
Japan Tuna Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Species, Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Tuna Market Size and Share:
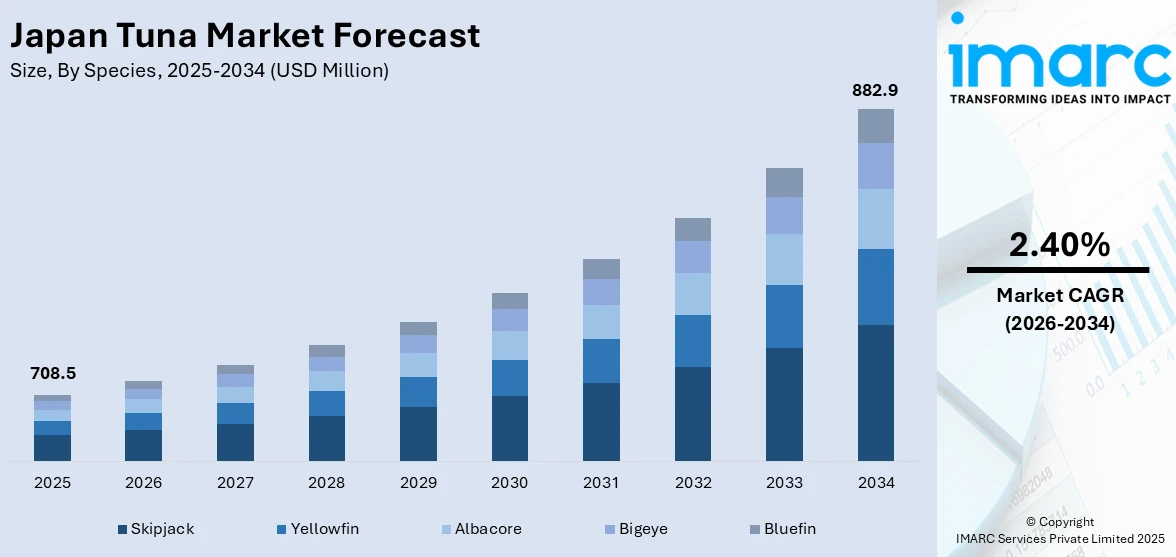
The Japan tuna market size was valued at USD 708.5 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 882.9 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.40% from 2026-2034. The market is witnessing significant growth due to its cultural and culinary significance and global leadership in tuna processing and trade. Moreover, the rising demand for sustainable and traceable tuna, the shift toward processed and ready-to-eat tuna products, and technological advancements in tuna fishing and processing are expanding the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 708.5 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 882.9 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 2.40% |
Tuna holds a prominent place in Japan’s culinary traditions, with dishes like sashimi, sushi, and maguro donburi forming an integral part of Japanese cuisine. This deep-rooted cultural association drives consistent domestic demand for high-quality tuna. Japanese consumers exhibit a preference for fresh, premium-grade tuna, particularly bluefin, which is considered a delicacy. For instance, in January 2025, a 608-pound bluefin tuna was auctioned for $1.3 million at Tokyo's Toyosu market, acquired by seafood wholesaler Yamayuki and the Michelin-starred Onodera Group. The country's sophisticated palate for tuna, coupled with its historical reliance on seafood, ensures a stable and robust market. Furthermore, tuna’s versatility across various preparation methods, ranging from traditional dishes to modern fusion cuisine, bolsters its appeal to a wide demographic, including younger generations.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Japan’s position as a global leader in tuna processing, distribution, and trading significantly influences its tuna market. Major Japanese ports, such as Tsukiji and its successor Toyosu, serve as international hubs for tuna auctions and trade, reinforcing Japan's pivotal role in the global tuna supply chain. Advanced fishing technologies and cold-chain logistics ensure the availability of high-quality tuna in domestic markets. For instance, in 2024, Japan's Fisheries Agency announced that WCPFC will expand Japan's Pacific bluefin tuna catch quotas from 2025, increasing large tuna quotas by 50% and smaller ones by 10%. Additionally, Japan’s extensive trading networks facilitate imports of raw tuna from international suppliers, meeting fluctuating domestic demand and ensuring year-round supply. This dynamic interplay between domestic consumption and international trade strengthens Japan's position as a key player in the global tuna industry.
