India’s Race to Lead the Lithium-Ion Battery Industry: Exploring Costs and Opportunities

Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable power sources widely used in devices such as cell phones, laptops, and electric vehicles. These batteries store energy by transferring lithium ions between the anode and cathode electrodes, with the electrolyte facilitating this movement and generating free electrons at the anode. Key types of lithium-ion batteries include those with lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, lithium nickel manganese cobalt, and lithium manganese oxide. Lithium-ion batteries come in a range of capacities from 0 mAh to 6000 mAh. They offer several advantages, including a high energy-to-weight ratio, excellent charge retention, and generally longer lifespans with more charge/discharge cycles compared to other rechargeable batteries.
According to recent findings by IMARC Group, the India lithium-ion battery market size reached US$ 2.8 Billion in 2023. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 8.7 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 12.9% during 2024-2032. The rise in electric vehicles is increasing the demand for high-energy-density batteries that provide longer driving ranges and shorter charging times. Additionally, initiatives by the Government of India aimed at reducing carbon footprints by promoting electric vehicle production and sales are further boosting the demand for lithium-ion batteries. Advances in battery technology, including improved performance, higher energy densities, longer lifespans, and faster charging capabilities, along with reduced costs, are making these batteries more accessible for various applications. Furthermore, the growing demand for consumer electronics, the expansion of renewable energy storage, and the use of lithium-ion batteries in backup power systems for data centers, telecommunications, and emergency power supplies are expected to drive continued market growth in the coming years.
Recent Industry Investments:
- A Tata Group subsidiary, Agratas Energy Storage Solutions Private Limited, and the Gujarat Government signed an agreement to set up India's first gigafactory for Lithium-Ion batteries in the state in June 2023. The group will initially invest Rs 13,000 crore for setting up a 20-gigawatt (GW) unit.
- Ola Electric has announced plans to build a 100 GWh Giga factory. With an initial capacity of 5 GWh, construction on this project has already begun, and it is expected to be fully operational by the end of the fiscal year 2023. The 115-acre site of this Giga factory can be found in Krishnagar, Tamil Nadu. The plant intends to produce all the supply chain components to reduce reliance on battery supplies abroad.
- Amara Raja Batteries Limited inaugurated the most extensive Gigafactory in Telangana, with a projected investment of Rs 9,500 crore over the forthcoming decade.
- Kabra Extrusiontechnik announced in February 2023 that its board approved the plan to set up a new manufacturing plant in North India to manufacture new-age Lithium-ion battery packs and other ancillary products through its wholly-owned subsidiary.
- In March 2022, Reliance Industries acquired Lithium Werks, a Dutch maker of lithium iron phosphate batteries, for US$ 61 Million through its subsidiary Reliance New Energy Solar.
Case Study on Cost Model of Lithium-ion Battery
Objective: One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a large-scale lithium-ion battery plant. We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a lithium-ion phosphate (LFP) prismatic cell manufacturing plant in India. The proposed facility was designed with an annual production capacity of 20 million cells, with 15 million units of LFP 3.2V/104Ah and 5 million units of LFP 3.2V/300Ah, housed within a 510,000 square meter area.
