
- Machinery and Equipment
- Others
The transportation sector accounts for the largest market share. With the sector’s heightened focus on lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and lower emissions, there has been a significant rise in the demand for aluminum. Automakers are increasingly incorporating aluminum in vehicle frames, battery enclosures, and body panels to meet stringent fuel economy and emissions regulations. The rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) is further accelerating aluminum consumption, as EV manufacturers prioritize lightweight designs to extend battery range. Additionally, the aerospace industry relies on robust aluminum alloys for aircraft fuselages and structural components. Rising urbanization and global trade are also increasing demand for aluminum in rail, marine, and commercial transport, supporting continued market growth.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East
- Africa
North America accounts for the largest market share, driven by rising demand from the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. The shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) and lightweight materials is accelerating aluminum adoption in manufacturing. Government policies promoting decarbonization and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) are encouraging investment in low-carbon aluminum production. The construction sector’s demand for energy-efficient materials is further augmenting aluminum use in building facades, window frames, and infrastructure. Additionally, the U.S. and Canada are expanding aluminum recycling initiatives to reduce dependence on primary production. Strategic investments in renewable-powered smelting and recycling technologies are strengthening the region’s aluminum industry growth.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Analysis
In 2024, the US accounted for around 77.50% of the total North America low-carbon aluminium market. The market is expanding due to a rising focus on reducing carbon emissions in the manufacturing sector and the strict implementation of favorable policies across the region. A key development is the finalization of national pollution levels for cars and trucks (model period 2027-2032) in March 2024. These standards aim to cut 7.2 billion tons of CO2 emissions, improve air quality, and save drivers USD 6,000 over a vehicle's lifetime. The regulations support the clean vehicle industry, create jobs, and enhance competitiveness. Ongoing innovations in production technologies, such as electrolytic reduction, are further augmenting the growth of low-carbon aluminium, which plays a key role in electric vehicle manufacturing. Moreover, the emerging trend of greener solutions is encouraging investment in low-carbon aluminium production, creating a sustainable supply chain, and positioning the U.S. as a leader in clean-tech solutions.
Europe Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Analysis
The market in Europe is witnessing stable growth, driven by the European Union’s strict environmental regulations and ambitious carbon reduction targets. The EU's Green Deal and industrial decarbonization initiatives encourage industries to adopt low-carbon solutions, including aluminium production, to achieve climate neutrality by 2050. The European Aluminium 2024 Environmental Profile Report highlights impressive progress, with a 5% reduction in carbon emissions from primary aluminium since 2015, now at 6.3 kg CO2 per kg—nearly 60% lower than the global average. By 2023, 78% of the electricity consumed in manufacturing was derived from renewable sources, a significant increase from 67% in 2015. Recycling has reduced carbon emissions by 22%, while semi-fabrication processes like extrusion have cut emissions by 44%. These advancements reflect Europe’s leadership in low-carbon aluminium production. The heightened demand from sectors such as automotive, construction, and packaging, along with government incentives, is driving further investment in sustainable production technologies and circular economy practices, enhancing Europe’s global competitiveness.
Asia Pacific Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Analysis
The low-carbon aluminium market in the Asia Pacific region is growing rapidly, driven by its position as a substantial producer and consumer of aluminium. China is leading efforts to cut carbon emissions through advanced technologies like electrolysis and renewable energy-powered smelting. For instance, on July 2, 2024, RUSAL became the first foreign company to receive the China Green Power Aluminium Certificate for 50,000 tonnes of aluminium from its Bratsk Aluminium Smelter. With over 90% renewable electricity, RUSAL’s aluminium has a carbon footprint under 4 tonnes per tonne. India’s expanding manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive and construction, is augmenting the demand for low-carbon aluminium. Governments across the region are implementing stricter environmental regulations and offering incentives for sustainable practices, accelerating the transition to greener production methods. The rise in electric vehicle adoption, especially in China, is further driving demand for low-carbon aluminium, as it plays a crucial role in EV manufacturing. Investments in clean energy and infrastructure are expected to continue propelling the market forward.
Latin America Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Analysis
In Latin America, the market is growing rapidly, propelled by rising environmental awareness and the need to meet global sustainability standards. Countries like Brazil, with abundant renewable energy resources, are well-positioned to transition to low-carbon aluminium production. The region is adopting cleaner technologies, such as renewable energy-powered smelting, to reduce emissions and energy consumption. Additionally, efforts to improve recycling rates are helping lower the carbon intensity of aluminium production. The demand for low-carbon aluminium in sectors like automotive, construction, and packaging is fueling the market growth. Notably, on January 14, 2025, Colombia's GALTCO project, with an annual capacity of 300,000 metric tonnes, was announced. Powered by renewable energy, it will produce aluminium with a carbon footprint of 5 tonnes per ton. The USD 3 Billion project will augment Colombia's industrial capacity, create jobs, and support sustainable development, positioning Latin America as a key player in the global market.
