
Japan Gas Turbine Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Design Type, Rated Capacity, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
Japan Gas Turbine Market Size and Share:
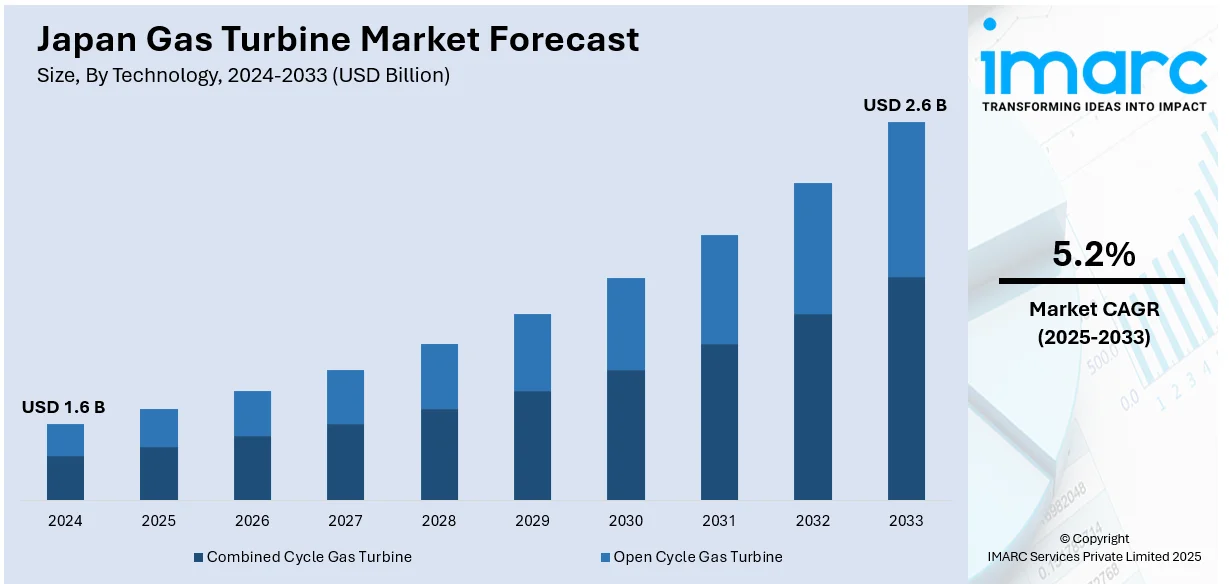
The Japan gas turbine market size was valued at USD 1.6 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 2.6 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.2% from 2025-2033. The market is driven by increasing demand for efficient, reliable power generation and the shift toward cleaner energy solutions. Government initiatives supporting energy infrastructure modernization and advanced technologies, such as combined-cycle power plants, are propelling the Japan gas turbine market share. Additionally, replacing aging power plants with advanced gas turbines, coupled with technological advancements in efficiency and maintenance, aligns with Japan’s sustainability and emission reduction goals.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 1.6 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 2.6 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 5.2% |
The growing demand for dependable and efficient power generation is a significant driver of the Japan gas turbine market. Japan's emphasis on energy security and its transition toward cleaner energy sources have fueled investments in gas turbines, known for their high efficiency and low carbon emissions. Additionally, the government's initiatives to modernize energy infrastructure and adopt advanced technologies, such as combined-cycle power plants, further bolster the market. On 10th April 2024, In June 2023, Japan updated its Basic Hydrogen Strategy, which committed more than JPY 15 trillion (USD 98.8 billion) to hydrogen-related technologies, including fuel cells and water electrolysis, with an aim to use 12 million tons of hydrogen a year by 2040. In FY2024, Tokyo's budget for hydrogen projects jumped to JPY 20.3 billion (USD 134 million), emphasizing fuel cell vehicles including buses and trucks, and developing green hydrogen facilities. These steps are part of Japan's more general drive to incorporate hydrogen into energy systems, including feeding into gas turbines. Moreover, the rising need for flexible power systems to balance renewable energy intermittency is also creating a positive Japan gas turbine market outlook, which can quickly respond to fluctuations in power demand.
