
E-Waste Management Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Material Type, Source Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
E-Waste Management Market Size and Share:
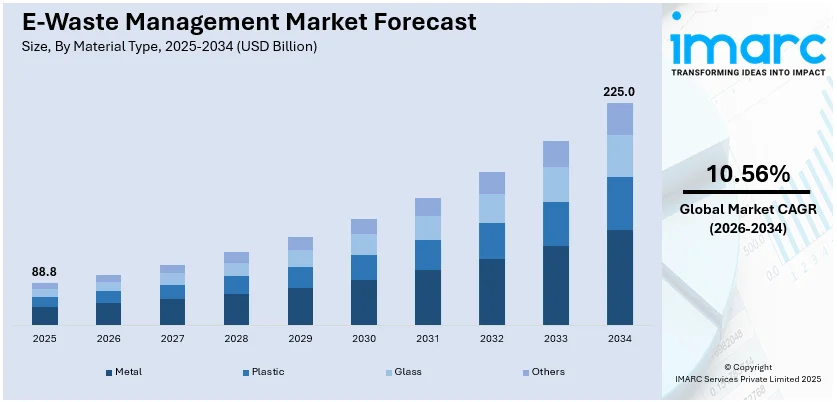
The global e-waste management market size was valued at USD 88.8 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 225.0 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 10.56% during 2026-2034. Asia Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of over 47.8% in 2025. The significant investments in recycling infrastructure, growing research and development activities, increasing number of key players seeking environmental certifications, and growing awareness about the importance of e-waste disposal are some of the factors propelling the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 88.8 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 225.0 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 10.56% |
Numerous vital factors propel the global e-waste management industry, which are also indicative of the increasing environmental and economic worries about electronic waste. One of the major trends is the rapid growth of consumer electronics such as computers, cell phones, and household appliances fueled by increasing consumer demand and technological progress. Gitnux expected global consumer electronics to reach an all-time high of around USD 1.5 trillion in 2024. As individuals increase their consumption of electronics, the product life is eventually shortened and hence produce more e-waste. In addition to this, this market is impacted significantly by stringent regulations imposed on the recycling and disposal of electronic trash by laws such as the Basel Convention and the WEEE Directive.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The United States has emerged as a key regional market for e-waste management. Key factors driving the United States e-waste management market include consumers' awareness toward electronics products, latest technologies in practice, and an increase in awareness over health and environmental issues. With the arrival of latest technology products, older ones form a substantial amount of e-waste. State-level regulatory rules regarding e-waste recycling and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) promote proper end-of-life management of this waste stream among producers as well as consumers. Similarly, corporate sustainability initiatives are pertinent as companies are in search of minimizing their environmental footprint with an adherence to ESG regulation. The financial worth of e-waste and the precious metals, such as gold, silver, and rare earth elements, has also motivated the search for advanced recycling methods.
E-Waste Management Market Trends:
Rapid Technological Advancements
Newer and latest electronic devices dominate the market, which eventually makes the older ones obsolete. This process is popularly known as "planned obsolescence," which keeps driving consumers to upgrade their electronic devices from time to time, which leads to continuous generation of e-waste. Shorter lifecycles of electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets result in frequent disposal of such products and thus contribute to e-waste. A recent study survey found that TVs have the longest expected lifespan of any consumer tech product at 6.5 years, followed by desktop computers (5.7 years), multi-function printers (5.6 years), and smartphones (4.8 years). Although today, TVs currently possess the longest expected life span, their lifetime has decreased significantly. Features in the new technology along with high performance propel individuals to discard their old devices and acquire new ones. That results in a huge percentage of electronic waste.
Growing Environmental Concerns
The world’s generation of electronic waste is rising five times faster than documented e-waste recycling, the UN’s fourth Global E-waste Monitor (GEM) revealed recently. A record 62 million tonnes (Mt) of e-waste was produced in 2022, Up 82% from 2010; On track to rise another 32%, to 82 million tonnes, in 2030; Billions of dollars’ worth of strategically valuable resources squandered, dumped; Just 1% of rare earth element demand is met by e-waste recycling. As consumers and businesses become more conscious of the ecological consequences of improper electronic waste disposal, they are seeking responsible and sustainable solutions. E-waste contains hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and flame retardants. When improperly disposed of in landfills or incinerated, these substances can leach into soil and water sources, posing serious health and environmental risks. Concerns about soil contamination, water pollution, and air quality degradation are driving individuals and organizations to opt for safe and eco-friendly e-waste management practices. Governments worldwide have implemented regulations and directives to ensure the proper disposal and recycling of e-waste. These regulations create a legal framework that enforces responsible management practices and encourages compliance.
