
Japan Telehealth Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Communication Technology, Hosting Type, Application, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
Japan Telehealth Market Size and Share:
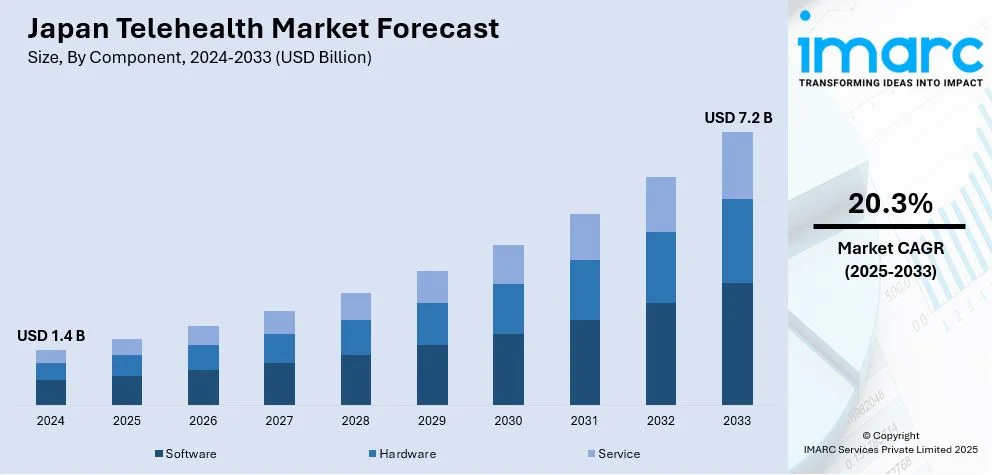
The Japan telehealth market size was valued at USD 1.4 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 7.2 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 20.3% from 2025-2033. The market is witnessing significant growth due to Japan’s aging population and advanced digital healthcare infrastructure. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics, expansion of telemedicine for mental health services, and the adoption of remote patient monitoring are expanding the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.4 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 7.2 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 20.3% |
The rapidly aging population in Japan serves as an impetus for the rapid growth of telehealth services. With more than 28% of its population aged 65 and over, Japan is putting increasing stress on its healthcare system due to the mounting demand for medical care. Telehealth is, therefore, the answer, as it allows remote consultations for elderly patients to access healthcare services from home and avoid travel to care facilities. This, besides resolving the challenges of access to healthcare in rural and remote parts, considerably alleviates the burden on hospitals and clinics, thereby improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
The highly developed digital healthcare infrastructure of Japan supports the proliferation of telehealth services. The Japanese government has been investing in healthcare technology including telemedicine platforms and electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitate medical services and improve patient outcomes. For instance, in 2024, MEDIROM Healthcare Technologies announced that M3, Inc. or its affiliate is participating in the Series A financing round of MEDIROM MOTHER Labs, focusing on advancing telehealth solutions, with a pre-money valuation of JPY9 billion. The country’s high internet penetration rate and sophisticated mobile networks further enable the widespread adoption of telehealth solutions. This infrastructure, combined with strong government support and increasing consumer trust in digital health solutions, creates a favorable environment for the telehealth market to flourish in Japan.
Japan Telehealth Market Trends:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics is transforming the Japanese telehealth landscape. AI is being leveraged to enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment plans, and streamline administrative tasks. Machine learning algorithms are being used to analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and identify potential health risks. With Japan’s strong focus on technological innovation, AI-driven telehealth solutions are increasingly being adopted to improve healthcare efficiency and decision-making processes. For instance, in 2024, Google invested in Ubie to enhance digital health with generative AI. Ubie’s AI Symptom Checker helps 12 million users monthly, while its Medical Navigator supports 1,700 medical institutions across Japan. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots are enabling patients to access instant medical consultations, further promoting the adoption of telehealth services.
Expansion of Telemedicine for Mental Health Services.
There is a growing trend towards the expansion of telemedicine for mental health services. For instance, in 2024, Japan's digital health market is projected to reach $6.15 billion, with continued growth at an annual rate of 7.29%, driven by increasing adoption of telemedicine and e-Health solutions. Mental health awareness in Japan has risen significantly, with a particular emphasis on addressing stress, anxiety, and depression among the aging population and working professionals. Telehealth offers a convenient and accessible platform for mental health consultations, reducing the stigma associated with seeking therapy and allowing patients to receive care in private and comfortable settings. This trend is further supported by Japan’s healthcare system, which increasingly recognizes the importance of mental health services in overall well-being.