Manufacturing Process:
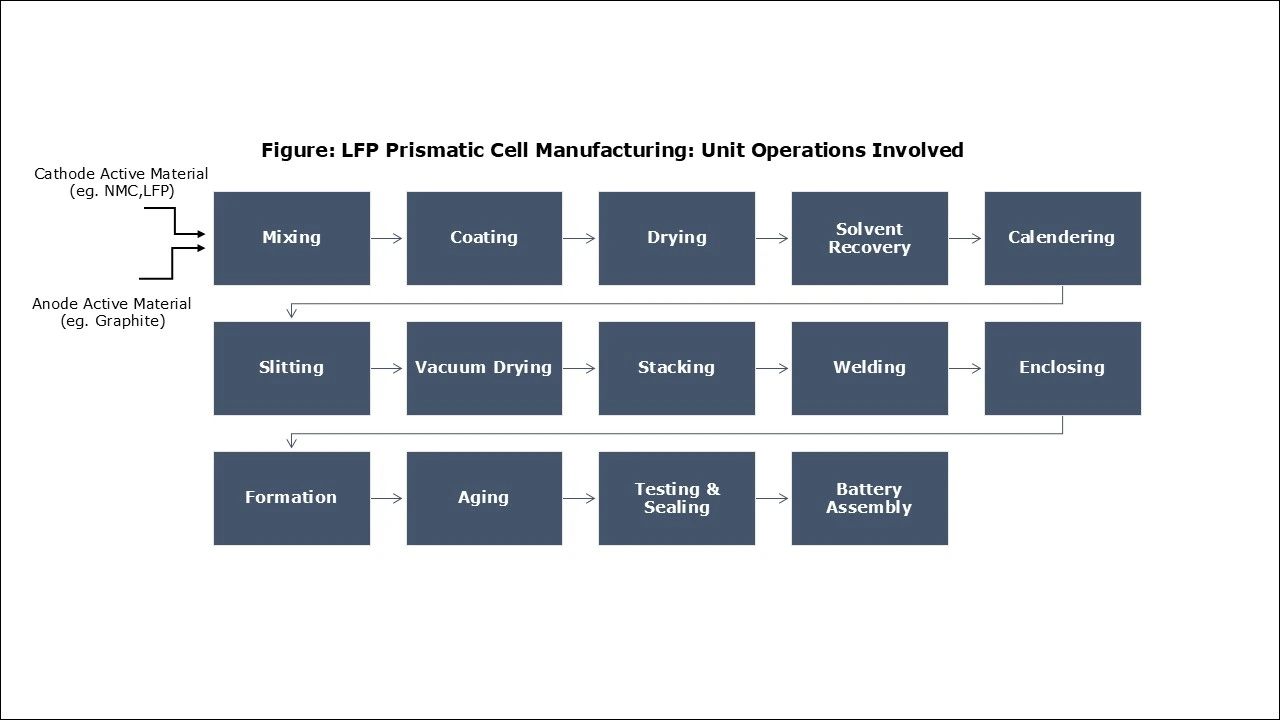
Mass Balance and Raw Material Required: The raw materials required for manufacturing LFP prismatic cells include lithium carbonate, anhydrous iron phosphate, graphite, LiPF6 (electrolyte), aluminum foil (positive current collector), copper foil (negative current collector), polypropylene (separator), aluminum (casing), and others.
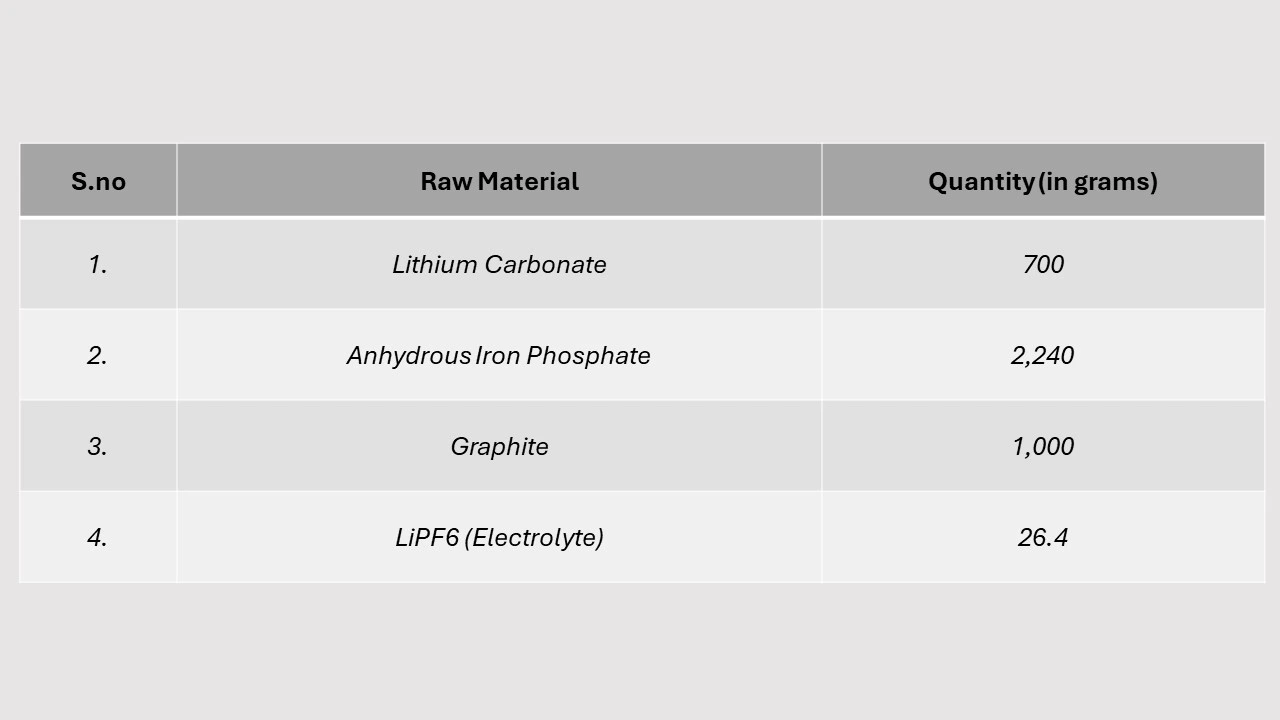
Table: Mass Balance of LFP Prismatic Cell: Raw Materials Required for 1 KWh of Product Manufactured
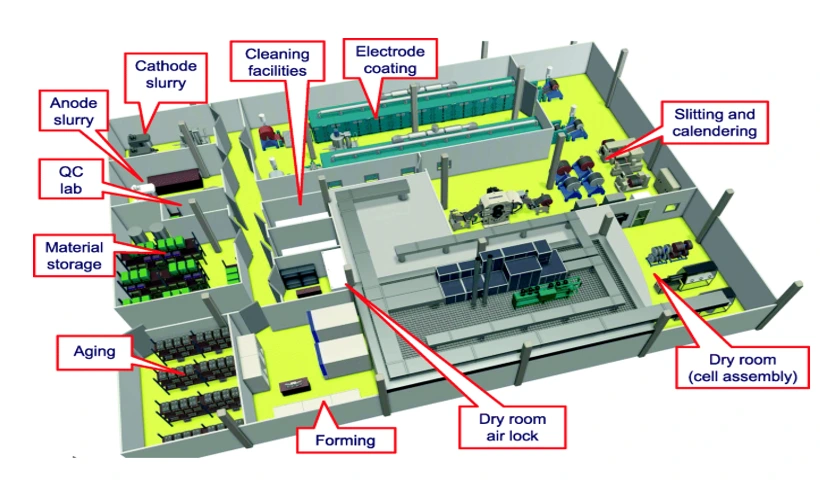
Plant Layout:
List of Machinery:
The following equipment was required for the proposed plant:
- Ingredients, Coating, and Preparation of Electrode
- Cathode Feeding System
- Cathode Mixer Anode
- Feeding System
- Anode Mixer Slurry
- Buffer Tank
- Cathode Double-Sided Extrusion Coating Machine