The industrial sector's expansion, which relies on gas turbines for cogeneration and energy optimization, is significantly supporting the market. Industries in Japan are increasingly adopting gas turbines to reduce operational costs and comply with stringent environmental regulations. Thus, this is positively influencing the market. Technological advancements, including digital monitoring and maintenance solutions, are enhancing the efficiency and lifespan of gas turbines, making them a more attractive investment. On 17th January 2024, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and Kansai Electric Power (KEPCO) unveiled plans to commission a next-generation CO2 capture pilot plant at Japan's Himeji No.2 Power Station, capturing 5 tons/day using flue gas from its gas turbine, which will start operating in FY2025. This project, with MHI since 2022 partnering with ExxonMobil, is to help develop carbon capture technology, minimize environmental impact, and increase competitiveness. Additionally, remote monitoring via MHI's ΣSynX system will enable automated operations, aligning with MHI's 2040 carbon neutrality goals. Furthermore, the aging fleet of conventional power plants in Japan is being replaced with advanced gas turbines, which offer higher efficiency and lower emissions, aligning with the country's sustainability goals.
Japan Gas Turbine Market Trends:
Adoption of Hydrogen-Ready Gas Turbines
Japan is at the forefront of adopting hydrogen-ready gas turbines, aligning with its carbon neutrality goals by 2050. Companies are innovating gas turbines capable of running on hydrogen or hydrogen-natural gas blends, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This trend is supported by the government’s investment in hydrogen infrastructure along with the development of hydrogen supply chains. On 12th September 2024, EBARA Corporation announced construction of the world's first full-scale testing center for liquid hydrogen pumps in Futtsu City, Chiba, Japan. The company has invested around 16 billion yen to advance the hydrogen infrastructure. The facility will test performance with actual liquid hydrogen to support the development of a supply chain in Japan and worldwide. This initiative follows Japan's drive to promote the adoption of hydrogen in social infrastructure and energy systems, including potentially in gas turbines. Moreover, the integration of hydrogen-ready turbines into Japan’s energy ecosystem showcases a shift toward sustainable power generation, driven by the need to diversify energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Expansion of Distributed Power Generation Systems
Distributed power generation is gaining traction in Japan due to its ability to enhance energy resilience and provide localized power solutions. Gas turbines play a critical role in this trend, particularly for microgrids and industrial facilities seeking self-sufficient energy systems. In addition, distributed generation systems reduce transmission losses, improve energy reliability, and cater to remote areas. This trend is bolstered by advancements in compact turbine designs, enabling seamless integration into decentralized power networks, thereby enhancing energy independence while reducing grid dependency. On 9th October 2024, GE Vernova signed a contract to provide three 7HA.03 gas turbines for Kansai Electric's Nanko power station in Osaka, Japan, to replace older LNG-based assets to enhance efficiency and lower carbon emissions. The plant produces up to 1.8GW and is supporting Japan's net-zero goals and comes with turbines that can burn up to 50% hydrogen, with a path to 100% in the future. GE Vernova, that has been working in Japan for more than 130 years, will also supply field services.
Focus on Digitalization and Predictive Maintenance
Digital transformation is one of the Japan gas turbine market trends, with a focus on predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Leveraging artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, gas turbines now feature advanced monitoring systems that detect performance issues in real time. Furthermore, predictive maintenance reduces downtime and reduces repair prices, improving overall system reliability. This trend aligns with Japan's pursuit of technological innovation to optimize industrial operations and energy infrastructure, ensuring efficient turbine performance while meeting stringent environmental and operational standards. On 1st April 2024, Sweden's SeaTwirl cooperated with Sumitomo Corporation Power & Mobility to harness Japan's vast 424GW offshore floating wind energy potential with vertical-axis floating wind turbine technology. The alliance combines SeaTwirl's creative design solutions with the client engagement competencies of Sumitomo for Japan's particular ocean conditions - extreme depths and over 4,000 islands. The activity supports Japan's strategy for the inclusion of renewable power within its mix in addition to energy systems from gas turbines.