Japan Tuna Market Trends:
Rising Demand for Sustainable and Traceable Tuna
As environmental issues rise globally, consumers and companies in Japan are increasingly focusing on buying sustainably sourced tuna. More people are concerned about overfishing and dwindling tuna reserves, and hence the demand for certified sustainable tuna products, including MSC-certified tuna, is increasing. For instance, in May 2024, Kyowa and Meiho became the first Japanese tuna fisheries using purse seine gear to achieve MSC certification for environmental sustainability. Operating in the Western Central Pacific Ocean, they target skipjack and yellowfin tuna, sold domestically and internationally, opening access to international markets where MSC tuna sales reached 178,000 metric tonnes. Sourcing transparency is yet another major trend in the consumers' search for origin and supply chain details in tuna products. The companies have reacted by taking blockchain and other technologies onboard, thereby satisfying consumers while upholding the credibility of Japan as a responsible seafood market leader.
Shift Toward Processed and Ready-to-Eat Tuna Products
The busy life of modern Japanese consumers increases the desire for more convenience foods, of which ready-to-eat and processed tuna products are part. Canned tuna, flavored tuna pouches, and pre-prepared sushi kits are popular, especially with the younger crowd and those residing in the cities. This shift is further reinforced by the growth of e-commerce platforms and convenience stores, which have enhanced the accessibility of these products. For example, in November 2024, Genki Global, the operator of Genki Sushi and Uobei brands, achieved a significant milestone with 242 international outlets, surpassing its domestic count of over 185 locations. Companies are also introducing value-added offerings, such as lower sodium and greater protein, to catch the health-minded consumer, which, in turn, is acting as another growth-inducing factor.
Technological Advancements in Tuna Fishing and Processing
Technological advancements are transforming the tuna industry of Japan. These include innovations like precision sonar and environmentally-friendly nets in fisheries that enhance fishing efficiency and minimize harm to the ecosystem. Moreover, advanced cold chain logistics and state-of-the-art freezing techniques preserve the freshness of the catch during refrigeration, enabling Japan to export premium-grade tuna to global markets efficiently. For example, from the beginning of 2024, Japan has been importing an average of nearly 50,000 MT of deep-frozen tuna fillets every nine months, indicating the impact of innovations in cold-chain logistics and freezing techniques in maintaining the quality of tuna that could be exported.
Japan Tuna Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Japan tuna market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on species and type.
Analysis by Species:
- Skipjack
- Yellowfin
- Albacore
- Bigeye
- Bluefin
Skipjack tuna is a small, fast-swimming species that reproduces in large numbers. It is abundant in tropical and subtropical waters and is a key species for the Japanese market, particularly for canned tuna. Its relatively low price and mild flavor make it popular in sushi and sashimi, thus maintaining its demand.
Yellowfin tuna, characterized by the yellow dorsal fin, is considered one of the most prized fish species for its firm texture and rich flavor. This species plays a significant role in Japan's high-end sushi and sashimi market. It's also used in steaks and sashimi preparations, appealing to both domestic and international consumers. Its widespread availability and exceptional quality have solidified its role as a cornerstone of Japanese culinary practices.
Albacore tuna is often called white meat tuna because of its lighter-colored flesh. It is mainly used in canned tuna and sushi preparations in Japan. Albacore has a milder flavor and delicate texture, making it a popular choice for more subtle dishes. Its high-fat content contributes to a smoother, more refined taste, fitting various culinary preferences.
Bigeye tuna is highly valued in the Japanese tuna market due to its large eyes and deep-bodied form. It has rich, fatty meat that is preferred for premium sushi and sashimi. High-quality bigeye tuna with a higher fat content is especially favored for high-end dishes, further bolstering Japan's reputation for exquisite tuna cuisine.
