
Indian Cold Chain Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Segment, Product, Sector, Organised and Unorganised, and States, 2026-2034
Indian Cold Chain Market Summary:
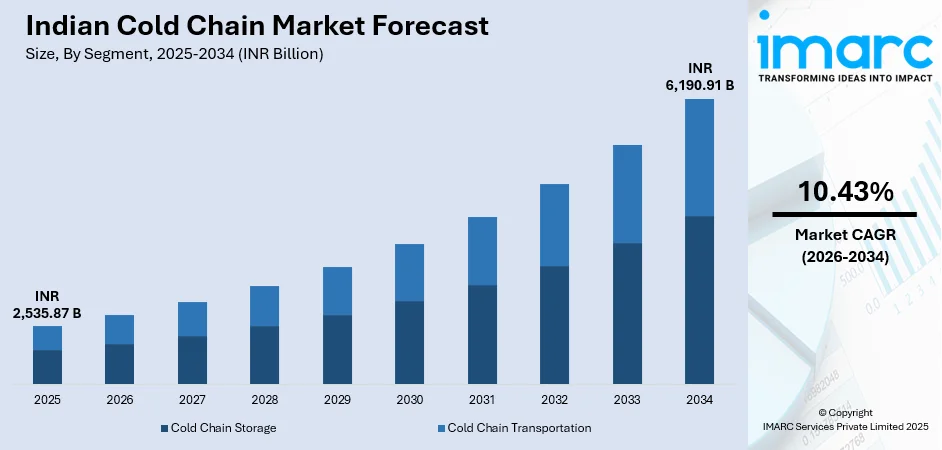
The Indian cold chain market size was valued at INR 2,535.87 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach INR 6,190.91 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 10.43% from 2026-2034.
The Indian cold chain market is experiencing robust expansion driven by the growing organized retail sector, rising consumption of perishable food products, and increasing demand from the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries. The market benefits from evolving consumer dietary preferences toward fresh produce and the expanding e-commerce grocery delivery ecosystem that requires temperature-controlled logistics infrastructure across urban and rural geographies.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Segment: Cold chain storage dominates the market with a share of 68% in 2025, driven by extensive warehousing infrastructure development and growing demand for temperature-controlled preservation facilities.
-
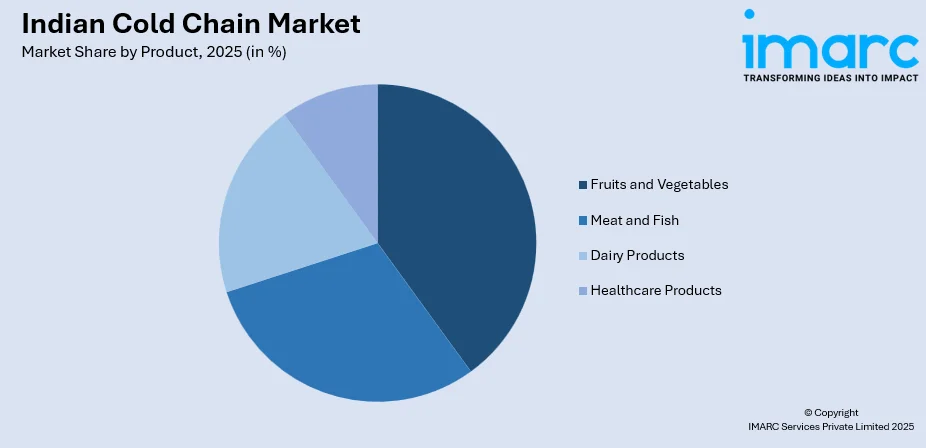
By Product: Fruits and vegetables lead the market with a share of 37% in 2025, owing to India's position as a leading global producer of horticultural produce requiring refrigerated storage.
-
By Sector: Private dominates the market with a share of 72% in 2025, attributable to substantial private investments in modern cold chain infrastructure and logistics networks.
-
By Organised and Unorganised: Unorganised leads the market with a share of 80% in 2025, reflecting the fragmented nature of the industry with numerous small-scale operators.