- Anode Double-Sided Extrusion Coating Machine
- NMP Recycling System
- Cathode Rolling and Slitting Integrated Machine.
- Anode Rolling and Slitting Integrated Machine.
- Cathode Laser Die-Cutting
- Anode Laser Die-Cutting
- Assembly, Liquid, Injection and Formation
- Stacking Machine
- Assembly Welding Line
- High Vacuum Baking Line
- Fully Automatic Liquid Injection Machine
- Formation Line Feeding
- Manufacturing Execution System
- Power Equipment
- Drying Unit
- Air Compressor Unit
- Vacuum Unit
- Nitrogen Production Unit
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
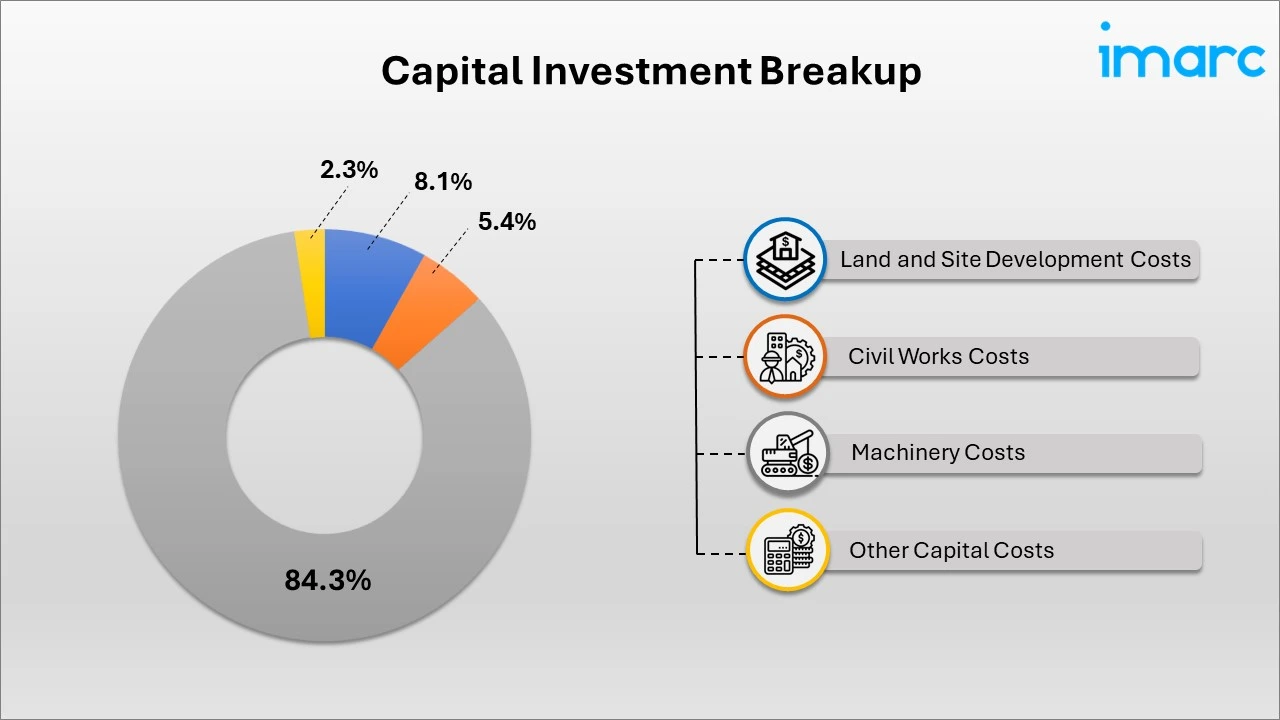
- Breakup by Capital Investment: The total capital cost for establishing the proposed plant is approximately INR 6,600 crore. Machinery costs comprise 84.3% of the total capital costs for the LFP prismatic cell manufacturing