Resource Scarcity
Electronic devices contain a wealth of valuable resources, including precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, as well as critical minerals and rare earth elements. As the demand for these resources continues to rise due to their use in various industries, there is a growing interest in recycling and recovering them from e-waste. According to an industrial report, recycling rates globally are low. Even in the EU, which leads the world in e-waste recycling, just 35% of e-waste is officially reported as properly collected and recycled. Globally, the average is 20%; the remaining 80% is undocumented, with much ending up buried under the ground for centuries as landfill. Recycling e-waste conserves these finite resources and reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional mining and extraction processes. The circular economy concept, which promotes recycling and reusing materials, has gained momentum, further emphasizing the importance of resource recovery from e-waste. This shift toward a more sustainable and resource-efficient approach is driving investment in e-waste recycling technologies and contributing to the expansion of the market.
E-Waste Management Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market report, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on material type, source type and application.
Analysis by Material Type:
- Metal
- Plastic
- Glass
- Others
Metal leads the market with around 62% of market share in 2025. Electronic devices, starting from cell phones to computer systems and household appliances contain a significant amount of valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, and palladium. They are used in parts like circuit boards, connectors, and wiring. These materials are an essential resource to the electronics industry. But in addition to this is the economic motivation to recycle and recover these metals. With increasing demand for these materials across the globe, recycling e-waste is more efficient and less expensive than conventional mining and extraction. For both companies and e-waste management firms, this provides a strong financial incentive to focus on metal recovery. In many cases, metals are also less environmentally hazardous than other e-waste materials, such as chemicals or plastics. This diminishes resistance as well as regulatory burdens associated with the recycling and recovery of metals from e-waste.
Analysis by Source Type:
- Consumer Electronics
- Industrial Electronics
- Others
Consumer electronics leads the market in 2025. Consumer electronics are diverse devices such as mobile phones, tablets, laptops, television sets, and household appliances. They are widespread in the homes worldwide, and technological developments in these devices creates frequent replacements of older devices; thus, there is a high and constant flow of e-waste. In addition to this, consumer electronics tend to have shorter lifecycles than many other sources of e-waste, mainly because of shifts in consumer preferences, design trends, and technological advancement. To get the latest features, improved performance, and aesthetic appeal, the consumer tends to discard their older devices for newer ones and thereby contributes to the huge volume of e-wastes generated. Furthermore, consumer electronics are relatively small in size and portable. Therefore, they are very accessible and convenient for consumers to dispose of, resulting in a high turnover rate in this category.
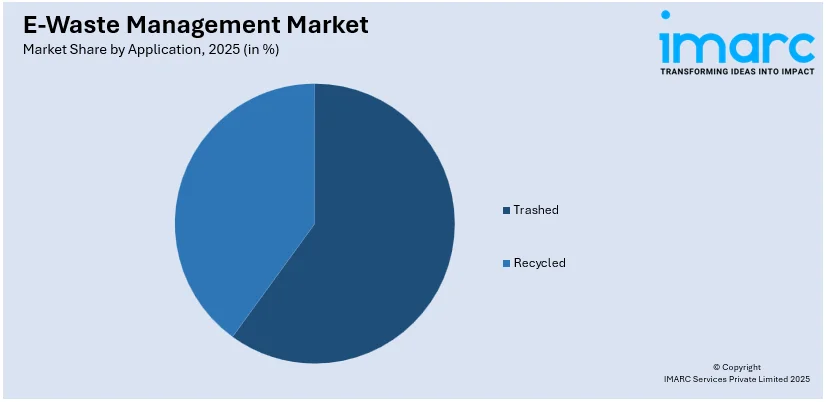
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Trashed
- Recycled
Trashed leads the market with around 52.7% of market share in 2025. As technology advances rapidly, many electronic devices become outdated, malfunction, or experience technical failures. Consumers and businesses alike often perceive repairing these devices as less cost-effective than replacing them with newer models. Consequently, a significant portion of electronic equipment ends up being classified as "trashed" rather than being refurbished or recycled. Additionally, there is a lack of awareness and accessibility to repair and refurbishment services, especially for older or less common electronic products. This limitation further contributes to the accumulation of trashed electronic equipment. Moreover, the disposable culture surrounding electronics, coupled with planned obsolescence by manufacturers, encourages consumers to discard their old devices in favour of newer ones, adding to the "trashed" category. This trend creates a substantial volume of electronic waste, emphasizing the need for effective e-waste management strategies to address the environmental and resource implications associated with this segment.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
In 2025, Asia Pacific accounted for the largest market share of over 47.8%. The region is home to some of the world's most populous countries, including China and India, where rapid economic growth and urbanization have led to a significant increase in the adoption of electronic devices. With a larger population, there is naturally a higher volume of electronic waste generated. Additionally, Asia Pacific is a major hub for electronics manufacturing, with many global technology companies having their production facilities in the region. This results in a concentration of electronic manufacturing waste, including defective components and obsolete products. Other than this, the regulatory landscape of the region for e-waste management has been evolving, with several countries in Asia Pacific introducing or strengthening regulations to address the growing e-waste problem. These regulations have encouraged the development of a formal e-waste management industry in the region. Moreover, the increasing awareness about environmental and health hazards associated with improper e-waste disposal is driving both individuals and businesses in Asia Pacific to seek responsible e-waste management solutions.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States E- Waste Management Market Analysis
In 2025, the United States accounts for over 78% of the e-waste management market in North America. The e-waste management market is on the increase in the United States, given the high level of electronic consumption coupled with stiff environmental regulations. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the U.S. had generated more than 6.9 million tons of e-waste by 2022 and is projected to reach 9 million tons by 2030. EPA, an arm of the government, has managed initiatives such as the National Strategy for Electronics Stewardship, encouraging recycling and safe disposal of e-waste. The EPA estimated that the recycling rate of e-waste in the U.S. was about 15% in 2023; this offers a significant yet still untapped potential in recycling infrastructure. California has already incorporated EPRs into their state regulatory framework, providing for the manufacturers' responsibility for managing the end-of-life recycling of their products.