-
Key Players: The Indian cold chain market features a competitive landscape comprising established national logistics providers alongside emerging technology-driven startups, both offering integrated, end-to-end temperature-controlled supply chain solutions to support food, pharmaceutical, and agricultural distribution across domestic and export markets.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The cold chain industry in India is undergoing transformative growth catalyzed by fundamental shifts in food consumption patterns and healthcare logistics requirements. India's position as the world's largest milk producer and second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables necessitates extensive cold chain infrastructure for reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring product quality. The rapid expansion of organized food retail formats is driving demand for integrated cold chain solutions connecting farm gates to consumer doorsteps. Government initiatives including the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana and the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture are accelerating infrastructure investments across states. The pharmaceutical sector's growth trajectory and vaccine distribution requirements are creating specialized demand for GDP-compliant temperature-controlled storage and transportation facilities, further boosting private investments and technological adoption nationwide.
Indian Cold Chain Market Trends:
Technology Integration and Digital Transformation
The market is witnessing accelerated adoption of advanced technologies including Internet of Things sensors, automated storage and retrieval systems, and artificial intelligence-driven route optimization. In 2025, Tag‑N‑Trac’s AI and IoT tracking cut a pharma company's shipment excursions from 1.93% to 0.3%, boosting efficiency. Real-time temperature monitoring and blockchain-enabled traceability solutions are enhancing supply chain visibility and compliance with quality standards. Digital platforms are enabling better coordination between farmers, logistics providers, and retailers for efficient cold chain utilization.
Multi-Commodity and Multi-Temperature Facilities
The industry is shifting from traditional single-commodity storage toward versatile multi-temperature warehousing facilities capable of handling diverse product categories simultaneously. In 2025, Swisslog showcased its AutoStore Multi-Temperature Solution, a scalable system storing frozen, chilled, and ambient goods together, reducing separate facilities and simplifying cold chain operations. Controlled atmosphere storage and quick-switch evaporator technologies are enabling operators to optimize capacity utilization across seasonal variations. This evolution is particularly significant for reducing infrastructure redundancy and improving return on investment for cold chain operators.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Environmental sustainability is reshaping cold chain infrastructure development with growing emphasis on energy-efficient refrigeration systems and renewable energy integration. In 2025, India issued comprehensive guidelines for solar-powered cold storage, enhancing design, performance, and operation to boost energy efficiency and sustainability for food and pharmaceutical storage. The India Cooling Action Plan is driving adoption of low global warming potential refrigerants and sustainable cooling technologies. Solar-powered cold storage solutions and phase-change material containers are gaining traction for last-mile distribution in areas with unreliable grid connectivity.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Indian cold chain market is set for steady growth over the forecast period, driven by government infrastructure initiatives, increasing urbanization, and rising demand for fresh and processed foods. Additionally, the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors are creating specialized requirements for vaccine distribution and biopharmaceutical logistics, further boosting market expansion. Investments in temperature-controlled storage, transportation, and logistics solutions are expected to support the sector’s long-term development and operational efficiency across industries. The market generated a revenue of INR 2,535.87 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of INR 6,190.91 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 10.43% from 2026-2034.
Indian Cold Chain Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Segment | Cold Chain Storage | 68% |
| Product | Fruits and Vegetables | 37% |
| Sector | Private | 72% |
| Organised and Unorganised | Unorganised | 80% |
Segment Insights:
- Cold Chain Storage
- Cold Chain Transportation
The cold chain storage dominates with a market share of 68% of the total Indian cold chain market in 2025.
The commanding position of cold chain storage reflects the fundamental infrastructure requirements for preserving temperature-sensitive products across extended periods. The segment encompasses multi-purpose warehouses, controlled atmosphere facilities, and specialized pharmaceutical storage units serving diverse industry verticals. The ICCVAI Scheme under PM Kisan Sampada Yojana offers up to ₹10 crore for multi-temperature storage and logistics, boosting private investment in modern agricultural storage in 2025. Government subsidies and financial assistance schemes have accelerated private sector investments in modern storage infrastructure across agricultural production centers.
Rising awareness of post-harvest losses and stringent food safety standards is boosting demand for advanced storage solutions with precise temperature and humidity management. Adoption of automation technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems, is improving operational efficiency and maximizing capacity. Operators increasingly prefer multi-temperature facilities that can handle diverse product categories, enabling optimized infrastructure utilization and enhanced financial performance across the cold storage and logistics value chain.
Product Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Meat and Fish
- Dairy Products
- Healthcare Products
The fruits and vegetables lead with a share of 37% of the total Indian cold chain market in 2025.
