
Indonesia Real Estate Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Property Type and Region, 2026-2034
Indonesia Real Estate Market Summary:
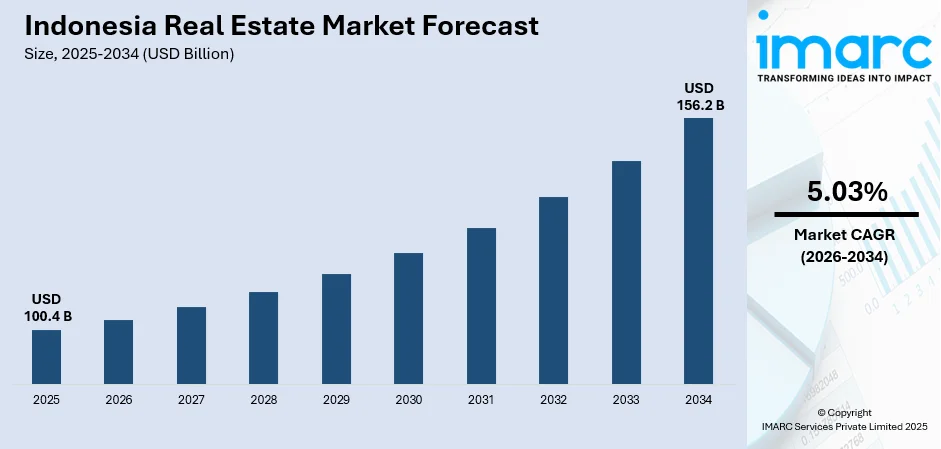
The Indonesia real estate market size was valued at USD 100.4 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 156.2 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.03% from 2026-2034.
The market growth is fueled by accelerating urbanization dynamics, government-led infrastructure modernization programs, and expanding middle-class purchasing power supported by favorable monetary policy adjustments. Moreover, strategic infrastructure corridors streamlined mortgage accessibility through reduced lending rates, and comprehensive affordable housing initiatives collectively drive the demand across residential and commercial property segments, positioning the market for sustained long-term growth, thereby expanding the Indonesia real estate market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
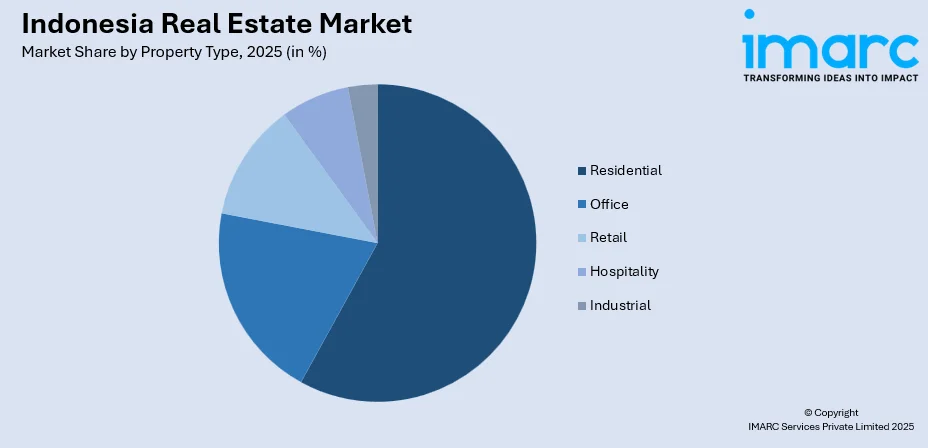
By Property Type: Residential dominates the market with a share of 58.02% in 2025, driven by demographic expansion and government housing programs addressing the substantial backlog.
-
By Region: Java leads the market with a share of 56% in 2025, supported by established transport networks and concentrated economic activity across metropolitan centers.
-
Key Players: The Indonesia real estate market exhibits moderate competitive intensity characterized by established domestic developers competing alongside international investors across diverse property segments and price tiers. Some of the key players include Lippo Group, PT Agung Podomoro Land Tbk, PT Ciputra Development Tbk, PT Intiland Development Tbk, PT PP (Persero) Tbk, PT Tokyu Land Indonesia, PT. Pakuwon Jati Tbk, and Sinar Mas.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Infrastructure modernization initiatives are fundamentally reshaping property valuations and development patterns across Indonesian markets. Completed toll-road networks spanning 2,816 kilometers by January 2024 have enhanced connectivity between Sumatra, Java, and Sulawesi, immediately elevating land values in corridor zones while unlocking previously underserved development areas. Furthermore, other infrastructure investments are dramatically shortening commute times across Greater Jakarta and catalyzing residential expansion into satellite districts. Large-scale projects demonstrate investor confidence in vertical development solutions addressing urban land scarcity. The ongoing Nusantara capital construction has mobilized IDR 51,35 trillion in Stage 1 investment, creating immediate requirements for housing, commercial offices, and civic facilities to accommodate projected population influx. The President of Indonesia, once more presided over the groundbreaking ceremony for Phase VI of the Nusantara Capital City project. The event occurred over two days, June 4 and 5, 2024, and was attended by numerous investors from various industries. The substantial advancements in Nusantara's infrastructure development reflect hope in reaching the established goals. At the Phase VI groundbreaking event, five companies from the education and research fields, along with three supporting businesses, took part, resulting in a total investment of IDR 1.75 Trillion.