Middle East and Africa Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Analysis
The low-carbon aluminium market in the Middle East and Africa is gaining momentum given the UAE and Saudi Arabia investing in clean technologies, such as renewable energy-powered smelting and waste heat recovery, to diversify economies and reduce oil dependency. Being a hub for the energy-efficient plants that produce aluminium, the region is encouraged by the government's incentives to lower their emissions. As of October 14, 2024, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states, spearheaded by the UAE, will start venturing into green aluminum production anticipating the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) in the near future. Emirates Global Aluminium, UAE, and Ma'aden, Saudi Arabia are establishing themselves in decarbonization using solar power and other low-carbon technologies to stay ahead in market competitiveness. Countries such as South Africa in Africa are embracing low-carbon aluminium production using renewable resources such as solar and wind. Green tech investments are being driven by the growing demand in sectors such as automotive, construction, and packaging. As infrastructure improves, Africa is poised to play a key role in the international low-carbon aluminium industry.
Competitive Landscape:
The global market is becoming increasingly competitive as producers focus on technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and sustainable sourcing. Companies are investing in carbon-free electrolysis, AI-driven process optimization, and hydrogen-based reduction to enhance efficiency and lower emissions. Recycling expansions are increasing secondary aluminum use, aligning with demand from automotive, aerospace, and packaging industries. New entrants are leveraging regional renewable energy for cost-effective production. Cross-industry collaborations with battery manufacturers and renewable energy firms are driving innovation, while ESG policies and regulatory pressures are intensifying competition, emphasizing carbon transparency and circular economy initiatives.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the low-carbon aluminium market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Vedanta Aluminium & Power
- Century Aluminum Company
- RUSAL
- Norsk Hydro ASA
- Alcoa Corporation
- China Hongqiao Group Limited
- Emirates Global Aluminum PJSC
- Capral Limited
- Constellium SE
- Novelis
Latest News and Developments:
- November 18, 2024: EMR secured a EUR 3.4 Million grant from the Advanced Propulsion Centre (APC) to develop a low-carbon aluminum plant using 100% recycled content for automotive components. Partnering with Stellantis, Constellium, Brunel University, BCW Treatments, and Riskoa, the project aims to cut emissions, enhance circular manufacturing, and drive economic growth in UK industry.
- August 6, 2024: Marubeni Corporation finalized the first sale of Rio Tinto’s RenewAl low-carbon aluminum billets in Asia to FUJISASH Group, supporting sustainable building materials. Produced at NZAS, the billets feature digital traceability via START, enhancing supply chain transparency. Marubeni aims to expand low-carbon aluminum applications and drive cross-industry ESG collaboration for decarbonization.
- May 17, 2024: Nissan announced plans to fully transition to low-CO₂ emission aluminum by 2030, using green and recycled aluminum to cut emissions by 50-95%. Starting in fiscal year 2024, Nissan will adopt sustainable aluminum for wheels, chassis, axles, and harness wires in Japan, the U.S., and Europe, replacing 20% of newly mined aluminum.
- April 17, 2024: Masdar and Emirates Global Aluminium (EGA) formed an alliance to advance low-carbon aluminum production using renewable energy. The partnership explores solar power, battery storage, and green hydrogen for EGA’s UAE operations and new global aluminum facilities. EGA, producing one in 25 tonnes of global aluminum, aims to expand CelestiAL solar aluminum production, supporting sustainable industry decarbonization.
- February 1, 2024: Hydro announced a EUR 180 Million investment to build a new aluminum recycling plant in Torija, Spain, aiming to decarbonize European industries. The facility, set to begin production in 2026, will process up to 70,000 tonnes of post-consumer scrap and generate 120,000 tonnes of low-carbon aluminum each year. Hydro’s CIRCAL aluminum, with 75% post-consumer scrap, will feature a CO₂ footprint below 1.9 kg CO₂/kg aluminum, supporting transport, construction, and renewable energy sectors.
Low-Carbon Aluminium Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million Tons |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Production Pathway at Smelter Levels Covered | Primary Aluminum Production, Recycled or Secondary Aluminum Production |
| Non-Commercialized Pathways Covered | Aluminum Carbothermic Reduction, Direct Reduction of Alumina (Hydrogen-Based Electrolysis), Processing Using Intermediates Derived from Alumina |
| Applications Covered | Transportation, Building and Construction, Electrical Industry, Consumer Goods, Foil and Packaging, Machinery and Equipment, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Vedanta Aluminium & Power, Century Aluminum Company, RUSAL, Norsk Hydro ASA, Alcoa Corporation, China Hongqiao Group Limited, Emirates Global Aluminum PJSC, Capral Limited, Constellium SE, Novelis, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the low-carbon aluminium market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global low-carbon aluminium market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the low-carbon aluminium industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The low-carbon aluminium market was valued at 19.3 Million Tons in 2024.
The low-carbon aluminium market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.70% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of 27.71 Million Tons by 2033.
The market is majorly driven by increasing renewable energy integration in smelting, advancements in recycling technologies, and the adoption of low-carbon smelting methods like hydrogen-based reduction. Regulatory pressures, corporate ESG commitments, growing demand in automotive and construction, and carbon pricing mechanisms further accelerate market expansion and sustainability initiatives.
North America currently dominates the low-carbon aluminium market. This dominance is fueled by the rising demand from automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors, the shift to EVs, government decarbonization policies, and expanding recycling and renewable-powered smelting investments.
Some of the major players in the low-carbon aluminium market include Vedanta Aluminium & Power, Century Aluminum Company, RUSAL, Norsk Hydro ASA, Alcoa Corporation, China Hongqiao Group Limited, Emirates Global Aluminum PJSC, Capral Limited, Constellium SE, and Novelis, among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