The dominant position of fruits and vegetables reflects India's status as the world's second-largest producer of horticultural commodities requiring temperature-controlled storage to minimize post-harvest losses. The segment addresses critical preservation needs for highly perishable produce including tomatoes, onions, potatoes, mangoes, and grapes that constitute significant agricultural output. Seasonal production patterns necessitate extensive storage infrastructure for year-round market availability and price stabilization. In 2025, Haryana planned advanced cold storage and warehousing at Hisar’s Maharaja Agrasen Airport, with controlled-temperature facilities and air cargo links to boost horticultural exports.
The rapid growth of organized retail and e-commerce grocery platforms in India is driving demand for integrated cold chain solutions linking production centers to urban markets. Farm-gate pre-cooling units and pack houses are increasingly critical for preserving quality from harvest to distribution. Simultaneously, export-focused cold chain infrastructure is expanding to enable premium Indian fruits and vegetables to reach international markets efficiently, ensuring freshness, reducing post-harvest losses, and meeting stringent global standards.
Sector Insights:
- Private
- Cooperative
- Public
The private dominates with a market share of 72% of the total Indian cold chain market in 2025.
India’s cold chain market is largely led by the private sector, driven by strong demand for temperature-controlled logistics. Private operators have established extensive storage networks spanning key agricultural regions and urban consumption centers. Government subsidy schemes have further stimulated investment by lowering capital costs and improving project viability. This support has accelerated the development of modern cold storage infrastructure, enhancing efficiency in the handling, preservation, and distribution of perishable goods nationwide while reducing post-harvest losses.
Leading corporate logistics providers are rapidly expanding their cold chain networks through organic growth and strategic acquisitions to offer comprehensive end-to-end solutions. Increased foreign direct investment is driving technology transfer and the adoption of international best practices. The entry of organized players is professionalizing the sector by implementing standardized operating procedures, quality certifications, and operational efficiencies, thereby improving reliability, safety, and consistency, and fostering a more robust and efficient cold chain ecosystem across India.
Organised and Unorganised Insights:
- Organised
- Unorganised
The unorganised leads with a share of 80% of the total Indian cold chain market in 2025.
The commanding share of the unorganised segment reflects the historically fragmented nature of India's cold chain industry characterized by numerous small-scale operators serving localized markets. Many existing facilities were established primarily for single-commodity storage, particularly potatoes, operating with limited technological sophistication. Regional operators continue serving traditional agricultural supply chains connecting local production to nearby wholesale markets. In 2025, India approved 395 ICCVAI projects, adding 25.52 lakh MT capacity and supporting FPOs, SHGs, and small enterprises with subsidies to modernize and connect cold chains.
The segment is steadily transforming as market consolidation integrates smaller operators into organized supply chain networks. Increasing quality benchmarks and stricter food safety regulations are prompting unorganised players to upgrade infrastructure and enhance operational practices. Supportive government capacity-building programs, coupled with improved access to institutional financing, are enabling these players to professionalize operations, adopt modern technologies, and align more closely with industry standards, fostering a gradual shift toward a more structured and compliant cold chain ecosystem.
States Insights:
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Punjab
- Gujarat
- Bihar
- Andhra Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Karnataka
- Haryana
- Chhattisgarh
- Rajasthan
- Orissa
- Tamil Nadu
- Others
Uttar Pradesh leads India’s cold chain market due to its large-scale agricultural production, particularly potatoes. Extensive infrastructure supports fruits, vegetables, and dairy, catering to diverse agro-climatic zones. The state’s focus on temperature-controlled storage ensures efficient post-harvest management and strengthens supply chains for domestic distribution and emerging export opportunities.
West Bengal ranks among the top cold chain markets, with strong infrastructure for vegetable and potato preservation. Kolkata’s port connectivity supports export-oriented logistics, while regional agricultural production drives consistent demand for temperature-controlled storage. The state’s cold chain system plays a key role in sustaining both local markets and international trade in horticultural and seafood products.
Punjab’s intensive agricultural economy drives extensive cold chain development. Infrastructure supports fruits, vegetables, and dairy, ensuring efficient distribution domestically and internationally. Government initiatives promoting food processing industries are stimulating investments in integrated cold chain solutions that connect farm production to processing facilities, enhancing storage efficiency and reducing post-harvest losses.
Gujarat’s cold chain network serves diverse agricultural and industrial needs. Irrigated agriculture supports year-round production of high-value horticultural crops requiring temperature-controlled preservation. Industrial development and port connectivity strengthen logistics for domestic and export markets, while investments in cold storage facilities support efficient distribution and reduce post-harvest losses across multiple sectors.