Bluefin tuna represents the ultimate for sushi and sashimi with its rich, oily flesh and the "otoro" in particular. Its market share on the high end of the market is dominated by the Pacific Bluefin. These are the rarest of the lots and have great flavor, thereby fetching a heavy price. Hence, it forms a symbol of Japanese culinary supremacy and is widely used in such premium dishes.
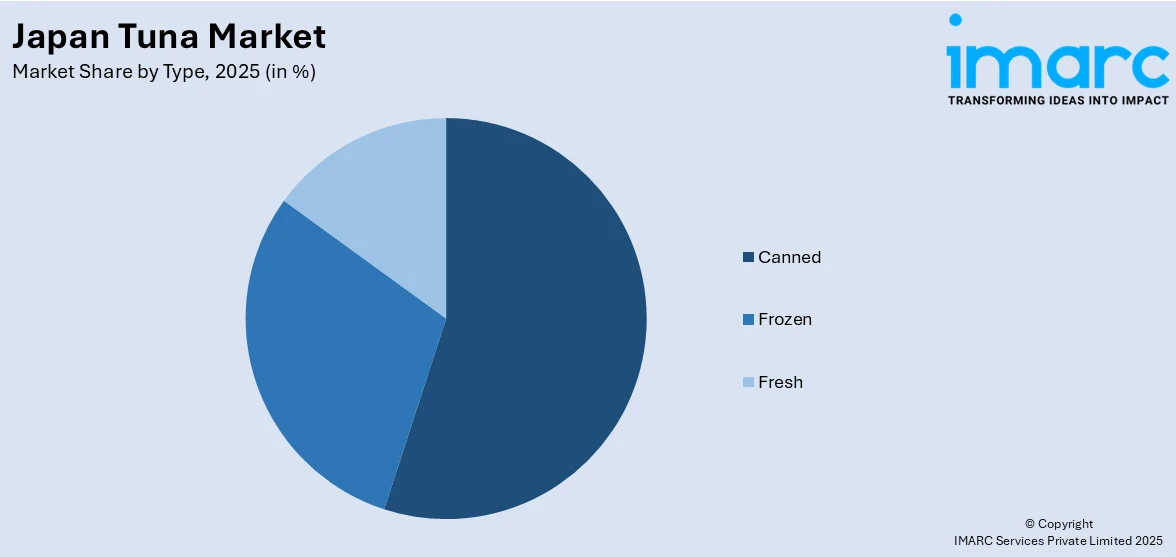
Analysis by Type:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Canned
- Frozen
- Fresh
Canned tuna is a staple in Japan's culinary scene, as it is very convenient and affordable. It is versatile and can complement a variety of meals, including salads, sandwiches, and rice bowls. With a long shelf life and versatility, canned tuna is able to satisfy the needs of home cooks and commercial establishments alike, ensuring a constant supply of tuna for everyday meals.
Frozen tuna plays a key role in the Japanese market, particularly for restaurants and food services that require bulk quantities. It offers a cost-effective solution, allowing for the preservation of high-quality tuna over longer periods. Frozen tuna is often used in sushi and sashimi, with careful thawing techniques ensuring flavor and texture are maintained.
Fresh tuna is considered a precious product in Japan, especially among sushi and sashimi fans. High-grade fresh tuna, including Bluefin and Bigeye, are most in demand in the market due to their high flavor and texture content. It's at the peak of dining experiences found in the finest restaurants and specialty markets throughout the country.
Regional Analysis:
- Kanto Region
- Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region, including Tokyo, is the epicenter of Japan's tuna market. Known for its bustling fish markets, such as Tsukiji (and now Toyosu), Kanto serves as a primary distribution hub for fresh and high-quality tuna. This region caters to premium sushi and sashimi restaurants, fueling the country’s demand for top-grade tuna, particularly Bluefin.
The Kinki region, home to Osaka and Kyoto, is known for its thriving seafood markets and traditional cuisine. It plays a crucial role in Japan’s tuna industry by providing a steady supply of fresh and frozen tuna to restaurants specializing in sushi, sashimi, and other seafood dishes. The region’s demand for diverse tuna types supports both domestic and international markets.