Japan Gas Turbine Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Japan gas turbine market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on technology, design type, rated capacity, and end user.
Analysis by Technology:
- Combined Cycle Gas Turbine
- Open Cycle Gas Turbine
The combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) segment dominates the Japan gas turbine market due to its superior efficiency and environmental benefits. CCGTs utilize waste heat from gas turbines to power steam turbines, significantly increasing energy output and reducing emissions. This technology is ideal for large-scale power generation, making it a preferred choice for utilities and industries. As Japan prioritizes decarbonization and cost-effective energy solutions, the adoption of CCGT systems is rising, driven by their high performance and low operational costs.
Open cycle gas turbines (OCGTs) are gaining traction in Japan for their flexibility and rapid startup capabilities. These turbines are commonly used for peak power demands and emergency backup applications due to their ability to deliver immediate power. OCGTs are particularly valuable in balancing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources including wind and solar. Japan’s growing need for energy reliability and quick-response systems positions OCGTs as a crucial technology, especially in regions with variable power demand.
Analysis by Design Type:
- Heavy Duty (Frame) Type
- Aeroderivative Type
Heavy-duty (frame) gas turbines are a cornerstone of large-scale power generation in Japan, offering durability, reliability, and high power output. These turbines are well-suited for base-load operations, making them ideal for power plants catering to consistent energy demand. Their robust design allows for long operational life and lower maintenance costs. As Japan transitions to more sustainable energy systems, heavy-duty turbines integrated with advanced technologies are being adopted to meet the need for efficient, long-term energy solutions while ensuring reduced environmental impact.
Aeroderivative gas turbines are gaining prominence in Japan due to their lightweight design, flexibility, and superior efficiency in distributed and peak power applications. Derived from aviation technology, these turbines are optimized for rapid deployment and can operate efficiently in small-scale power generation or backup systems. Their modular design allows for easy maintenance and scalability, making them a preferred choice for industries and remote regions. Japan’s emphasis on energy diversification and flexibility drives the growing adoption of aeroderivative turbines across various sectors.
Analysis by Rated Capacity:
- Above 300 MW
- 120-300 MW
- 40-120 MW
- Less Than 40 MW
Gas turbines with capacities above 300 MW are pivotal in Japan's large-scale power generation landscape. These turbines are essential for base-load operations, offering exceptional efficiency and reliability in meeting extensive electricity demands. Their integration into combined-cycle power plants ensures reduced emissions and higher energy output. As Japan focuses on energy modernization, this segment plays a critical role in addressing the nation’s large-scale energy and sustainability goals effectively.
The 120-300 MW segment is a key contributor to Japan’s medium-scale energy infrastructure, catering to regional utilities and industrial power needs. These turbines are ideal for combined-cycle configurations, providing an optimal mix of performance and cost efficiency. Their ability to support flexible operations makes them valuable for areas with variable power demand. Growing energy demands and modernization efforts drive this segment’s adoption in Japan’s energy market.
Turbines with a capacity of 40-120 MW are widely used in smaller power plants and industrial setups requiring consistent energy. They are preferred for distributed power generation and cogeneration applications due to their adaptability and compact design. As industries in Japan seek reliable and efficient energy solutions to reduce operational costs and meet environmental standards, this segment continues to expand in significance.
Gas turbines with capacities under 40 MW are primarily utilized in decentralized power systems and remote areas. Their small size and operational flexibility make them ideal for localized energy generation, including microgrids and backup systems. These turbines are particularly valuable for industries and rural regions requiring quick, efficient power solutions. The push for energy resilience and independence supports the Japan gas turbine market demand.