Bihar shows strong potential for cold chain expansion due to significant fruit and vegetable production. Current infrastructure is insufficient, leading to post-harvest losses. Government initiatives are prioritizing investments in cold storage and transportation networks to enhance farmer incomes, improve market access, and ensure better preservation of perishable commodities.
Andhra Pradesh demonstrates efficient cold chain infrastructure supporting mangoes, chillies, and other export-oriented crops. High utilization reflects alignment with agricultural production patterns. Port connectivity facilitates seafood exports and imports of temperature-sensitive products. The state’s cold chain systems emphasize specialized solutions to maintain quality and extend shelf life for domestic and international markets.
Madhya Pradesh is expanding cold chain infrastructure in response to growing horticultural production and food processing investments. Onion and tomato storage demands specialized solutions to manage seasonal supply fluctuations. Central location enables logistics networks that serve multiple regional markets, positioning the state as a strategic hub for temperature-controlled distribution.
Maharashtra’s cold chain market serves diverse agricultural and industrial sectors, including grapes, onions, and dairy. Mumbai’s commercial hub drives demand for organized retail, food service, and pharmaceutical logistics. Cold storage infrastructure supports domestic and export markets, ensuring reliable distribution and preservation of perishable commodities across multiple industries.
Karnataka combines horticultural production with a growing pharmaceutical sector, requiring GDP-compliant cold chain solutions. Bengaluru’s industrial and technology growth fuels healthcare logistics demand. Specialized storage solutions for fruits like mangoes and grapes extend shelf life, supporting both domestic consumption and export-oriented supply chains with controlled atmosphere preservation.
Haryana benefits from proximity to the National Capital Region, stimulating investments in cold storage and transportation infrastructure. Agricultural production of fruits, vegetables, and dairy generates strong demand for farm-gate and regional distribution solutions. Industrial corridors and logistics parks further encourage development of integrated cold chain facilities serving domestic markets.
Chhattisgarh is emerging in cold chain development, driven by agricultural diversification and government-backed investments. Cold storage for fruits, vegetables, and forest produce from tribal areas is expanding, while the growing food processing sector encourages integrated solutions linking production to consumption centers, reducing post-harvest losses and improving supply chain efficiency.
Rajasthan is improving cold chain capacity to support horticultural production in irrigated areas. Vegetables, fruits, and spices require temperature-controlled storage for domestic and export markets. Jaipur’s role as a logistics hub attracts investments in integrated facilities, enhancing regional distribution networks and improving the efficiency of perishable goods management.
Orissa’s cold chain potential is driven by fisheries and horticulture growth. Port infrastructure enables seafood exports, while government support for food processing stimulates storage investments. Expansion of cold storage facilities enhances domestic distribution and strengthens export capabilities, creating opportunities for temperature-controlled supply chains across the state’s agricultural production zones.
Tamil Nadu’s cold chain infrastructure supports diverse agricultural and industrial sectors. Chennai’s port and industrial activities create demand for temperature-controlled logistics serving pharmaceuticals, automotive, and food industries. Specialized solutions for fruits, vegetables, and flowers ensure quality preservation for domestic distribution and export markets, enhancing supply chain efficiency.
Remaining states contribute to India’s cold chain landscape with varying development levels. Northeastern states are supported by government subsidies for cold storage expansion, while hill states such as Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir focus on specialized storage for apples and controlled atmosphere solutions to preserve perishable produce.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Indian Cold Chain Market Growing?
Organized Retail Expansion and E-Commerce Growth
The rapid growth of organized retail and e-commerce grocery platforms is reshaping cold chain demand in India. Modern retail chains need integrated temperature-controlled supply chains to maintain product freshness, while online grocery and quick commerce platforms drive demand for last-mile cold storage near urban centers for rapid fulfillment. The Indian e-commerce market, valued at USD 129.72 billion in 2025, is projected to reach USD 651.10 billion by 2034, growing at a 19.63% CAGR from 2026–2034. These trends are accelerating investment in modern cold storage infrastructure, automation, and temperature-controlled logistics to meet rising consumer expectations and quality standards.