Adoption of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
The adoption of remote patient monitoring (RPM) technologies is gaining momentum in Japan, particularly for chronic disease management. RPM allows healthcare providers to track patients' vital signs, glucose levels, blood pressure, and other health metrics in real-time, enabling proactive care and timely interventions. For instance, in 2024, OMRON Healthcare acquired Luscii Healthtech, a leader in digital health and remote consultation platforms. Luscii offers a customizable platform for home care, addressing over 150 diseases, including chronic conditions. This technology is especially beneficial for Japan’s aging population, as it reduces the need for frequent hospital visits and allows patients to manage their conditions more effectively at home. Remote monitoring also supports the shift toward preventive healthcare, which is a key focus for Japan’s healthcare system.
Japan Telehealth Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Japan telehealth market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on component, communication technology, hosting type, application, and end user.
Analysis by Component:
- Software
- Hardware
- Service
The telemedicine software in Japan encompasses applications for virtual consultations, appointment scheduling, and EHR management, while many companies are integrating AI-based tools for diagnostics, remote patient monitoring, and engagement. By now, when combined with remote healthcare solutions and other interventions designed to streamline healthcare workflows, this software makes healthcare accessible, lowers the wait time for services, and improves healthcare efficiency to a great extent for the elderly.
Telehealth hardware in Japan comprises instruments like wearables, remote monitoring devices, and telemedicine kits that facilitate the real-time transmission of health data. The gadgets here include smartwatches that continuously monitor heart rates and blood pressure cuffs to perform continuous health status tracking: healthcare providers will now be able to use this information to monitor chronic conditions remotely, intervene early when needed, and thus provide better patient care while minimizing hospital visits.
Telehealth services in Japan includes consultations by video; teletherapy for mental health; and management of chronic diseases. Providers give remote access to doctors, specialists, and mental health professionals who can assess and treat patients who do not have easy access to physical health clinics. With patient-centric services, convenience and flexibility are built into every step of service setup, thus meeting the increasing inquiries into accessible healthcare for both urban and rural residents.
Analysis by Communication Technology:
- Video Conferencing
- mHealth Solutions
- Others
Japan's telehealth market is driven by video conferencing technology, allowing remote consultations between health practitioners and patients. Hence, this technology allows real-time interaction, reducing the necessity for in-person visits, ensuring timely medical advice, and especially helping the elderly population by allowing healthcare services and specialists to be accessed easily from home. This way, overall patient care and convenience are enhanced.
Mobile health solutions in Japan are health services delivered directly to patients via mobile applications and devices. These mobile health solutions allow health metrics such as blood pressure and glucose levels to be monitored remotely while providing access to health data through smartphones. Other capabilities of mHealth apps are to promote engagement among patients via reminders, health tracking, and virtual consultations, making healthcare systems more accessible and efficient in Japan's telehealth market.
Analysis by Hosting Type:
- Cloud-Based and Web-Based
- On-Premises
The advent of the cloud-based hosting and web-based hosting solutions is revolutionizing the Japanese telehealth industry, as it promises features such scalability, security, and access for delivering services online. Such online features enable healthcare providers to store and retrieve patient information remotely and allow real-time consultation with scheduling efficiency and continuous monitoring. The approach is poised to improve health accessibility with an aging population in Japan, increased flexibility, and uninterrupted patient care that is cloud-based.
On-premise hosting caters to telehealth in Japan, so that healthcare organizations can have more control over their data security and privacy. This form of telehealth infrastructure is preferred by hospitals and clinics that have very stringent regulations since it provides a private platform for telehealth on dedicated infrastructure. On-premises systems provide secure telecommunication, patient data management, and on-demand telemedicine services to satisfy all regulatory requirements on patient care under local health legislation with maximum reliability in high-stakes care environments.
