
India ATM Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Solution, Screen Size, Application, ATM Type, and Region, 2025-2033
India ATM Market Size and Share:
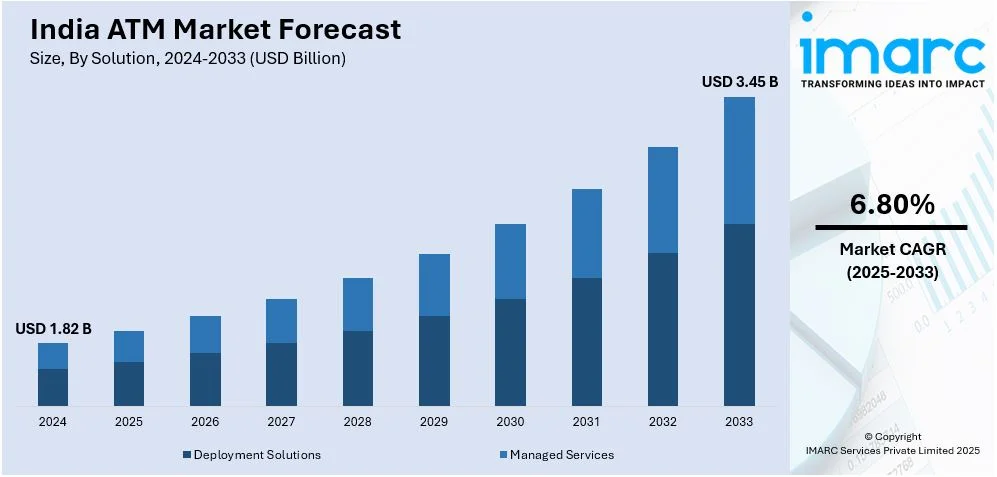
The India ATM market size was valued at USD 1.82 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 3.45 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.80% during 2025-2033. The market is driven by persistent cash reliance, especially in rural areas with limited digital payment infrastructure. Government financial inclusion initiatives and expanding banking penetration enhance demand. Technological advancements in biometric ATMs and cash recyclers enhance efficiency, while urbanization increases transaction volumes. Regulatory support for white-label ATMs and the need for 24/7 banking services are further expanding the India ATM market share, despite rising digital payment adoption.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 1.82 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 3.45 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 6.80% |
The India ATM market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for cash transactions despite the growth of digital payments. A major portion of the population, especially in semi-urban and rural areas, relies heavily on cash due to limited access to digital infrastructure and low financial literacy. Additionally, government initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) have expanded banking access, enhancing the need for ATMs to serve unbanked and underbanked regions. India's digital economy contributed a substantial INR 31.64 lakh crore (approximately USD 395,500 Million) to INR 26.92 lakh crore (approximately USD 336,500 million) (FY22) to the national GDP in the fiscal year 2023, accounting for 11.74% of the GDP. By December 2024, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) had already handled over INR 23 lakh crore (approximately USD 287,500 Million) worth of transactions, with 641 banks brought onto the UPI system, a step towards mechanized banking services. The telecom sector, for this reason alone, saw a staggering 285% growth in internet bandwidth and put up a total of 4.6 lakh 5G towers. DigiLocker, which also crossed 46.5 crore users, and Aadhaar face authentications went beyond 100 crores. Complemented by initiatives such as BHASHINI, ONDC, and the sprawling 6.92 lakh km fiber network created under BharatNet, India's changing digital infrastructure is changing the ATM landscape and driving greater demand for innovative, self-service banking solutions. The rising adoption of automated banking solutions by financial institutions to enhance customer convenience further propels India ATM market growth. These factors collectively contribute to the steady expansion of ATM networks across India.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Technological advancements and the introduction of innovative ATM models, such as cash recyclers and biometric-enabled machines, are key drivers in the India ATM market. Banks and financial institutions are increasingly deploying advanced ATMs to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. The growing emphasis on financial inclusion and the expansion of banking services in remote areas also fuel ATM installations. Furthermore, the rise in disposable income and consumer spending has led to higher cash withdrawals, sustaining the India ATM market demand. India had 48.83 crore cash withdrawals from ATMs as of January 2025, and the average monthly withdrawal value grew 5.51% in 2024 to INR 1.43 crore (approximately 0.179 Million). While we are witnessing rapid growth in digital transactions, cash remains at the heart of financial transactions. The Reserve Bank of India's fee increase in 2021 has contributed to the expansion of ATMs, and the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has established a INR 7 interchange fee for balance inquiries in Nepal and Bhutan. Regulatory support from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to enhance security and accessibility further strengthens market growth, ensuring ATMs remain a critical banking touchpoint.
