
Japan Factory Automation & Industrial Controls Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, End Use Industry, and Region, 2025-2033
Japan Factory Automation & Industrial Controls Market Size and Share:
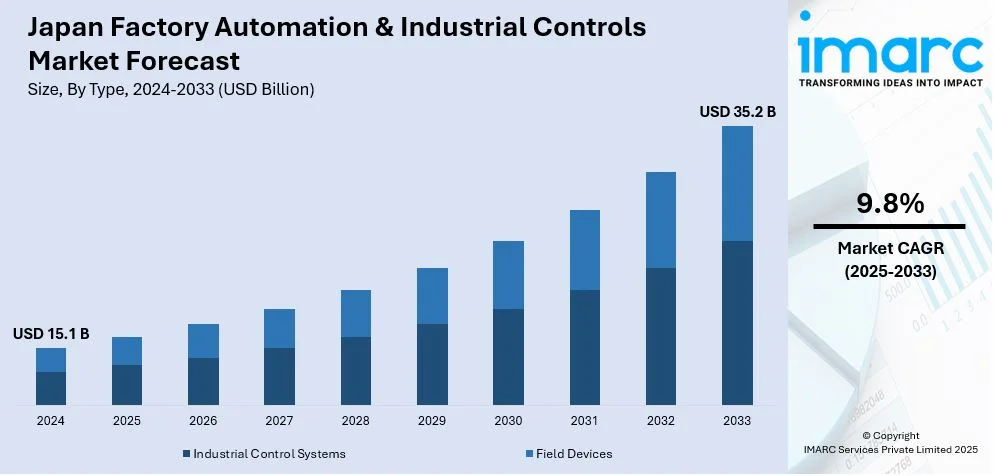
The Japan factory automation & industrial controls market size was valued at USD 15.1 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 35.2 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.8% from 2025-2033. The market is witnessing significant growth due to the escalating demand for operational efficiency and cost reduction and government support for Industry 4.0 adoption. Moreover, the incorporation of machine learning and artificial intelligence, the adoption of collaborative robots, and smart factories, and IoT integration are expanding the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 15.1 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 35.2 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 9.8% |
With rising labor costs and a shrinking workforce due to Japan’s aging population, manufacturers are increasingly turning to automation to optimize production processes. For instance, in May 2024, major Japan-based firmsagreed to increase monthly pay by 5.58%, or ¥19,480 on average, following the first tally from spring labor-management wage talks by the Japan Business Federation. Factory automation allows companies to reduce labor costs, improve production speed, and ensure consistent product quality. The drive for operational efficiency, combined with stringent quality control standards, is propelling the adoption of industrial control systems. Automation also helps businesses remain competitive in the global market by meeting the growing demand for customized products with shorter lead times.
The Japanese government is actively supporting the adoption of factory automation and industrial controls through various policies and initiatives aimed at promoting Industry 4.0. In response to challenges such as an aging workforce and the need for increased productivity, Japan’s government has introduced programs to encourage the integration of advanced technologies in manufacturing. Initiatives such as the “Connected Industries” policy focus on fostering collaboration between industries, academia, and government to drive the digital transformation of factories. Financial incentives and subsidies for automation projects further motivate companies to invest in cutting-edge technologies, thereby accelerating market growth. For instance, in November 2024, Japan’s government plans a budget amendment allocating JPY1.5–1.6 trillion ($9.8–10.5 billion) to support advanced semiconductor development and AI initiatives, including funding Rapidus for 2nm chip production. These government efforts, combined with a strong industrial base, are positioning Japan as a global leader in automation technologies, ensuring continued expansion in the factory automation and industrial controls market.
Japan Factory Automation & Industrial Controls Market Trends:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
One of the most significant trends in Japan’s factory automation sector is the increasing integration of AI and machine learning into industrial processes. For instance, in January 2024, Mitsubishi Electric developed an AI that analyzes manual task efficiency on production sites in minutes, reducing analysis time by up to 99%. It uses a probabilistic generative model for improved productivity. These technologies are enhancing the capabilities of automation systems by enabling machines to learn from data, adapt to new conditions, and optimize operations. AI-driven predictive maintenance, for instance, helps prevent equipment failure by anticipating maintenance needs based on historical data, reducing downtime and operational costs. Furthermore, AI algorithms are improving production scheduling and process control, contributing to more effective and flexible manufacturing landscapes.
