Optimizing Nitrocellulose Production: A Comprehensive Cost Analysis

What is Nitrocellulose?
Nitrocellulose, also known as cellulose nitrate or guncotton, is a chemically modified form of cellulose known for its exceptional film-forming capabilities, strong adhesion, and biodegradability.
Key Applications Across Industries:
It is widely used in applications such as wood coatings, printing inks, leather finishes, automotive paints, nail varnishes, and more.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
According to an IMARC study, the global nitrocellulose market was valued at USD 946.1 Million in 2025. Looking ahead, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.28% from 2026 to 2034, reaching a projected value of USD 1,379.8 Million by 2034.
The market's growth is driven by nitrocellulose's adaptability and wide range of applications. Key factors fuelling this expansion include its use in automotive coatings for premium finishes, increasing demand in the pharmaceutical industry for drug delivery systems, and its vital role in lacquers and printing inks for packaging and publishing. Ongoing technological advancements and research and development efforts have enabled the creation of tailored nitrocellulose solutions, enhancing both performance and sustainability. The rising demand for customized and eco-friendly derivatives, coupled with growth in the automotive and pharmaceutical sectors, further supports the market's upward trajectory.
Case Study on Cost Model of Nitrocellulose Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients has approached us to conduct a feasibility study for establishing a mid to large-scale nitrocellulose manufacturing plant in Croatia.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We have developed a comprehensive financial model for the plant's setup and operations. The proposed facility is designed with an annual production capacity of 5,000 tons of nitrocellulose.
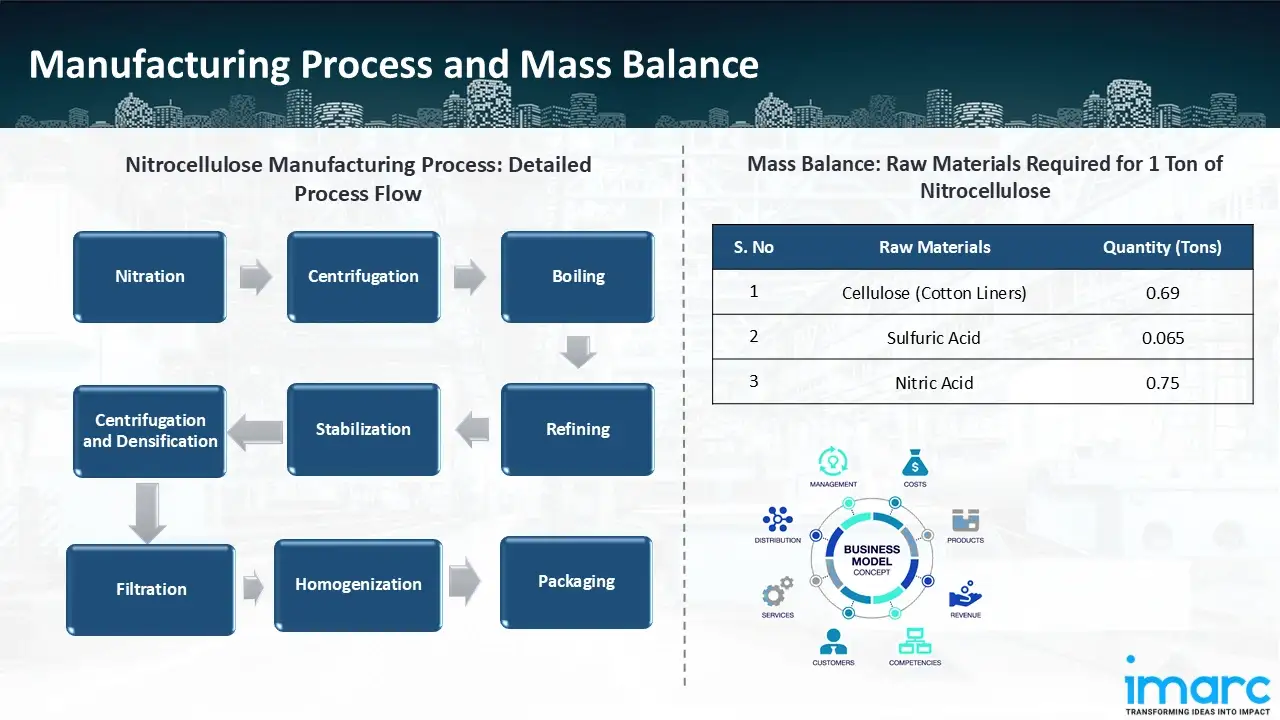
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process of nitrocellulose begins with nitration, where cellulose (derived from cotton or wood pulp) is treated with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids. This reaction replaces the hydroxyl groups in cellulose with nitro groups, creating nitrocellulose, which is highly flammable and reactive. The nitrated product then undergoes centrifugation to remove excess acids and water, reducing acid content for safer handling. Subsequently, the nitrocellulose is boiled in water to eliminate residual acids and impurities, ensuring thorough cleansing of by-products from the nitration process. The material is then subjected to refining, involving mechanical processing to achieve the desired consistency and remove additional impurities, further preparing it for stabilization. During stabilization, techniques are applied to enhance chemical stability and prevent spontaneous decomposition, improving safety and shelf life. The stabilized nitrocellulose is then filtered to remove remaining solids or contaminants, ensuring purity. Next, it undergoes homogenization to achieve a uniform texture and consistency, essential for industrial applications like coatings, inks, and explosives. Following this, the nitrocellulose is again centrifuged and densified, removing residual water or solvents and compacting the material for ease of handling. Finally, the nitrocellulose is packaged in drums or cardboard boxes for storage and transportation.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The primary raw materials utilized in the nitrocellulose manufacturing plant include cellulose (cotton liners), sulfuric acid, and nitric acid. For a plant producing approximately 1 tons of nitrocellulose, the raw material requirements are as follows: cellulose (0.69 tons), sulphuric acid (0.07 tons), and nitric acid (0.75 tons).