Indonesia Real Estate Market Trends:
Transit-Oriented Development Accelerates Vertical Urban Expansion
Metropolitan areas across Indonesia are witnessing pronounced shifts toward high-density vertical construction formats as urban population concentration intensifies and available land parcels diminish. Developers are strategically positioning multi-story residential and mixed-use complexes adjacent to mass rapid transit stations, light rail corridors, and integrated transportation hubs to maximize accessibility and appeal to mobility-conscious buyers. This spatial reorganization reflects both demographic pressures and evolving lifestyle preferences favoring convenience and reduced commuting burdens. Transit-adjacent properties command premium valuations while experiencing faster absorption rates compared to peripheral developments lacking comparable connectivity advantages. On December 1, 2025, Indonesia declared a major investment of about Rp 16.65 trillion (roughly USD 1.1 billion) in the New Development Bank (NDB), highlighting a strategic effort to enhance infrastructure development and encourage sustainable economic advancement throughout the region. This significant investment demonstrates Indonesia's dedication to enhancing regional financial collaboration and increasing its involvement in the NDB, the multilateral development bank created by BRICS nations — Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
Government-Led Housing Programs Expand Affordable Supply Channels
Comprehensive social housing initiatives are systematically addressing longstanding supply deficits through coordinated public-private partnership mechanisms and targeted fiscal incentives. National programs prioritize construction of affordable units priced within reach of low-to-middle income households, supported by subsidized mortgage products carrying favorable interest rates and reduced down-payment requirements. State enterprises finance essential infrastructure including roads and utilities while private developers construct housing units, enabling scale economies and accelerated project completion timelines. These collaborative frameworks are particularly effective in secondary cities where land remains affordable, allowing developers to deliver mixed-income neighborhoods that simultaneously fulfill social housing targets and generate commercial returns. In 2025, The central bank of Indonesia announced that it will assist the government's affordable housing initiative by buying bonds in the secondary market.
Digital Platforms Transform Property Search and Transaction Processes
Online real estate marketplaces and digital transaction platforms have fundamentally altered how buyers research properties, evaluate options, and complete purchases across Indonesian markets. Prospective homeowners increasingly rely on comprehensive web-based listings featuring virtual tours, neighborhood analytics, and integrated financing calculators to inform decision-making processes before engaging with physical showrooms. In 2025, the Indonesian government has introduced a new policy to provide subsidies for loan interest to small property developers and individual homeowners. This initiative seeks to assist in the development of affordable housing, tackling the country's substantial housing deficit. Developers will obtain a 5% interest subsidy on loans for a maximum of five years, while homeowners borrowing up to 500 million rupiah (around USD 30,000) will enjoy an interest subsidy that varies from 5.5% to 10%, based on the size of the loan. The state has designated 200 trillion rupiah to public banks for the implementation of this initiative.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
Indonesia's real estate sector is positioned for robust expansion driven by synchronized demographic, infrastructure, and policy tailwinds converging across the forecast horizon. The market generated a revenue of USD 100.4 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 156.2 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.03% from 2026-2034. Apart from this, various government initiatives are strengthening logistics corridors and elevating demand for both residential and commercial assets throughout Java and emerging eastern regions.
Indonesia Real Estate Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Property Type | Residential | 58.02% |
| Region | Java | 56% |
Property Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Residential
- Office
- Retail
- Hospitality
- Industrial
Residential dominates with a market share of 58.02% of the total Indonesia real estate market in 2025.
Residential properties maintain clear market leadership anchored by persistent demographic expansion, cultural preferences favoring homeownership, and comprehensive government initiatives addressing housing deficits. Various residential housing programs by the government prioritizes affordable unit construction across rural and urban zones, delivering tangible supply increases that directly address the backlog constraining lower-income household access. Pre-sales remain concentrated in landed houses outside Jakarta's inner ring where land costs remain manageable, though apartments and vertical condominiums are capturing growing share in Surabaya and Bandung as scarcity intensifies. Government-backed VAT relief and subsidized mortgage programs with down-payment support have compressed entry barriers, widening the funnel of first-time buyers while anchoring long-term sectoral expansion.