Adoption of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
The utilization of collaborative robots, or cobots, is gaining traction in Japan’s industrial automation landscape. Cobots are developed to work by assisting human operators, improving productivity and ensuring safety in operations. Unlike conventional industrial robots, which often operate in isolation or require protective barriers, cobots are flexible and adaptable, making them ideal for small-batch production, assembly tasks, and environments with variable workflows. For instance, in October 2024, OMRON launched the TM25S collaborative robot, featuring a 25kg payload, 1900mm reach, and compact design, ideal for palletizing, mobile manipulation, and welding with easy integration into workflows. This trend is especially relevant in sectors like electronics and automotive manufacturing, where customization and precision are essential. The rise of cobots is also helping address labor shortages, particularly in Japan’s aging workforce.
Smart Factories and IoT Integration
The move towards smart factories, powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), is another key trend in Japan’s factory automation market. IoT-enabled devices and sensors provide real-time data on equipment performance, inventory levels, and production processes. For instance, in February 2025, Fujitsu announces the launch of its Cloud Service Generative AI Platform in Japan, offering enhanced data security and productivity solutions while addressing concerns about data leakage and compliance. This data-based tactic facilitates manufacturers to take more informed decisions, optimize supply chains, and ensure higher product quality. The adoption of smart factory solutions is being driven by the need for greater operational visibility, increased agility, and the desire for energy-efficient production. As Japan embraces Industry 4.0, the integration of IoT with factory automation is becoming increasingly essential for maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
Japan Factory Automation & Industrial Controls Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Japan factory automation & industrial controls market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on type and end use industry.
Analysis by Type:
- Industrial Control Systems
- Distributed Control System (DCS)
- Programable Logic Controller (PLC)
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
- Human Machine Interface (HMI)
- Others
- Field Devices
- Machine Vision
- Industrial Robotics
- Sensors and Transmitters
- Motors and Drives
- Safety Systems
- Others
The role of various industrial controls such as DCS, PLC, SCADA, and MES is important in Japan's factory automation market. These systems allow real-time monitoring, automation, and optimization of production processes to increase operational efficiency, quality computation, and flexibility. With their integration into smart manufacturing initiatives, they enhance seamless data flow, predictive maintenance, and minimized downtime in industries.
Field devices such as machine vision, robotics, sensors, and safety systems are among the most essential elements in Japan's industrial controls landscape. These devices empower accurate monitoring, control, and automation at the production floor level, thus enhancing operational efficiency, improving quality, providing assurance of safety, and ensuring optimum energy use in advancing manufacturing in sectors like automotive, electronics, and chemicals.
Analysis by End Use Industry:
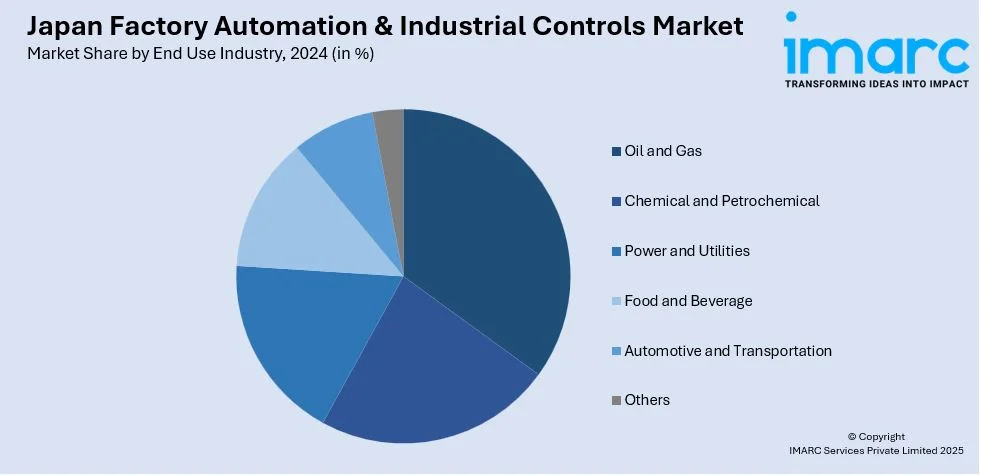
- Oil and Gas
- Chemical and Petrochemical
- Power and Utilities
- Food and Beverage
- Automotive and Transportation
- Others
The exploration, extraction, and refining processes in Japan's oil and gas industry are heavily automated with respect to factory automation and industrial controls. These automation systems, like DCS and PLC, optimize operations and monitor safety and critical equipment in real-time for improved uptime, reliability, and reduced operational risk.