Analysis by End User:
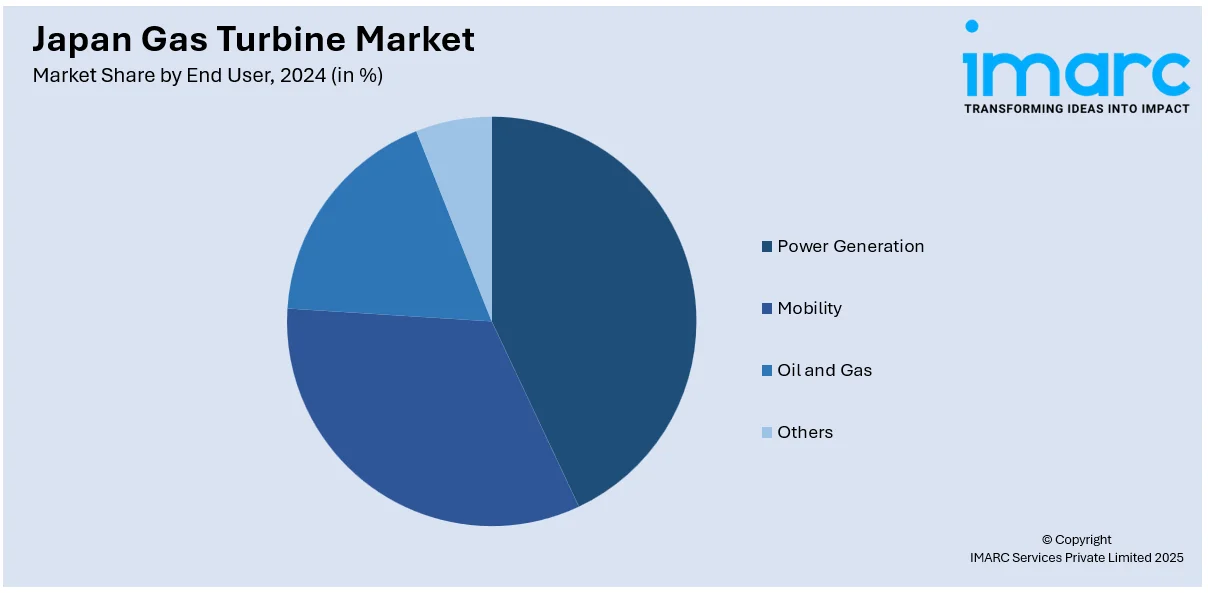
- Power Generation
- Mobility
- Oil and Gas
- Others
Gas turbines are a backbone of Japan's power generation sector, providing efficient and reliable electricity. They are widely used in combined-cycle plants, offering low emissions and high energy output. Their ability to balance renewable energy variability has made them essential in Japan’s clean energy transition. The increasing need for sustainable, flexible, and modern power infrastructure drives the adoption of advanced turbine technologies.
The mobility segment utilizes gas turbines for specialized applications such as marine propulsion and auxiliary power in aviation. Their lightweight, compact design and ability to produce high power output make them an optimal choice for transportation systems. Japan's focus on reducing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency in mobility solutions is accelerating the integration of innovative gas turbine technologies in this segment, promoting sustainable and high-performance transportation infrastructure.
In Japan’s oil and gas industry, gas turbines are vital for operations such as mechanical drives and on-site power generation. Their robustness and reliability ensure efficient performance in demanding environments, including offshore platforms and processing facilities. With the industry prioritizing energy efficiency and emission reduction, gas turbines are increasingly used for their ability to deliver cost-effective, environmentally friendly solutions, making this segment a critical contributor to the market's growth.
Regional Analysis:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region, Japan's most populous and industrially advanced area, is a key market for gas turbines. Its high energy demand is driven by extensive urbanization and a concentration of industries. Gas turbines play a vital role in powering combined-cycle plants and ensuring reliable electricity. As the region focuses on reducing emissions and integrating renewable energy, the adoption of advanced turbine technologies is accelerating, supporting its sustainable energy goals.