Government Infrastructure Development Initiatives
Various government programs are catalyzing substantial cold chain investments across states. In July 2025, the Union Cabinet approved ₹6,520 crore under PMKSY, allocating ₹1,000 crore for 50 multi‑product food irradiation units to expand cold chains and cut post‑harvest losses. Credit-linked subsidy schemes providing significant capital cost support have improved project viability and attracted private sector participation. The Agriculture Infrastructure Fund is facilitating financing for post-harvest management infrastructure including cold storage facilities at farm gates and market yards. National Logistics Policy initiatives targeting improved supply chain efficiency are promoting integrated cold chain network development connecting production centers to consumption markets.
Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Sector Demand
India's expanding pharmaceutical industry and healthcare sector are generating specialized cold chain requirements for temperature-sensitive drug storage and distribution. In August 2025, Celcius Logistics launched “Celcius+,” a ₹50 crore pharma cold chain arm with 100 refrigerated vehicles, enhancing temperature‑controlled transport for medicines, vaccines, and biologics across 100+ Indian cities. The biologics and vaccine segment requires GDP-compliant cold chain infrastructure maintaining strict temperature controls throughout the supply chain. Clinical trial logistics and biopharmaceutical distribution are creating demand for multi-temperature storage facilities with precise monitoring capabilities. Government vaccination programs have highlighted the critical importance of reliable cold chain networks reaching rural areas for effective healthcare delivery.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Indian Cold Chain Market is Facing?
High Capital Investment Requirements
The cold chain industry faces significant financial barriers as establishing comprehensive storage and transportation infrastructure requires substantial capital investment. Many smaller operators struggle to secure financing for infrastructure development, limiting industry scalability and modernization. Long gestation periods for investment recovery create challenges for project viability, particularly in regions with lower storage utilization rates.
Infrastructure Gaps and Regional Imbalances
Significant regional disparities in cold chain infrastructure create supply chain inefficiencies with southern and northeastern states particularly underserved. The concentration of existing facilities in few states leaves vast agricultural production areas without adequate cold storage access. Farm-gate infrastructure including pack houses and pre-cooling facilities remains critically deficient across most production regions.
Operational Cost Pressures
High electricity costs and unreliable power supply in many regions create operational challenges for cold storage facilities requiring continuous refrigeration. Energy expenses constitute a substantial portion of operating costs, affecting profitability and service pricing competitiveness. The shortage of trained personnel for cold chain operations limits industry capacity for technology adoption and efficiency improvements.
Competitive Landscape:
The Indian cold chain market exhibits a highly fragmented competitive structure with organized logistics providers, regional operators, and specialized cold chain companies serving diverse market segments. Leading players are pursuing capacity expansion strategies through organic investments and strategic acquisitions to establish integrated end-to-end cold chain capabilities. Technology-driven startups are disrupting traditional operations through digital platforms enabling better asset utilization and supply chain visibility. Foreign logistics companies are expanding their Indian presence through partnerships and direct investments, introducing global best practices and advanced infrastructure standards. Industry consolidation is accelerating as larger players acquire regional operators to expand geographic coverage and customer portfolios across temperature-controlled logistics services.
Recent Developments:
-
In July 2025, Callan JMB Inc. has established Callan JMB Services (India) Pvt Ltd to provide temperature-controlled warehousing and logistics in Pune, Maharashtra, focusing on pharmaceutical and critical storage solutions. The move supports distribution across all temperature ranges, including -80°C for clinical trial materials.
Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | INR Billion, Million Metric Tons |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Segment Covered | Cold Chain Storage, Cold Chain Transportation |
| Product Covered | Fruits and Vegetables, Meat and Fish, Dairy Products, Healthcare Products |
| Sector Covered | Private, Cooperative, Public |
| Organised and Unorganised Covered | Organised, Unorganised |
| States Covered | Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Punjab, Gujarat, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Indian cold chain market size was valued at INR 2,535.87 Billion in 2025.
The Indian cold chain market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.43% from 2026-2034 to reach INR 6,190.91 Billion by 2034.
Cold chain storage dominated the market with a 68% share, driven by extensive warehousing infrastructure development, government subsidy schemes, and growing demand for temperature-controlled preservation facilities across agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors.
Key factors driving the Indian cold chain market include organized retail expansion, e-commerce grocery growth, government infrastructure development initiatives, rising consumption of perishable food products, and increasing demand from healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors.
Major challenges include high capital investment requirements, significant regional infrastructure imbalances, operational cost pressures from electricity expenses, shortage of trained personnel, and fragmented industry structure limiting economies of scale.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