India ATM Market Trends:
Digital Payment Rise Driving ATM Evolution
India’s ATM market is rapidly transforming in tandem with the country’s growing reliance on digital banking. The Ministry of Finance revealed that digital payment transactions increased from 2,071 crore in FY 2017–18 to 18,737 crore in FY 2023–24, reflecting a 44% CAGR. In just five months of FY 2024–25 (April–August), volumes already hit 8,659 crore, highlighting sustained momentum. While digital payment adoption rises, ATMs remain crucial as hybrid access points—offering cash withdrawal along with digital functions. Consumers typically initiate ATM transactions using debit or credit cards, followed by PIN authentication and guided screen navigation. As more users blend digital banking with physical interfaces, ATMs are being upgraded for greater ease, security, and speed, reinforcing their role in a transforming financial ecosystem.
Expanding ATM & CRM Infrastructure Across Urban and Rural India
India’s ATM and Cash Recycler Machine (CRM) network is witnessing significant expansion, driven by the demand for broader financial access. As per Reserve Bank of India data from April 2024, the country had approximately 2.18 lakh ATMs and CRMs, including 1.27 lakh on-site units and 92,000 off-site installations. This infrastructural shift reflects a deliberate move to take banking beyond traditional branches. Off-site ATMs and CRMs are particularly vital in underserved regions, ensuring round-the-clock financial access without a full-scale bank. These machines not only facilitate withdrawals but also support functions including cash deposit, mini statements, and balance checks. Their increased deployment enhances banking reach and supports both urban mobility and rural inclusion, underlining their growing significance in India’s diversified financial architecture.
Financial Inclusion Improvement through Government-Led Initiatives
The Indian ATM market plays a pivotal role in advancing financial inclusion, especially through government-led efforts such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). Celebrating its 10th anniversary in August 2024, the scheme has enabled the opening of over 53 crore bank accounts with cumulative deposits totaling INR 2.31 Lakh Crore. Notably, 55.6% of these accounts are held by women, and 66.6% are located in rural and semi-urban areas. As banking penetration deepens, ATMs become a vital access point for newly banked individuals—particularly where branches are scarce. Through ATMs, beneficiaries can check balances, withdraw subsidies, and perform essential transactions. With such large-scale financial inclusion, demand for accessible ATM services is expected to increase, creating a positive India ATM market outlook.
India ATM Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the ATM market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on solution, screen size, application, and ATM type.
Analysis by Solution:
- Deployment Solutions
- Onsite ATMs
- Offsite ATMs
- Work Site ATMs
- Mobile ATMs
- Managed Services
Deployment solutions stand as the largest component in 2024, holding around 54.3% of the market. This can be supported by the increasing demand for efficient and scalable ATM networks. Banks and financial institutions are adopting advanced deployment models, including onsite, offsite, and mobile ATMs, to enhance accessibility, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. Offsite ATMs dominate the market as they offer greater convenience and wider coverage, while mobile ATMs are gaining traction for their flexibility in serving remote locations. Additionally, the integration of solar-powered and white-label ATMs is expanding financial inclusion. Companies are also focusing on cost-effective deployment strategies, such as outsourcing installation and maintenance, to optimize operational efficiency. The rise of smart cities and digital banking infrastructure further accelerates the adoption of innovative deployment solutions across India.
Analysis by Screen Size:
- 15" and Below
- Above 15"
15" and below leads the market in 2024 due to its cost-effectiveness and widespread adoption in conventional ATMs. These compact screens are commonly used in basic cash dispensers and entry-level machines, making them ideal for high-volume deployments in urban and semi-urban areas. Their smaller size allows for space-efficient installations in retail outlets, petrol pumps, and small bank branches. Additionally, these screens consume less power, reducing operational costs for banks and white-label ATM operators. While they lack advanced interactive features, their reliability and affordability make them a preferred choice for standard transactions. However, with the growing demand for enhanced user interfaces, this segment faces competition from larger, more interactive displays, particularly in premium banking locations.