For the chemical and petrochemical industry in Japan, automation and control systems give a lot of support in the optimization of complicated production processes. DCS, SCADA, and sensors monitor temperature, pressure, and chemical reactions to assure consistent product quality, safety, and energy efficiency. Other lesser advantages include regulatory compliance and lower environmental impact in manufacturing operations.
Factory automation and industrial control systems are crucial for the power and utilities sector in Japan to survey and manage energy production and distribution. SCADA and PLC systems provide real-time feedback for optimizing grid management, while improving efficiency and safety, and supporting predictive maintenance, thus securing stable and reliable energy delivery.
Automations and control systems in the food and beverage industry assure quality assurance, safety, and compliance with food standards in Japan. PLCs, HMIs, and sensors control production lines, monitor temperatures, and track inventory, thereby enabling accurate manufacturing processes and reducing waste and further improving operational efficiency in food processing and packaging.
In the automotive and transportation industries in Japan, factory automation and industrial controls optimize assembly lines, manage robotics, and monitor automotive manufacturing processes. PLCs and machine vision systems increase precision in assembly and diminish defects to facilitate superior throughput, while industrial robots render cost-efficient production in high-volume, low-cost environments, thus increasing overall productivity.
Regional Analysis:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The Kanto region, which comprises Tokyo and Yokohama, acts as an advanced manufacturing and technology hub driving demand on factory automation and industrial controls. As the area is well concentrated with electronics, automotive, and semiconductor industries, the automation systems help in precise and efficient working, thereby nurturing the growth of PLCs, robotics, and sensors for streamlined production.
Kansai, which includes Osaka and Kyoto, has a strong manufacturing base in automotive, electronics, and machinery. The area innovation in industrial automation contributes to heavy adoption of DCS, SCADA systems, and robotics. The systems thereby improve production efficiency, raise product quality, and support the region's massive export-oriented industries.
Central Japan, especially in Nagoya, functions as an automotive manufacturing hub. The market for factory automations in the Central region stands to benefit as the demand for robotics, PLCs, and industrial control systems able to manage high-volume production lines is extremely high. These solutions assist the automotive and aerospace manufacturers in improving precision, reducing defects, and optimizing resource usage to better their competitive standing.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of Japan's factory automation and industrial controls market is exhibited by the establishment of both global and local players. Major international companies, such as Siemens, Mitsubishi Electric, and Rockwell Automation, dominate the market with advanced solutions in industrial control systems, robotics, and automation. Local firms like Yokogawa Electric, Omron, and FANUC are also significant contributors, leveraging Japan’s technological expertise and innovation capabilities. These companies continuously invest in research and development to enhance product offerings, focusing on areas like AI-driven automation, predictive maintenance, and energy-efficient solutions, ensuring strong competition and market growth. For instance, in February 2025, Yokogawa Electric Corporation launched the updated OpreX™ Collaborative Information Server, enhancing application assembly, external connectivity, and enabling optimized production management and remote monitoring for swift decision-making.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Japan factory automation & industrial controls market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In June 2024, Keyence introduced the VS Series vision system, featuring fixed and on-hand camera options with automatic field-of-view adjustments. The system includes the VS-L, VS-S, and VS-C models, offering zoom, auto-focus, and versatile inspection capabilities. The VS-C model is compatible with Keyence’s C-Mount lenses, excluding auto zoom.
- In February 2024, Fanuc unveiled the M-710iD/50M robot, marking the first update to its M-710i series in 17 years. The new model features a 50 kg payload, enhanced wrist load capacity, and a curved J2 arm for improved accessibility and reduced interference, expanding its capabilities for industrial applications.
Japan Factory Automation & Industrial Controls Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered |
|
| End Use Industries Covered | Oil and Gas, Chemical and Petrochemical, Power and Utilities, Food and Beverage, Automotive and Transportation, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan factory automation & industrial controls market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan factory automation & industrial controls market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan factory automation & industrial controls industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The factory automation & industrial controls market in Japan was valued at USD 15.1 Billion in 2024.
The growth of Japan's factory automation and industrial controls market is driven by the need for increased productivity, cost reduction, and enhanced quality in manufacturing. Technological advancements, labor shortages due to an aging population, and government initiatives promoting Industry 4.0 are also significant growth drivers in the market.
The Japan factory automation & industrial controls market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.8% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 35.2 Billion by 2033.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