plant. The civil works include the construction of factory buildings, offices, internal roads, drainage systems, worker accommodations, warehouse facilities, and a water treatment plant. The land designated for the LFP prismatic cell manufacturing plant must comply with the standards set by the relevant authorities.
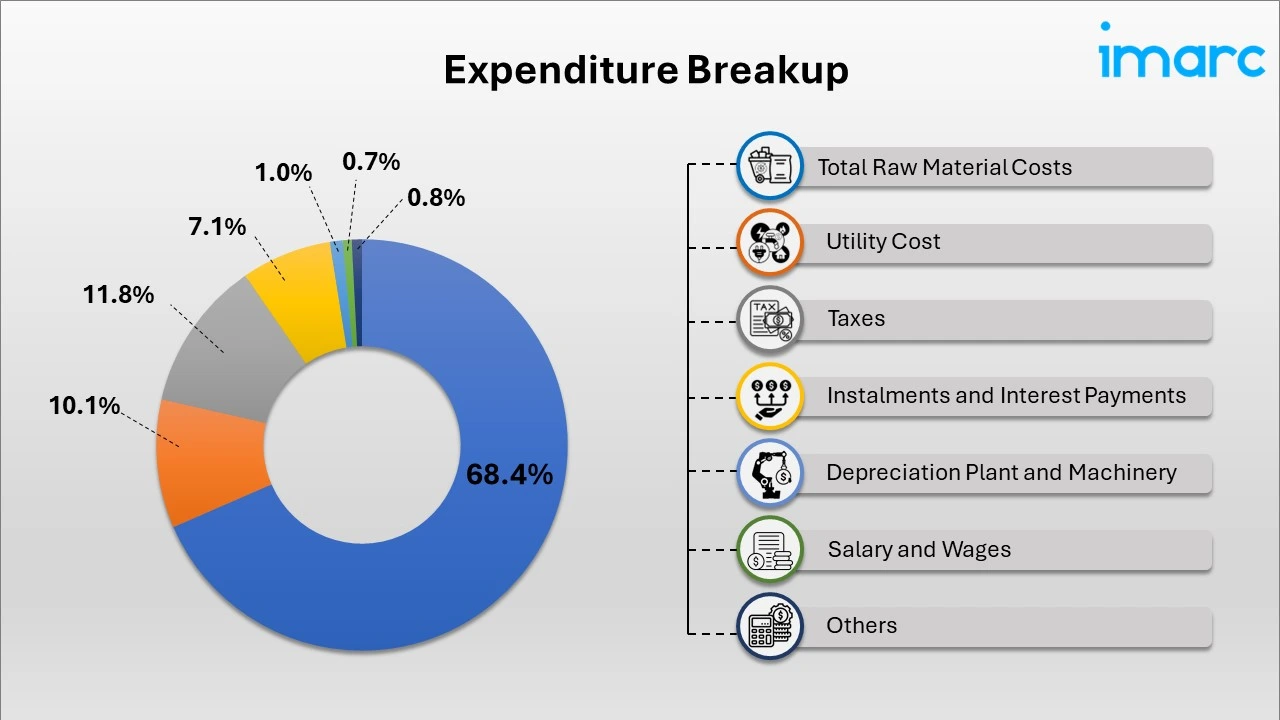
- Breakup by Expenditure: Raw materials account for the largest share of total expenditures, at 68.4%. This is followed by salaries and wages, utility costs, installment payments, interest payments, and various other expenses. Other expenses include transportation charges, packing costs, repair and maintenance, overheads, depreciation, miscellaneous fixed assets, and other costs. Overall expenditures are expected to increase by 33.3% in the seventh year of operation compared to the first year.