Analysis by Application:
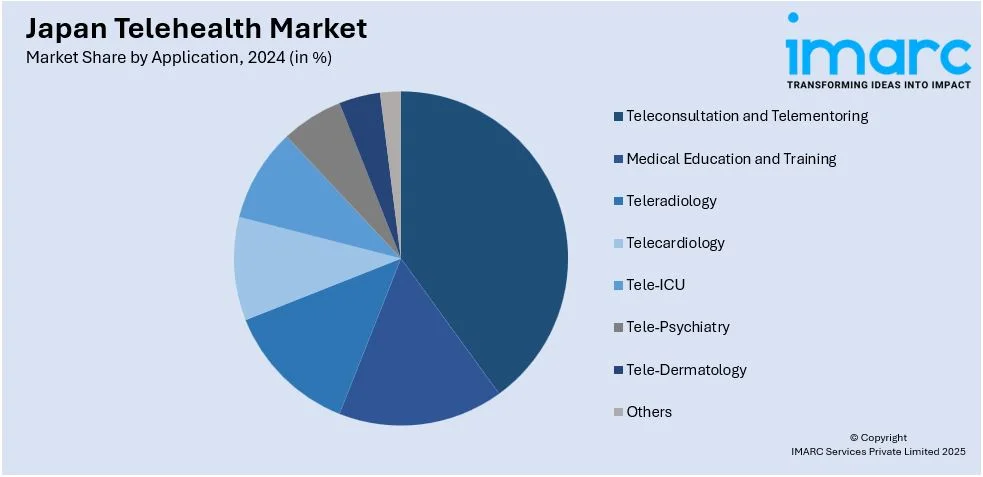
- Teleconsultation and Telementoring
- Medical Education and Training
- Teleradiology
- Telecardiology
- Tele-ICU
- Tele-Psychiatry
- Tele-Dermatology
- Others
Teleconsultation and telementoring in Japan bring medical experts closer to patients for consultations and technical consults as well. Doctors can contact specialists immediately for hard cases to increase accurate diagnosis and treatment decision-making. It improves the quality of health care delivered and better outcomes for patients across the really difficult geographical areas where healthcare professionals are usually lacking in numbers.
Telehealth applications for medical education and training provide a forum for healthcare providers in Japan to attend virtual workshops, lectures, and symposia. This allows continued education and skill upgrading so that practitioners are up to date with the latest developments in medicine. Tele-education thus affords an opportunity to gain access to experts' locations of knowledge, especially for healthcare workers in distant sites or marginalized areas.
This application enables Teleradiology in Japan to allow an expert in the field of radiology to interpret remotely X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. This availability of data enables radiologists to access and analyze the imaging results from any location, thereby rendering the diagnosis more efficient and faster. Such an application is very helpful mostly for rural society where there might not be a specialized radiologist near by an end-user, ensuring timely diagnosis and making it easy for the patients to take critical care.
Patients suffering from heart diseases can remain at home while the telecardiology applications in Japan provide them with remote cardiovascular monitoring and assessment. Wearable devices and mobile applications allow patients to transfer real-time data, which is then analyzed by cardiologists. This makes heart specialists easily accessible as well as consistent with the care and timely intervention for the patients, especially in remote areas.
Tele-ICU services of remote monitoring are now available in Japan and it takes on the condition of providing such highly specialized care to critically ill patients and subjecting them to constant surveillance. Intensive care medicine has previously been remote; however, with high-resolution cameras and data transmission, intensivists are involved in the day-to-day collection and monitoring of vital signs from patients, and they can provide intervention or even treatment as necessary. Such an application improves the efficiency of ICU care through timely intervention but also reduces the cost burden placed on hospitals, particularly the less well-equipped.
Tele-psychiatry opens up mental health services access points for urban and rural patients, providing access to mental health services remotely. Video consultations and secure messaging services allow the mental health professionals to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients with psychiatric disorders. Notably, this application benefits the elderly population since it provides mental health services conveniently and without stigma.
Tele-dermatology in Japan allows a remote consultation by which images of skin-related problems can be forwarded to dermatologists, who will analyze the images and provide a diagnosis without requiring the patient to physically visit the clinic. Access to the service improves, especially for rural patients, while providing a dermatological service very efficiently.
Analysis by End User:
- Providers
- Patients
- Payers
- Others
The telehealth paradigm in Japan enhances healthcare provision through remote consultations, monitoring, and diagnostics. Telehealth extends doctors', specialists', and hospitals' reach into underdeveloped areas; simultaneously, it relieves the pressure on physical facilities, increases workflow efficiency, and assists providers in real-time patient monitoring, promoting timely interventions and assuring a high quality of care.
From the patients' perspective, telehealth promotes convenient access to services in Japan, reducing waiting times. Patients, particularly those in rural or remote areas, are able to access healthcare from their homes. Telehealth also enables individuals with chronic conditions and mobility problems to receive continuous care, while mental health services provide a safe and stigma-free environment for consultations.
Telehealth creates opportunities to decrease in-person visit costs for health plans, government programs, and health insurers in Japan. This means that, through tele-consultations and tele-monitoring, payors can optimize resource utilization, gain greater control over healthcare expenditures, and incentivize preventive care, thereby aiding in the better sustainability of the system and patient care outcomes.
Regional Analysis:
- Kanto Region
- Kinki Region
- Central/Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region, including Tokyo, is a hub for Japan’s telehealth market, with the highest concentration of healthcare institutions and tech innovation. Major hospitals and health insurance companies offer telehealth services, enabling wide access to virtual care. Urban infrastructure supports the rapid adoption of telemedicine, especially for consultations and mental health services.
