
Japan Railroad Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Distance, End Use, and Region, 2025-2033
Japan Railroad Market Size and Share:
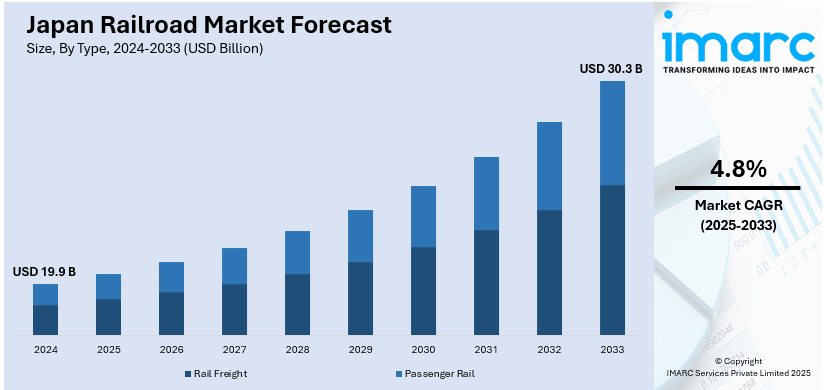
The Japan railroad market size was valued at USD 19.9 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 30.3 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.8% from 2025-2033. The market is driven by robust need for both freight and passenger transportation, and rapid technological innovations. Additionally, substantial government investments in infrastructure and sustainability initiatives are driving the growth of the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 19.9 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 30.3 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 4.8% |
The Japan railroad industry is propelled by a rising demand for efficient and dependable transportation solutions. Japan’s dense population, particularly in urban areas like Tokyo and Osaka, necessitates seamless and high-frequency rail services. For instance, as per industry reports, in 2024, Tokyo has emerged as the most populous city globally, with more than 37 million of population. Furthermore, the high-speed Shinkansen, or bullet train, network plays a vital role in addressing the demand for rapid intercity travel, while urban transit systems support daily commuting needs. Additionally, Japan's focus on enhancing the convenience and accessibility of rail services, coupled with technological advancements, ensures that the sector continues to meet the evolving demands of both passengers and businesses.
Government investment in the development and modernization of Japan’s rail infrastructure serves as a significant market driver. For instance, in 2024, JR Central, a prominent Japan-based railway company, announced its capital investment for FY 2025, with 674.0 billion yen allocated for the consolidated group and 630.0 billion yen for the non-consolidated investment. With ongoing efforts to expand high-speed rail networks and integrate advanced technologies, the government continues to promote rail transport as a sustainable and efficient alternative to road and air travel. Moreover, investments also support the transition to eco-friendly rail systems, such as fully electrified networks and the integration of renewable energy sources. These initiatives not only enhance the environmental sustainability of the rail sector but also contribute to economic growth by improving connectivity and fostering regional development.
Japan Railroad Market Trends:
Growth in High-Speed Rail Services
Japan’s high-speed rail market is constantly expanding, with the Shinkansen network emerging as a crucial driver of this trend. For instance, industry reports state that as of 2024, the Shinkansen network covered over 3,000 kilometers, connecting major cities like Tokyo, Osaka, and Fukuoka. Moreover, the amplifying requirement for more effective, faster travel has resulted in a steady investment in exceptional-speed rail infrastructure, with new routes rapidly being planned. This proliferation caters to the Japan’s robust focus on improving connectivity and lowering travel times, further fortifying high-speed rail as a chief segment of Japan's rail transportation industry.
Expansion of Regional Rail Networks
The extension of regional rail networks is emerging as a principal trend in Japan’s railroad sector as it targets to improve connectivity in scarcely populated region. Enhanced rail infrastructure across rural zones fosters economic expansion by facilitating better access to urban areas and supporting local sectors. Such developments also bolster tourism by offering effective transportation to historically significant or scenic places. In addition, augmenting regional networks aids in alleviating congestion in key metropolitan cities by distributing travel need more evenly across the nation, contributing to a more sustainable as well as balanced transportation network. For instance, as per industry reports, rural tourism is a chief factor that can aid in alleviating congestion and pressure on urban tourist sports, with 97% of the visitors acknowledging interest in exploring regional areas of Japan.