Middle-market dwellings sustained by rising white-collar incomes and flexible financing schemes from fintech lenders catering to creditworthy professionals. Secondary market transactions retained a major percentage of share benefiting from established infrastructure and perceived value certainty, while primary launches are accelerating to qualify for temporary VAT exemptions that deliver compelling savings. Ready-stock inventory under the KPR subsidy program reached 87.736 units between October 2024 and January 2025, showcasing renewed developer focus on immediate handover capabilities that satisfy government milestones for social housing allocations while meeting buyer preferences for move-in ready homes.
Regional Insights:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
Java leads with a share of 56% of the total Indonesia real estate market in 2025.
Java holds a dominant position in Indonesia’s real estate market, driven by a high concentration of economic activity and population. Cities attract continuous demand for housing, office space, and retail properties. Growing infrastructure projects, better connectivity, and steady job creation pull people from other islands, pushing up property needs. Developers find steady returns here because demand stays strong across segments. With limited land in prime urban areas, prices often rise faster than in other parts of the country. That keeps investor interest high and supports ongoing development of mixeduse complexes and residential communities.
In the residential sector, Java leads because buyers prioritize proximity to work, education, and services. Middleclass growth and easier financing options boost purchases of apartments and landed homes. Commercial real estate also benefits from Java’s role as the business center of Indonesia. Retail centers, logistics hubs, and new business districts expand faster here than elsewhere. Local governments continue upgrading transport and utilities, which makes new areas appealing to both residents and companies. Though other regions are emerging, Java’s scale of activity and population remains unmatched, anchoring national real estate trends and shaping how developers plan future projects.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Indonesia Real Estate Market Growing?
Tourism Sector Recovery and Hospitality Property Demand
Indonesia's tourism industry is experiencing robust recovery momentum, generating sustained demand for hospitality assets including hotels, resorts, and serviced accommodation across primary destinations and emerging markets. Bali welcomed 6.3 million foreign visitors in 2024, representing a 19.5% year-over-year increase that surpassed pre-pandemic levels and directly stimulated commercial property absorption. The tourism surge closed 2024 on a strong note for Jakarta and Bali hotel investments, underscoring the enduring appeal of Indonesian destinations to global travelers while reinforcing corporate travel patterns. Infrastructure enhancements including new roads and planned airport expansions are improving accessibility to previously underserved areas, unlocking development opportunities for mixed-use tourism complexes integrating retail, entertainment, and residential components.
Foreign Direct Investment Inflows and Regulatory Liberalization
International capital flows into Indonesian real estate have accelerated following regulatory reforms simplifying foreign ownership structures and streamlining investment approval processes. Indonesia attracted USD 47 billion in foreign direct investment during 2023 and Bali attracted foreign direct investment amounting to USD 710.2 million during the first half of 2024. The introduction of Golden Visa and Second Home Visa programs has substantially expanded foreign buyer participation, particularly in Bali where areas including Badung Regency and Denpasar recorded foreign property ownership increases. Foreign investment rules stipulating minimum expenditures for apartments and for landed homes naturally steer overseas purchasers toward mid-to-premium tiers, contributing sustained transaction volumes that stabilize market valuations while diversifying buyer demographics beyond domestic purchasers.
Industrial Sector Expansion and Warehousing Infrastructure Requirements
Manufacturing sector growth and e-commerce logistics demands are driving substantial absorption of industrial real estate including modern warehouses, distribution centers, and production facilities across strategic corridors. Indonesia's economy expanded by 5.0% during the first three quarters of 2025, and growth is expected to stay at this level into 2026 and 2027. Key expansion areas including Bekasi, Cikarang, and Karawang are experiencing concentrated development as automotive, fast-moving consumer goods, and third-party logistics sectors generate strong demand for warehouse space equipped with contemporary specifications. East Java's industrial estates exemplify this transformation, attracting electronics and automotive investments requiring adjoining worker housing and logistics hubs that collectively stimulate mixed-use development patterns.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Indonesia Real Estate Market is Facing?
Substantial Housing Backlog and Affordability Gap
Low-income households face the burden of a housing backlog across Indonesian territories, with budget constraints hampering program roll-outs despite government commitments to accelerate affordable unit construction. Allocations for social housing initiatives in 2025 are projected to decline below 2024 levels, limiting the pace at which supply deficits can be meaningfully addressed. The widening income gap between Java's economic centers and outer islands exacerbates affordability challenges, as numerous Indonesians cannot afford homeownership without substantial financial support or subsidies. Despite policy interventions including VAT exemptions and subsidized mortgages, rising property prices continue outpacing wage growth for lower-income segments, perpetuating barriers to homeownership and constraining market expansion among demographic groups most requiring housing access.