Europe E- Waste Management Market Analysis
The WEEE Directive of the European Union regulates the electronic waste management structure in Europe. It requires recycling and decreasing e-waste. In 2022, Europe produced 13.1 million metric tons of e-waste, which equals 30% of the global production- as reported by the United Nations University (UNU). According to the EU legislations, the body aims at recycling 65% of e-waste during 2025, strung further along other sustainability objectives. European Commission believes that Germany, France, the UK, and others already implemented circular e-waste recycling programs properly. However, with regard to the implementation of circular economy models in the European marketplace and its promotion to revisit products with a view to reusing and repairing products, the demand for those solutions in e-waste management goes up.
Asia Pacific E-Waste Management Market Analysis
Asia Pacific is presently the most rapidly growing market for e-waste management, primarily driven by rapid urbanization, increased consumption of electronics, and a large population base. As per the United Nations University (UNU), this region accounted for more than 50% of global e-waste generation in 2022, with China, India, and Japan in pole position. According to UNU, China alone produced more than 4.2 million tons of e-wastes in 2022 and will increase up to 7 million tons by 2030. According to the government of China, second-hand electronics and mobilization on recycling efforts open further opportunities to manage e-wastes. The government would also push for stricter enforcement of its new e-waste rules regarding improper disposal and whether recycling rates are improved, according to India's Ministry of Environment.
Latin America E-Waste Management Market Analysis
Although it is still in its nascent stages, the e-waste management market in Latin America is showing good potential, driven largely by the increasing generation of e-waste and government initiatives. Latin America had generated around 2 million tons of e-waste in 2022, while the largest contributors were Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina, according to the United Nations University. For instance, in Brazil, 1.5 million tonnes of e-waste were generated in 2022. Moreover, the National Solid Waste Policy of the country has now ordered that e-waste be recycled, and the Association of Electronic Recycling revealed that a very low recycling rate of about 3% of the e-waste properly recycled is indicated for this region. An important implication of this is the availability of several opportunities to improve infrastructure and awareness.
Middle East and Africa E-Waste Management Market Analysis
A key driver of the e-waste management market in the Middle East and Africa is the increasing use of electronic appliances, increasing urbanization, and government support towards sustainability. The United Nations University approximately puts that the region generated 1.5 million tons of e-waste in 2022 and projected to stand at 3 million tons by 2030. According to UAE Vision 2021, the UAE and South Africa are spearheading this project through the governments' initiatives and rising investments in e-waste recycling infrastructure. Electronic waste, mainly created by inappropriate disposal, is on an increasing trend, thus driving up demand for better recycling programs. According to South Africa’s Department of Environmental Affairs, the country is encouraging private and public-sector partnerships to handle e-waste efficiently, addressing environmental hazards associated with improper disposal.
Competitive Landscape:
Major players are investing significantly in recycling infrastructure. They establish state-of-the-art recycling facilities equipped with advanced technologies to efficiently process electronic waste. These investments enable the recovery of valuable materials from e-waste, reducing the need for raw material extraction and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, leading companies in the industry are expanding their operations globally. They establish a presence in regions with significant e-waste generation, such as Asia and Africa, to meet the growing demand for responsible e-waste management services. This global expansion allows them to tap into emerging markets and offer their expertise in handling electronic waste. Other than this, key players are actively engaged in research and development efforts to improve e-waste recycling technologies. They focus on developing innovative methods for recovering valuable metals, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental harm. These advancements not only enhance their competitive edge but also contribute to the industry's overall sustainability. Besides this, the leading companies collaborate with electronic device manufacturers to establish take-back programs and responsible disposal solutions. These partnerships promote the collection and recycling of electronic products at the end of their lifecycles, ensuring that e-waste is managed effectively and in compliance with regulations.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the e-waste management market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Aurubis AG
- Boliden AB
- Desco Electronic Recyclers CC
- Electronic Recyclers International Inc.