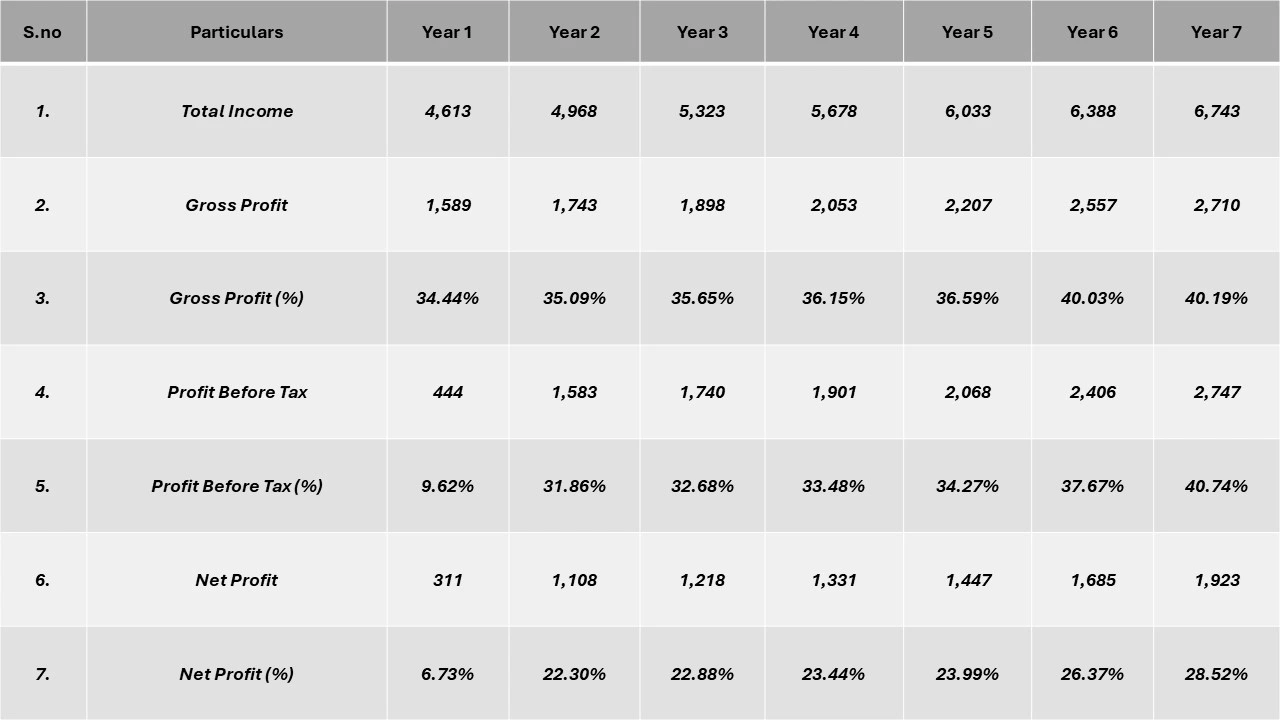
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis
(All values are in INR Crore, except % ages)
Conclusion
Our financial model for the LFP prismatic cell manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of producing 20 million cells annually—divided between LFP 3.2V/104Ah and LFP 3.2V/300Ah—we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights for strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