List of Machinery:
The following equipment was required for the proposed plant:
- Reactor
- Centrifuge
- Boiler
- Dryer
- Filling Machine
- Milling Machine
- Cooling System
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Investment (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
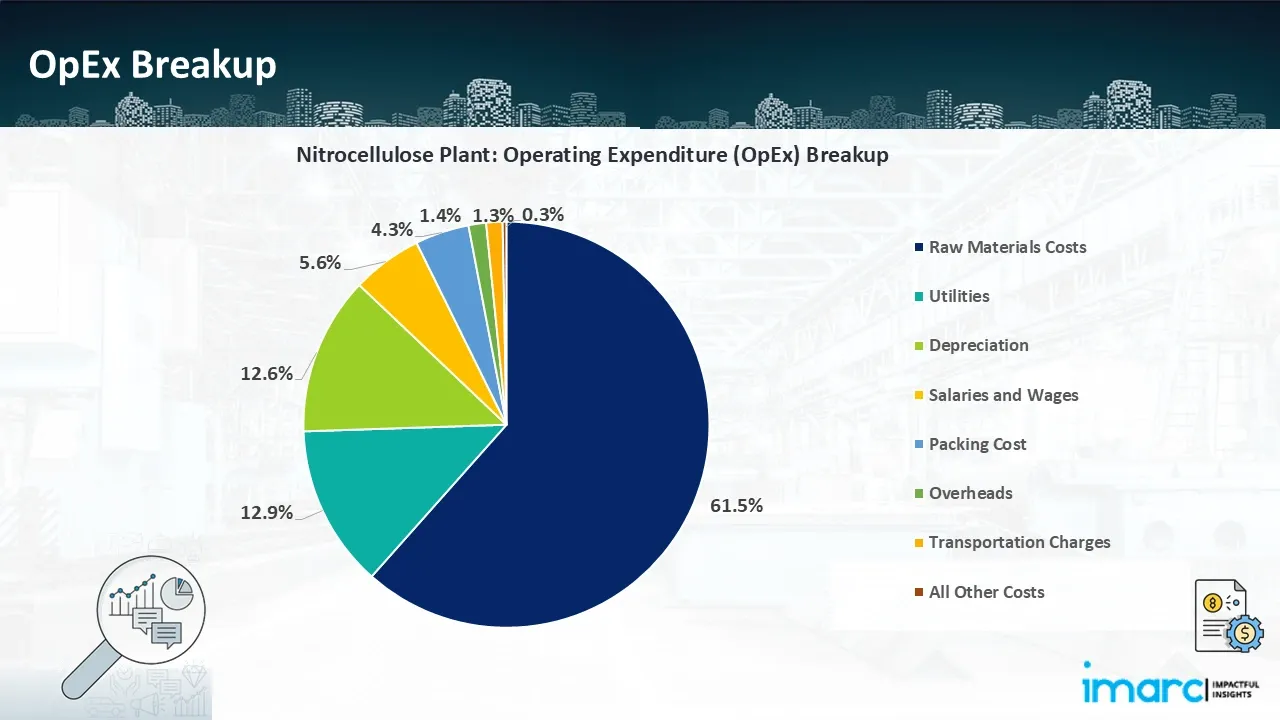
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth.