- MBA Polymers Inc.
- Sembcorp Industries
- Sims Lifecycle Services Inc.
- Stena Metall AB
- Tetronics Technologies Ltd.
- Umicore N.V.
- Veolia Environnement S.A.
- WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
Latest News and Developments:
- November 2024: Sembcorp announced that they’ve agreed to sell their waste and recycling assets, including Sembcorp Environment Pte. Ltd., to Indonesia-based TBS Investment as the group continues to realign its focus on energy. The transaction will be valued at USD 302.5 million, a 43% premium over its book value as of mid-2024.
- August 2024: Desco Electronic Recyclers announced that they have collaborated with the E-waste Recycling Authority (ERA) and Makro to create the 'eWaste Bins' initiative that supports improving e-waste disposal practices. In the program, recycling bins will be located in most Makro stores countrywide, allowing easier access for consumers to deposit their electronic waste, including handsets, laptops, and batteries. This convenient location strategy helps counter the usual barrier of long-distance travel for recycling, thereby increasing participation rates in e-waste management.
- January 2024: Stena Metall announced the launch of Stena Confidential, a new company providing secure, traceable, and circular services. With a focus on data security and compliance, it partners with Stena Recycling to meet the growing demands for secure e-waste management, with responsible recycling and data destruction across multiple markets.
- January 2024: Sims Lifecycle Services, a subsidiary of Sims Ltd, has teamed up with start-up MOLG to automate the repurposing of Open Compute Project (OCP)-compliant data center equipment. The concept behind OCP-compliant data centers is to be modular and scalable while using open standards and simplification designs that make its installation, repairing, and disassembly much quicker. This partnership will look to streamline e-waste management by recycling and repurposing data center hardware.
- November 2023: Veolia, the environment services leader, announced the worldwide deployment of a digital solution based on artificial intelligence in its e-waste management. In some of its digital solutions, the company focuses on the optimization of waste and e-waste management with an intelligent monitoring system. An example would be the waste-to-energy plants in France, which would achieve 90% waste characterization, improving waste recovery.
E-Waste Management Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Material Types Covered | Metal, Plastic, Glass, Others |
| Source Types Covered | Consumer Electronics, Industrial Electronics, Others |
| Applications Covered | Trashed, Recycled |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Aurubis AG, Boliden AB, Desco Electronic Recyclers CC, Electronic Recyclers International Inc., MBA Polymers Inc., Sembcorp Industries, Sims Lifecycle Services Inc., Stena Metall AB, Tetronics Technologies Ltd., Umicore N.V., Veolia Environnement S.A., WM Intellectual Property Holdings L.L.C, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the e-waste management market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global e-waste management market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyse the level of competition within the e-waste management industry and its attractiveness.
- The competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The process of gathering, recycling, repairing, and appropriately discarding used electronic equipment and parts is known as e-waste management. In order to promote sustainability and resource efficiency, it seeks to reduce the risks to the environment and human health posed by harmful compounds found in e-waste while recovering valuable materials for reuse, such as metals and plastics.
The e-waste management market was valued at USD 88.8 Billion in 2025.
IMARC estimates the global e-waste management market to exhibit a CAGR of 10.56% during 2026-2034.
The significant technological advancements, stringent government regulations promoting sustainable waste disposal, increasing awareness about the environmental and health impacts of e-waste are some of the factors driving the e-waste management market.
According to the report, metal represented the largest segment by material type, driven by its high economic value, driven by the recovery of precious and rare metals like gold, silver, copper, and palladium from electronic components.
Consumer electronics lead the market by source type owing to their high turnover rate, frequent upgrades, and short product lifecycles, leading to a significant volume of discarded devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
Trashed is the leading segment by application, driven by the lack of efficient recycling infrastructure, high costs associated with proper e-waste processing, and limited consumer awareness about recycling options.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa, wherein Asia Pacific currently dominates the global market.
Some of the major players in the global e-waste management market include Aurubis AG, Boliden AB, Desco Electronic Recyclers CC, Electronic Recyclers International Inc., MBA Polymers Inc., Sembcorp Industries, Sims Lifecycle Services Inc., Stena Metall AB, Tetronics Technologies Ltd., Umicore N.V., Veolia Environnement S.A., WM Intellectual Property Holdings L.L.C, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