Analysis by Application:
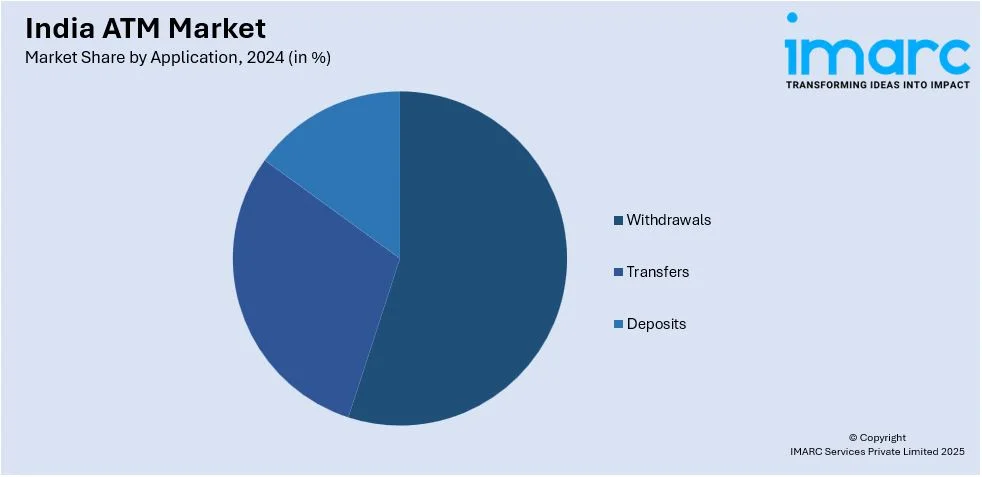
- Withdrawals
- Transfers
- Deposits
Withdrawal transactions lead the market with around 69.8% of market share in 2024. Cash continues to dominate in rural and semi-urban areas due to limited digital infrastructure and consumer preference for physical currency. ATMs with high-capacity cash dispensers are widely deployed to meet this demand, particularly in high-traffic locations such as markets and transportation hubs. Banks and white-label ATM operators prioritize withdrawal functionality to ensure liquidity and minimize downtime. The government's push for financial inclusion has further increased ATM penetration, making cash access easier for underserved populations. However, rising operational costs and security concerns pose challenges, prompting operators to adopt advanced cash management solutions to maintain efficiency in withdrawal-centric ATMs.
Analysis by ATM Type:
- Conventional/Bank ATMs
- Brown Label ATMs
- White Label ATMs
- Smart ATMs
- Cash Dispensers
Conventional/bank ATMs lead the market with around 34.7% of market share in 2024, offering reliable cash withdrawals and basic banking services. These machines are typically installed at bank branches and extend banking hours for customers. While they provide secure transactions through chip-and-PIN authentication, their high operational costs—including cash replenishment and maintenance—limit profitability. Banks are gradually modernizing these ATMs with advanced features including touchscreens and multilingual interfaces to enhance user experience. However, their growth is slowing due to the rise of cost-efficient alternatives such as white-label ATMs. Despite this, conventional ATMs remain crucial for customer retention, particularly in urban areas where banks aim to maintain a strong physical presence alongside digital channels.
Regional Analysis:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East and Northeast India
North India represents one of the significant markets for ATMs, driven by high population density and increasing banking penetration across states including Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, and Punjab. Urban centers such as Delhi-NCR and Chandigarh have a dense network of conventional and smart ATMs catering to tech-savvy customers, while rural areas rely on white-label and brown-label ATMs for basic cash access. Government initiatives such as the Jan Dhan Yojana have increased financial inclusion, increasing ATM demand in semi-urban and rural regions. The region is witnessing a shift toward advanced ATMs, particularly in metropolitan areas, though cash remains dominant due to persistent informal economic activities.
West and Central India, encompassing states including Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh, exhibit a balanced mix of urban and rural ATM adoption. Mumbai and Pune lead in smart ATM deployments, offering multifunctional services, while smaller cities and villages depend on white-label ATMs for financial inclusion. Maharashtra’s robust banking infrastructure supports high ATM density, but rural areas in MP and Chhattisgarh face connectivity issues, limiting ATM accessibility. The region benefits from proactive state policies promoting digital banking, yet cash dependency persists in agrarian economies. Cash recyclers are gaining traction in commercial hubs to reduce operational costs. Moreover, the region’s growth is driven by urbanization, but disparities in infrastructure require targeted ATM expansion in underserved zones.
South India stands out as the most advanced ATM market, with high banking penetration and digital literacy in states such as Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana. Cities such as Bengaluru and Hyderabad are early adopters of smart ATMs and cash-recycling technologies, aligning with the region’s tech-driven economy. Rural areas, though better served than in other regions, still rely on brown-label and white-label ATMs. Kerala’s high literacy rates and cooperative banking model ensure widespread ATM usage, including in semi-urban locales. The region’s robust digital payment ecosystem complements ATM networks, reducing pure cash dependency. South India’s mature market emphasizes innovation, with banks prioritizing multifunctional ATMs over basic cash dispensers.