The Kansai region, known for its industrial hubs and manufacturing centers, heavily relies on gas turbines for cogeneration and industrial power needs. With a significant share of Japan's energy consumption, this region emphasizes efficient and sustainable energy solutions. Gas turbines are increasingly utilized in flexible power systems to complement renewable energy and address peak demands, driving regional growth in the adoption of innovative turbine technologies.
The Chubu region, also known as Japan's industrial heartland, has a high energy demand for reliability and efficiency. Gas turbines have therefore been extensively used in various aspects of the power generation and industrial sectors to ensure unbroken operations and carbon footprint reduction. Chubu aims at contemporary energy structure modernization and energy-intensive industries support therefore becomes very critical in the process for advanced gas turbines that would promote energy efficiency in Japan.
Competitive Landscape:
The Japan gas turbine market is characterized by both local and international companies who are focusing majorly on innovation and efficiency. Industry majors in the key sectors are concentrating on developing high technologies to increase the capacity for power generation, decrease emissions, and fuel efficiency. A significant trend dominating the hydraulic turbine market in Japan is hybrid solutions, which entail a combination of gas turbines with renewable energy for the satisfaction of Japan's requirements for energy transition. Further, companies are investing in digitalization to enable predictive maintenance and operational optimization services. Coordination among manufacturers and utility companies is also increasing due to stakeholders' abilities to reach further and garner greater Japan gas turbine market growth. In addition, government policies drive the market to implement cleaner and greener energy results.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Japan gas turbine market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- October 09, 2024: Kansai Electric installed three GE Vernova 7HA.03 gas turbines at Osaka, Japan, at the 1,800 MW Nanko power station and replaced old-age equipment to bring in more efficiency and reduced emissions. The modification is in the direction of Japan's 2050 Net Zero objective.
- August 26, 2024: Mitsubishi Power announced providing its M501JAC hydrogen-ready gas turbine to Samsung C&T for a 475 MW cogeneration plant set up by TAQA and Japan's JERA Co. The power plant will generate electricity and steam to power the SATORP petrochemical complex of Saudi Aramco and TotalEnergies as part of Saudi Aramco and TotalEnergies' expansion in Jubail. This marks another example of Japan's leading-edge gas turbine technology used for industrial development in the Gulf region.
- August 12, 2024: Hygenco and Mitsubishi Power entered into an MoU for developing green hydrogen and ammonia-fired gas turbine combined cycle (GTCC) power plants with support from Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). The project will contribute to India's National Green Hydrogen Mission by transitioning GTCC power generation plants from natural gas to green hydrogen and ammonia, which would lead to a significant reduction in emissions. According to JICA, this collaboration is an important step forward for clean energy solutions and international cooperation.
- July 26, 2024: Japan's biggest power generator, JERA, announced it will start running the first 0.78-GW unit of its new 2.34-GW gas-fired power station in Chiba on August 1 to meet peak summer electricity demand. The new unit, which can power 2 million homes, is one of four at the facility, replacing an older 1.886-GW plant. This launch comes as Japan responds to rising demand following a recent heat wave.
Japan Gas Turbine Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Combined Cycle Gas Turbine, Open Cycle Gas Turbine |
| Design Types Covered | Heavy Duty (Frame) Type, Aeroderivative Type |
| Rated Capacities Covered | Above 300 MW, 120-300 MW, 40-120 MW, Less Than 40 MW |
| End Users Covered | Power Generation, Mobility, Oil and Gas, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan gas turbine market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan gas turbine market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan gas turbine industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Japan gas turbine market was valued at USD 1.6 Billion in 2024.
The growth of the Japan gas turbine market is driven by increasing demand for efficient, reliable power generation, the transition to cleaner energy solutions, government initiatives for energy infrastructure modernization, and advancements in technologies such as combined-cycle power plants.
IMARC estimates the Japan gas turbine market to exhibit a CAGR of 5.2% during 2025-2033, reaching USD 2.6 Billion by 2033.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