Sustainability Initiatives and Eco-Friendly Rail Systems
Sustainability has become a key focus within Japan’s railroad market, with the industry making significant strides toward reducing its environmental impact. Rail transportation is widely regarded as an environmentally friendly option, offering greater energy efficiency and producing fewer carbon emissions compared to road and air travel. The sector is further committed to enhancing its environmental performance through the adoption of energy-saving technologies, such as regenerative braking systems that capture and reuse energy during braking. Japan's railway companies are progressively adopting renewable energy solutions, including solar and wind power, to enhance the sustainability of their operations. For instance, in January 2025, Central Japan Railway Co. launched solar venture for bullet train barriers. Under this initiative, solar cells will be deployed on noise barriers along the Tokaido Shinkansen Line to provide electricity to stations and several other rail facilities. Japan railroad market outlook reflects that this emphasis on sustainability is positioning the sector to meet future environmental goals while ensuring continued growth and modernization of its infrastructure.
Japan Railroad Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Japan railroad market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type, distance, and end use.
Analysis by Type:
- Rail Freight
- Passenger Rail
Rail freight holds a substantial share of the Japan railroad market, primarily propelled by its efficacy in transporting huge volumes of goods over long distances. Japan's rail infrastructure aids the movement of a broad range of commodities, typically encompassing agricultural goods, raw materials, and manufactured products. The sector extensively profits from robust government aid targeted at minimizing road congestion and endorsing sustainability. In addition, with technological innovations in logistics and the magnifying focus on environmental awareness, rail freight provides an environmentally friendly and cost-saving solution, further fortifying its prominence in Japan's transportation industry.
The passenger rail segment commands a prominent Japan railroad market share, primarily due to the widespread use of commuter and high-speed rail services. The Shinkansen, a globally recognized high-speed rail system, has set a benchmark for punctuality, efficiency, and safety. Moreover, with dense urban populations and rising commuter demands, Japan’s passenger rail networks are vital for daily transportation. Furthermore, ongoing investments in infrastructure and innovations in customer service continue to enhance the appeal of passenger rail, making it an indispensable mode of transport in both urban and intercity markets, further solidifying its crucial position in the sector.
Analysis by Distance:
- Long Distance
- Short Distance
The long-distance rail segment holds a notable share of Japan's railroad market, principally boosted by the need for intercity traveling. Japan’s Shinkansen network, highly acknowledged for its high efficacy, exceptional speed, and better safety, plays a central role in connecting distant locations, positively impacting leisure as well as business travel. In addition, the dependability, convenience, and comfort of long-distance trains support their increasing popularity among travelers. Furthermore, with proliferation of high-speed rail lines and active advancements in rail infrastructure, long-distance rail travel remains an integral component of Japan’s transportation segment, escalated by the heightening focus on improving service quality and lowering travel durations.
The short-distance rail segment represents a substantial portion of Japan’s railroad market, driven by the dense population centers and the need for efficient daily commuting. Urban transit systems, including subways and local trains, are integral to daily life, offering fast and reliable transportation for millions of passengers. Furthermore, Japan's advanced rail networks support short-distance travel in metropolitan areas, providing seamless connections between residential, commercial, and industrial zones. With rising urbanization and increasing commuter demand, short-distance rail services are essential for managing daily transportation needs, ensuring their continued dominance in Japan’s market.
Analysis by End Use:
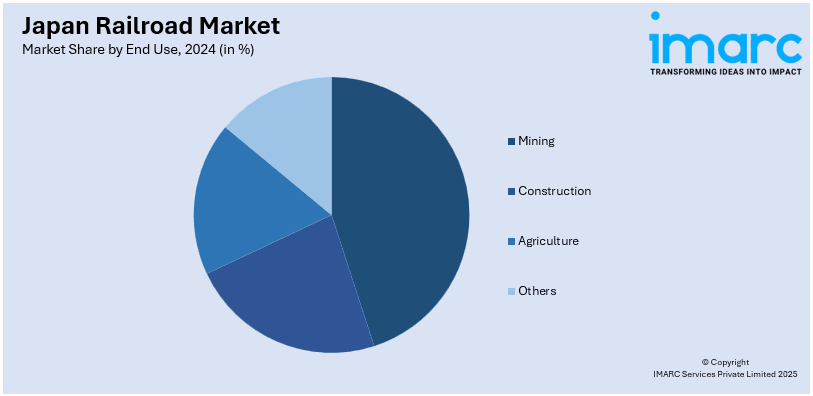
- Mining
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Others
The mining sector contributes significantly to Japan railroad market growth, with rail transport playing a key role in the movement of raw materials. Rail networks efficiently handle large quantities of minerals, ores, and coal from mining regions to processing facilities and ports. Japan's rail infrastructure is critical for facilitating the transportation of these heavy commodities, reducing reliance on road and sea transport. Furthermore, ongoing technological advancements in rail logistics and the growth of mining operations support the continued strength of this segment, ensuring reliable and cost-effective transportation of mining materials essential to Japan’s industrial economy.