East and Northeast India lag in ATM penetration due to geographical challenges, lower banking infrastructure, and economic disparities. States including West Bengal and Assam have seen gradual growth in white-label ATMs, particularly in semi-urban areas, but rural regions remain underserved. The Northeast’s difficult terrain and insurgency risks hinder ATM deployment, though government schemes aim to improve access. Kolkata and Guwahati are focal points for conventional and smart ATMs, while smaller towns face liquidity and maintenance issues. Financial inclusion efforts, such as the RBI’s priority on branchless banking, are slowly expanding ATM coverage. The region requires targeted investments and policy support to bridge the ATM accessibility gap compared to other zones.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of India's ATM market is characterized by intense rivalry among established banking technology providers, payment solution specialists, and financial service aggregators. Leading players are investing heavily in advanced ATM technologies such as cash recycling systems, biometric authentication, and AI-powered predictive maintenance to differentiate their offerings. Many are expanding into underserved rural markets through white-label ATM deployments while forming strategic partnerships with banks and fintech firms to enhance service capabilities. Several competitors are focusing on multi-functional kiosks that combine cash services with bill payments, account opening, and loan processing. The market is seeing consolidation as larger players acquire regional specialists to expand their networks. Cost optimization through shared ATM infrastructure and managed services has become a key strategy, along with compliance upgrades to meet changing RBI regulations. Innovation in compact and solar-powered ATM designs is gaining traction as players target low-infrastructure areas. The competition is increasingly shifting toward providing comprehensive cash management solutions rather than just ATM hardware.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the India ATM market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Euronet Worldwide, Inc.
- Hitachi Ltd.
- Diebold Nixdorf, Incorporated
- NCR Atleos Corporation
- AGS Transact Technologies Ltd.
- Vortex Engineering Private Limited
- ETSOL WATER SOLUTIONS PVT. LTD.
- Tata Communications Payment Solutions Limited
- Brinks India Private Limited
- Hyosung India Private Limited
- FIS Solutions Software India Private Limited
Latest News and Developments:
- January 2025: ASX-listed Findi acquired fintech firm BANKIT for INR 160 Crore via TSI to strengthen financial inclusion in India. With BANKIT’s 1.29 lakh+ outlets across 28 states, the deal supports Findi’s strategy to expand digital banking services and white label ATMs, especially in rural and semi-urban regions.
- November 2024: TSI (India), a subsidiary of Australian digital payments and financial services provider Findi, signed an INR 330 Crore deal to acquire Tata Communications Payment Solutions Ltd. The acquisition includes 4,600 Indicash ATMs and a white label ATM platform, expanding TSI’s reach and supporting its transformation into a full-service payments bank targeting underbanked communities.
- September 2024: Axis Bank unveiled two digital solutions at the GFF event: UPI-ATM for cardless cash withdrawals and deposits using any UPI app, and Bharat Connect for Business, an integrated B2B platform for managing payables, receivables, and financing. Both offerings aim to enhance digital banking accessibility and efficiency.
- August 2024: NPCI launched UPI interoperable cash deposit services, enabling card-less deposits at ATMs into any bank account. At the Global Fintech Fest, RBI also rebranded Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) to Bharat Connect, while open architecture ATMs were introduced to function as digital banking units with expanded services.
- April 2024: Hitachi Payment Services launched India’s first Upgradable ATM, convertible into a Cash Recycling Machine (CRM). Aligned with RBI’s UPI cash deposit push, the Make-in-India ATM enhances flexibility, reduces upgrade costs, and supports financial inclusion by enabling future cash deposit services at offsite locations across the country.
India ATM Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Solutions Covered |
|
| Screen Sizes Covered | 15" and Below, Above 15" |
| Applications Covered | Withdrawals, Transfers, Deposits |
| ATM Types Covered | Conventional/Bank ATMs, Brown Label ATMs, White Label ATMs, Smart ATMs, Cash Dispensers |
| Regions Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East and Northeast India |
| Companies Covered | Euronet Worldwide, Inc., Hitachi Ltd., Diebold Nixdorf, Incorporated, NCR Atleos Corporation, AGS Transact Technologies Ltd., Vortex Engineering Private Limited, ETSOL WATER SOLUTIONS PVT. LTD., Tata Communications Payment Solutions Limited, Brinks India Private Limited, Hyosung India Private Limited, FIS Solutions Software India Private Limited, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the India ATM market from 2019-2033.
- The India ATM market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the India ATM industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India ATM market was valued at USD 1.82 Billion in 2024.
Persistent reliance on cash in rural and semi-urban areas, government-led financial inclusion initiatives, technological advancements in ATMs, urbanization, and regulatory support for white-label and off-site ATMs are driving the growth of the India ATM market.
The India ATM market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.80% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 3.45 Billion by 2033.
Deployment solutions accounted for the largest India ATM segment market share in 2024, holding around 54.3% of the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