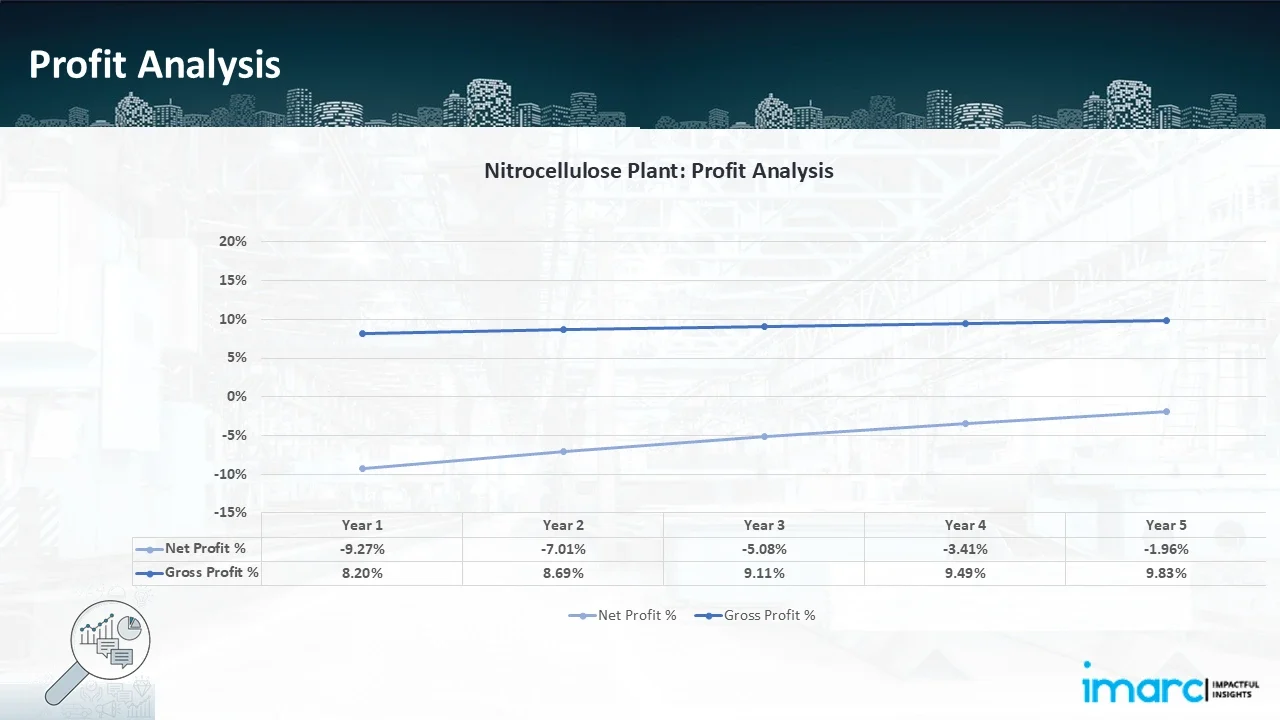
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: The proposed nitrocellulose plant, with an annual capacity of 5,000 tons of nitrocellulose, achieved an impressive revenue of US$ 13.31 Million in its first year. We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue reaching staying the same throughout the five years. Gross profit margin improved from 8.20% to 9.83% throughout the years, and net loss reduced from 9.27% to 1.96%, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the nitrocellulose manufacturing plant was meticulously designed to meet the client’s objectives. It provided a thorough analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. Tailored to the specific requirement of producing 5,000 tons of nitrocellulose annually, the model highlights key cost drivers and forecasts profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model offers the client valuable insights for strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering precise, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing projects.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2024, Poland announced plans to establish facilities for producing nitrocellulose and gunpowder essential for large-caliber ammunition. The agreement was signed by the Industrial Development Agency, Grupa Azoty, Polska Grupa Zbrojeniowa, and Mesko. These explosive production facilities are vital for advancing Poland's ammunition manufacturing capabilities.
- In October 2024, MSM Group, the Slovak subsidiary of the CSG industrial group, signed a purchase agreement with the U.S.-based publicly traded company IFF to acquire its nitrocellulose business, including the associated plant and the Walsrode Industrial Park located in Lower Saxony, Germany.
- In May 2024, the Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA) announced an expansion of export restrictions to Russia and Belarus, including nitrocellulose in the list of controlled items. This updated policy officially took effect on June 14, 2024.
- In May 2023, Eurenco, a French company and a European leader in energetic materials, announced the resumption of nitrocellulose production at its Bergerac facility.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics:
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Brief List of Our Services: Market Entry and Expansion:
- Market Entry and Opportunity Assessment
- Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking
- Procurement Research
- Pricing and Cost Research
- Sourcing
- Distribution Partner Identification
- Contract Manufacturer Identification
- Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
- Factory Setup
- Factory Auditing
- Company Incorporation
- Incubation Services
- Recruitment Services
- Marketing and Sales
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