The construction industry represents a significant market share in Japan's railroad sector, driven by the need to transport building materials, equipment, and machinery. Rail freight services are essential for moving large volumes of construction supplies, such as steel, cement, and lumber, from manufacturing facilities to project sites. Additionally, Japan's advanced rail networks offer efficient transportation solutions, supporting the construction sector’s growth. Moreover, the industry benefits from rail’s ability to handle heavy loads over long distances, contributing to the timely delivery of essential materials and bolstering the overall productivity of the nation's infrastructure projects.
Agriculture plays a vital role in Japan's railroad market, with rail transport facilitating the movement of agricultural products such as rice, vegetables, and livestock. Rail is a crucial mode of transport for connecting rural agricultural regions with urban centers and export terminals. The sector benefits from Japan's efficient rail systems, ensuring the timely delivery of perishable goods while reducing transportation costs. Furthermore, as Japan continues to prioritize food security and sustainable agricultural practices, rail networks will remain integral to the agricultural supply chain, supporting both domestic consumption and international trade.
Regional Analysis:
- Kanto Region
- Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region holds a critical market share in Japan’s railroad sector due to its large population and economic significance. This region encompasses Tokyo, Japan’s capital and a global financial hub, driving high demand for both passenger and freight rail services. The extensive rail network, including the Shinkansen and metropolitan transit systems, caters to millions of commuters daily. Additionally, Kanto’s robust infrastructure supports intercity and freight transportation, making it the central hub for logistics and business activity, thereby maintaining its leading position in the national railroad market.
The Kinki region, centered around Osaka, is a key player in Japan’s railroad market, supporting both heavy commuter traffic and regional connectivity. Osaka, Japan's second-largest metropolitan area, relies heavily on rail for daily transit, with a dense network of local and intercity services. The region is also a critical center for manufacturing, increasing demand for rail freight services to transport industrial goods. Furthermore, the Kinki region’s well-developed rail infrastructure, including the Shinkansen, ensures efficient travel and freight movement, bolstering its position as a significant contributor to the country's overall railroad market share.
The Chubu region, home to major cities like Nagoya, is vital to Japan’s railroad market due to its strategic location between the Kanto and Kansai regions. Nagoya, a key industrial and transportation hub, benefits from a well-integrated rail network that supports both commuter and freight services. The region plays a significant role in supporting the automotive and manufacturing industries, which rely on rail for moving goods efficiently. Additionally, the development of high-speed rail connections further enhances Chubu’s position in the broader Japanese railroad market, ensuring continued growth and connectivity.
The Kyushu-Okinawa region is an important segment of the Japanese railroad market, with Kyushu serving as the primary rail hub. The region benefits from its strategic location connecting southern Japan with other major areas. Kyushu’s Shinkansen lines and local rail systems ensure efficient travel for passengers and freight. Besides, the tourism sector also drives Japan railroad market demand, with visitors utilizing trains to explore the region's historical and natural attractions. Rail transport in the Kyushu-Okinawa region plays a crucial role in both domestic and international trade, making it a key market contributor in the country’s railroad landscape.
The Tohoku region, located in northern Japan, holds a significant share of the railroad market, with rail services playing a critical role in its economic and social infrastructure. The region’s reliance on rail for passenger transport is high, particularly for those traveling between cities and rural areas. The Tohoku Shinkansen provides fast, efficient connections to major urban centers, fostering economic development and tourism. Furthermore, the transportation of goods, especially agricultural products, is vital to the local economy. With continuous improvements in rail infrastructure, the Tohoku region remains a key player in Japan’s railroad market.