The Central/Chubu region, including Nagoya, serves as a critical area for tuna distribution and consumption. Known for both its coastal fisheries and access to fresh catches, it supports Japan’s middle market for tuna, focusing on both fresh and frozen varieties. It supplies a wide range of restaurants, from casual eateries to upscale sushi shops.
Kyushu-Okinawa, known for its rich coastal waters, is a major contributor to Japan's tuna market, particularly for fresh and frozen tuna. The region supplies a variety of tuna species to domestic markets, supporting both traditional sushi restaurants and larger fish distributors. The demand for affordable, quality tuna in Kyushu is significant, feeding local and regional preferences.
With its proximity to the Pacific Ocean, Tohoku, located in northern Japan, is crucial for tuna fishing. The region provides fresh catches, including high-quality tuna, to Japan’s broader market, particularly in the sushi and sashimi sectors. Tohoku’s contribution helps maintain the supply chain of tuna to various regions, supporting both traditional and modern food preparations.
The Chugoku region, known for its fishing ports and seafood trade, plays a vital role in the Japanese tuna market. Serving both fresh and frozen tuna to local markets and restaurants, this region provides a steady flow of affordable and premium tuna varieties. Its seafood industry supports local cuisine, from sushi to tuna-based dishes.
Hokkaido, Japan’s northernmost region, offers an abundance of high-quality tuna due to its proximity to cold, nutrient-rich waters. It is renowned for producing some of Japan's best fresh tuna, especially prized for sashimi. Hokkaido supplies premium tuna to top-tier sushi restaurants, playing a pivotal role in Japan’s luxury tuna market.
Shikoku, known for its beautiful coastline and fishing culture, is a key player in Japan's tuna market. The region is especially important for supplying fresh and frozen tuna to local markets and sushi establishments. Shikoku’s coastal towns support a steady stream of tuna, contributing to the nation’s diverse culinary preferences.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japanese tuna market is highly competitive, characterized by the presence of domestic and international players across the supply chain. Key domestic companies dominate the processing and distribution sectors, leveraging advanced technology and robust networks. International suppliers, such as from countries like Indonesia, Taiwan, and the United States, form an essential element of supplying imported raw tuna for Japan. Intensification in competition within the market comes due to increased demand from consumers toward more sustainable and traceable products, where companies invest in eco-certifications and innovative practices. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce is redefining the nature of retailing and generating new paths of competition. For example, in May 2024, Maruha Nichiro Corporation partnered with East Japan Railway and the University of Tokyo to popularize the "Planetary Health Diet," which, among other green food practices, aims to sustainably source tuna for the next 100 years.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Japan tuna market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2024, Osaka-based NH Foods launched a plant-based tuna sashimi alternative for Japan’s restaurant market. Designed to replicate the aroma and texture of raw tuna, this alt-seafood product offers an authentic dining experience.
- In February 2024, the Global Tuna Alliance (GTA) celebrated a major breakthrough with Meiho Co. Ltd., a Shiogama-based fish processor, becoming its first Japanese partner. This is significant for the GTA, as Japan, the world’s second-largest tuna fishing nation and a top consumer, plays a crucial role in global tuna sustainability.
Japan Tuna Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Species Covered | Skipjack, Yellowfin, Albacore, Bigeye, Bluefin |
| Types Covered | Canned, Frozen, Fresh |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan tuna market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan tuna market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan tuna industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan tuna market was valued at USD 708.5 Million in 2025.
Key factors driving Japan's tuna market include high domestic demand for sushi and sashimi, advancements in sustainable fishing practices, innovations in freezing and processing technologies, and growing exports of premium-grade tuna. Additionally, partnerships promoting eco-friendly practices and increasing consumer awareness of sustainability are shaping the market's growth and global competitiveness.
IMARC estimates the Japan tuna market to reach USD 882.9 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.40% during 2026-2034.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