The Kinki region, home to Osaka and Kyoto, is pivotal in Japan's telehealth market, driving demand for remote healthcare services in both urban and rural areas. Regional healthcare providers are adopting telehealth technologies for chronic disease management, while patients benefit from improved access to specialists, enhancing care delivery in remote and underserved locations.
The Chubu region’s telehealth market is supported by its mix of urban and rural areas. Telehealth services are growing, particularly in the aging population of rural areas. Virtual consultations and health monitoring help bridge the healthcare gap, offering services such as home care, chronic disease management, and remote rehabilitation, ensuring continuous care for elderly patients.
In Kyushu and Okinawa, telehealth is enhancing healthcare accessibility, particularly for underserved islands and rural areas. The region has adopted telemedicine for routine consultations and post-hospital care, helping residents access specialists from major cities. With a high elderly population, telehealth services play a critical role in managing chronic conditions and providing mental health support.
The Tohoku region, with its expansive rural areas, faces challenges in healthcare access. Telehealth is addressing this gap by providing remote consultations, diagnostic services, and follow-up care, especially for the elderly. The region is leveraging telemedicine to ensure consistent healthcare delivery, improving access to specialists and reducing travel time for remote patients.
In the Chugoku region, telehealth is becoming increasingly important for elderly care. Rural hospitals and clinics are utilizing telemedicine for remote monitoring of chronic diseases and consultations. The region is focused on increasing healthcare accessibility through virtual care, ensuring that rural populations receive timely medical services and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities.
Hokkaido, with its vast rural areas and harsh winters, benefits from telehealth by offering remote healthcare services to its isolated population. Telemedicine platforms enable rural residents to consult with doctors without the need to travel long distances. These services are particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions, mental health, and elderly care, ensuring access to consistent care.
The Shikoku region is adopting telehealth solutions to address healthcare access issues in its remote and rural communities. Telemedicine services are being expanded to provide consultations for general health concerns, chronic disease management, and specialized care. Telehealth is also supporting mental health services, providing a crucial lifeline for individuals in underserved areas.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the Japan telehealth market is characterized by a mix of established healthcare providers and emerging tech-driven startups. Key players include large Japanese health insurance companies and hospitals integrating telehealth services into their offerings, alongside global telemedicine platforms like Teladoc and American Well. For instance, in 2025, Wiley partners with M3 Digital Communications to expand its medical education programs in Japan. The collaboration will create and distribute new content for Japanese healthcare professionals, leveraging M3's digital marketing expertise. Domestic startups, such as M3, Inc. and LINE Healthcare, are leveraging Japan's robust digital infrastructure to provide specialized telehealth solutions, particularly for mental health and chronic disease management. Competition is intensifying as companies focus on enhancing user experience, expanding service offerings, and developing AI-driven healthcare tools to meet the growing demand for remote healthcare services.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Japan telehealth market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In February 2025, MediBuddy, India's biggest digital healthcare firm, joined hands with Japan's ELECOM to offer smart health IoT devices in India, hence moving forward in MediBuddy's aim to accessible preventive health care.
- In June 2024, Teijin Pharma and CureApp entered into a joint marketing and sales agreement for a medical device for treating hypertension called Prescription Digital Therapeutic App. The purpose of this collaboration between Teijin Pharma and CureApp is to introduce CureApp HT, which facilitates lifestyle modification to treat hypertension and serves to fulfill some unmet medical needs through the medium of distribution for digital therapeutics (DTx).
Japan Telehealth Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Software, Hardware, Service |
| Communication Technologies Covered | Video Conferencing, mHealth Solutions, Others |
| Hosting Types Covered | Cloud-Based and Web-Based, On-Premises |
| Applications Covered | Teleconsultation and Telementoring, Medical Education and Training, Teleradiology, Telecardiology, Tele-ICU, Tele-Psychiatry, Tele-Dermatology, Others |
| End Users Covered | Providers, Patients, Payers, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan telehealth market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan telehealth market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan telehealth industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The telehealth market in Japan was valued at USD 1.4 Billion in 2024.
The growth of Japan's telehealth market is driven by an aging population, rising demand for remote healthcare services, advancements in digital health technology, and government support for telemedicine adoption. Increased awareness of telehealth’s convenience and effectiveness, particularly in rural areas, also contributes to its expanding role in the healthcare system.
The Japan telehealth market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 20.3% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 7.2 Billion by 2033.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