The Chugoku region, located in western Japan, is a crucial component of the country’s railroad market, with rail playing a vital role in both passenger and freight transport. The region’s rail infrastructure supports local economies by connecting smaller cities with larger hubs like Osaka and Hiroshima. In addition, rail services in the Chugoku region are essential for industries such as manufacturing and agriculture, enabling the efficient movement of goods. The development of high-speed rail links and the ongoing focus on infrastructure improvements continue to strengthen Chugoku’s position within Japan’s railroad sector.
The Hokkaido region, Japan’s northernmost island, plays a key role in the national railroad market, particularly for long-distance and regional travel. Rail is the primary mode of transport for both passengers and freight, linking remote areas with major cities like Sapporo. The region’s rail network is crucial for industries such as agriculture and tourism, with seasonal spikes in travel demand. Despite its geographical challenges, Hokkaido’s rail infrastructure continues to develop, ensuring greater connectivity and supporting its contribution to the broader Japanese railroad market, particularly in handling cargo and seasonal tourism traffic.
The Shikoku region, located in southwestern Japan, has a specialized but important role in the railroad market. Rail transport in Shikoku supports daily commuting and the movement of goods across its smaller cities and towns. Though not as densely populated as other regions, Shikoku’s rail network is vital for local connectivity, especially in rural areas. The region also benefits from its location as a transportation link between Honshu and Kyushu, facilitating freight movement. Furthermore, ongoing investments in rail infrastructure ensure that Shikoku remains a critical player in Japan’s broader railroad market, focusing on both passenger and freight services.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape is represented by a blend of public and private operators, each specializing in various segments such as intercity, high-speed, and urban rail services. Competition centers around service quality, technological innovations like automation, and ongoing infrastructure investments. Moreover, the market is influenced by government policies aimed at improving efficiency, sustainability, and enhancing passenger experience. Furthermore, technological advancements, such as the development of autonomous and energy-efficient trains, play a significant role in shaping competitive strategies. For instance, as per industry reports, in September 2024, East Japan Railway Company confirmed its plans to launch automated Shinkansen trains, prominently known as high-speed bullet train, which are anticipated to become operation by FY2028. Additionally, ongoing investments in rail network expansion and modernization further intensify competition in the sector.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Japan railroad market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In September 2024, Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), a Japan-based prominent high-speed railway solutions provider, announced utilization of Amazon Web Services to improve its operations for Yamanashi Maglev Line. JR Central will develop its crucial IT infrastructure workloads on AWS platform and utilize its AI, ML, and IoT abilities to upgrade its data-based operations, significantly lower maintenance costs, and boost operational efficacy.
- In July 2024, Hokkaido Railway Co. announced plans to launch its new Blue Star and Red Star luxury sightseeing trains around March-May 2026, with a significant investment of USD 11.2 billion that will cover the expenditure to remodel its existing train model KiHa 143.
- In May 2024, Hankyu Corporation, Sumitomo Corporation, and the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) announced a strategic collaboration to maintain as well as operate Manila Light Rail Transit Line 1 (LRT-1). This venture encompasses transferring LRT-1 associated shares from Sumitomo to JICA and Hankyu, reflecting an active participation in the railway segment, particularly in enhancing and managing urban rail transit systems.
- In May 2024, Hitachi Ltd. a major Japan-based conglomerate, strategically acquired Thales SA business associated with rail signaling through its Britain-based rail subsidiary. The acquisition was closed with an investment of USD 1.78 billion.
Japan Railroad Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Rail Freight, Passenger Rail |
| Distances Covered | Long Distance, Short Distance |
| End Uses Covered | Mining, Construction, Agriculture, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan railroad market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan railroad market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan railroad industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan railroad market was valued at USD 19.9 Billion in 2024.
Key factors driving the market include increasing urbanization, government investments in infrastructure development, and the demand for efficient, high-speed rail systems. Additionally, Japan's focus on sustainability, technological innovations like autonomous trains, and rising passenger volumes contribute to the market's continued growth and modernization.
IMARC estimates the Japan railroad market to exhibit a CAGR of 4.8% during 2025-2033.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