Complex Land Acquisition and Regulatory Procedures
Land acquisition processes remain encumbered by regulatory complications, ownership disputes, and ambiguous legal frameworks that frequently result in development delays and elevated project costs. Indonesia ranks 73rd out of 190 countries for ease of obtaining construction permits, with bureaucratic obstacles causing lengthy approval timelines for environmental impact assessments and building authorization. While affordable housing policies are established at national levels, local governments handle implementation creating coordination challenges and procedural inconsistencies across jurisdictions. High-demand areas including Jakarta and Bali experience particularly acute complications where land ownership disputes and unclear title documentation prolong legal resolution processes, discouraging developers from committing capital until clarity emerges. These structural impediments slow housing supply additions while increasing transaction costs that ultimately transfer to end purchasers.
Premium Segment Oversupply in Urban Centers
Jakarta's condominium market navigates challenging conditions particularly within premium segments where rising inventory levels have outpaced end-user absorption, resulting in extended sales cycles and tempered price appreciation. Luxury developments targeting foreign buyers struggled during pandemic periods and continue seeking to regain previous momentum despite gradual demand recovery. Premium unit supply has accumulated faster than purchaser demand can absorb, creating competitive pressures that constrain pricing power and compress developer margins. The concentration of high-end inventory in central business districts faces particular headwinds as buyer preferences shift toward ready-to-occupy units in well-connected suburban corridors offering superior value propositions relative to premium urban towers commanding elevated per-square-meter costs.
Competitive Landscape:
The Indonesia real estate market demonstrates moderate competitive intensity featuring established domestic developers operating alongside international investors across diversified property segments and geographic markets. Major domestic players dominate residential and commercial development activities leveraging extensive land banks and established brand recognition. Foreign participants are progressively entering through joint ventures and direct investments, attracted by demographic growth trajectories and infrastructure improvement programs enhancing market fundamentals. Competition manifests across multiple dimensions including land acquisition capabilities, project execution speed, financing access, and brand positioning across price segments ranging from affordable social housing to premium luxury developments targeting affluent domestic buyers and international investors. Some of the key players include:
- Lippo Group
- PT Agung Podomoro Land Tbk
- PT Ciputra Development Tbk
- PT Intiland Development Tbk
- PT PP (Persero) Tbk
- PT Tokyu Land Indonesia
- PT. Pakuwon Jati Tbk
- Sinar Mas
Recent Developments:
-
In August 2025, Fahri Hamzah, Indonesia's Deputy Minister of Housing and Settlements, revealed intentions to construct 1 million vertical housing units in partnership with the Ministry of State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs).
-
In June 2025, Qatari firm Al Qilaa, via its Indonesian branch Al Qilaa International Indonesia, aims to construct 50,000 affordable apartment units in Indonesia as an initial phase of an extensive housing investment initiative, with construction set to start once licensing and land preparation are finalized.
Indonesia Real Estate Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Property Types Covered | Residential, Office, Retail, Hospitality, Industrial |
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Companies Covered | Lippo Group, PT Agung Podomoro Land Tbk, PT Ciputra Development Tbk, PT Intiland Development Tbk, PT PP (Persero) Tbk, PT Tokyu Land Indonesia, PT. Pakuwon Jati Tbk, Sinar Mas, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Indonesia real estate market size was valued at USD 100.4 Billion in 2025.
The Indonesia real estate market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.03% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 156.2 Billion by 2034.
Residential dominated the Indonesia real estate market with 58.02% share, driven by persistent demographic expansion, cultural homeownership preferences, and comprehensive government housing initiatives addressing supply deficits. The Three Million Houses program prioritizes affordable unit construction across rural and urban zones while VAT relief and subsidized mortgages compress entry barriers for first-time buyers
Key factors driving the Indonesia real estate market include strategic infrastructure development enhancing connectivity across regions, favorable monetary policy adjustments reducing mortgage costs, expanding middle-class population with rising purchasing power, and government-led affordable housing initiatives systematically addressing supply deficits through public-private partnerships.
Major challenges include an housing backlog constraining low-income household access, complex land acquisition procedures and regulatory obstacles causing development delays, and premium segment oversupply in urban centers particularly Jakarta where inventory accumulation outpaces end-user absorption creating extended sales cycles.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












