
Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Type, Application, End Use, and Region, 2025-2033
Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Size and Share:
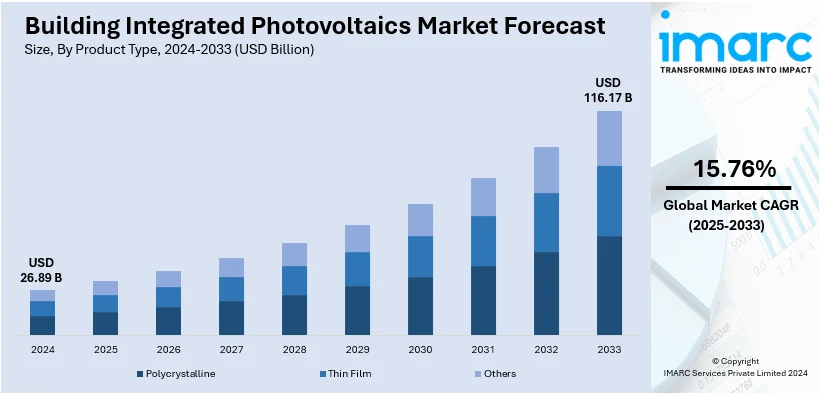
The global building integrated photovoltaics market size reached USD 26.89 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 116.17 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 15.76% during 2025-2033. Europe currently dominates the market, holding a market share of over 40.25% in 2024. Rapid technological advancements resulting in improved photovoltaic (PV) materials and favorable government support encouraging widespread product adoption are driving the market demand. In addition to this, the rise in green building practices is expected to create opportunities for the market growth.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033 |
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 26.89 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 116.17 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 15.76% |
The market for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) is fueled by the rising global preference for renewable energy sources and the increasing awareness of sustainable construction practices. Governments in various countries across the globe are encouraging BIPV systems among households and companies by providing incentives, and subsidies, and imposing strict energy efficiency regulations. The advancement of technology and efficiency improvements in solar panels as well as improved aesthetic integration have made BIPVs much more appealing in contemporary architecture. Moreover, rapid urbanization and the need for energy-efficient buildings are contributing to the market growth. BIPV has two functions - serving as a part of the overall structure in reducing overall construction and operational costs while also generating electricity. Furthermore, the focus on reducing carbon footprints and achieving net-zero energy goals in commercial as well as residential sectors drives the demand for BIPV solutions. These factors are significantly contributing to the growth of the building integrated photovoltaics market share on a global scale.
In the United States, the market is propelled by federal incentives like tax credits under the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), state-level renewable energy mandates, and green building certifications such as LEED. The rising demand for sustainable construction and energy-efficient buildings aligns with corporate sustainability goals. For instance, in June 2024, an international alliance of world-leading green building rating system organizations declared the launch of the novel global realistic guide to assist the $35 trillion investment required by 2030 to achieve global energy transition goals. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has cautioned that since buildings represent more than 30% of worldwide energy consumption and over 25% of emissions, many current structures will remain in 2050, requiring significant capital investments for sustainable upgrades to achieve climate goals. Advances in technology in solar panels and their materials have raised the level of integration and efficiency thus encouraging even wider adoption. The rapidly increasing urbanization and the development of smart cities, create possibilities for BIPVs in both commercial and industrial areas. Also, with increasing awareness about climate change and carbon reduction goals, a rise in electricity prices additionally fuels the demand for BIPV systems.
Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Trends:
Favorable Governmental Regulations
Governments across the world are increasingly recognizing the significance of renewable energy sources in coping with the effects of climate change and therefore, have implemented various initiatives to encourage their adoption. Incentives like tax exemptions, subsidies, or feed-in tariffs are frequently used in these initiatives. For example, feed-in tariffs give investors in BIPV a steady and predictable income stream by guaranteeing a specific amount for electricity produced from renewable sources. The French government provides a high feed-in tariff for electricity produced by buildings equipped with solar components. Additionally, in countries like India, the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana was approved by the government in February 2024 with the goal of increasing rooftop solar capacity and enabling residential homes to produce their own electricity. The plan will be implemented until FY 2026–2027 and has an expenditure of INR 75,021 crore (USD 8.86 Billion). Furthermore, some governments have set regulatory mandates requiring new buildings or renovations to incorporate energy-saving designs, which often include BIPV systems. These government initiatives are playing a crucial role in accelerating the building integrated photovoltaics market growth.
Technological Advancements Leading to Widespread Adoption
In the BIPV industry, technology is always developing to improve photovoltaic materials' efficiency and attractiveness. For example, the development of thin-film PVs, which are lighter and more flexible as compared to traditional silicon panels, are creating novel opportunities for BIPV applications. Similarly, innovations in solar cell design are leading to the development of colored and semi-transparent solar panels, which enables architects to integrate solar technology into building designs without negotiating aesthetics. In addition to this, there is ongoing research to improve the energy conversion efficiency of photovoltaic materials, which is projected to enhance the output of BIPV systems, thereby offering a favorable building integrated photovoltaics market outlook. According to an industrial report, global solar manufacturing capacity is expected to surpass 1,100 GW by the end of 2024, significantly surpassing the demand for photovoltaic panels. The industry had tremendous expansion in 2023, with the capacity of solar cells, wafers, and modules almost doubling from the last year.
Growing Green Building Practices
The use of sustainable and green building techniques is becoming more popular. Key building certifications, such as Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) and Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) award points are offered with the aim of encouraging the integration of renewable energy systems, including BIPV. These certifications are often pursued by developers to improve a building's marketability. Additionally, a growing number of businesses are opting to 'go green' to improve their corporate social responsibility profiles as societal concerns and awareness about climate change expand. This trend towards green buildings is boosting the building integrated photovoltaics market demand. Additionally, BIPV systems can substantially diminish a building's energy prices. By producing power on-site, they decrease the demand for overpriced grid electricity. They also save energy by lowering cooling expenses and enhancing the building's thermal insulation. Industry reports claims that green buildings can reduce emissions by 35% and maintenance expenses by 20%.
Building Integrated Photovoltaics Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global building integrated photovoltaics market report, along with forecasts at the global and regional levels from 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product type, application, and end use.
Analysis by Product Type:
- Polycrystalline
- Thin Film
- Others
Polycrystalline BIPV leads the market with around 68.9% of market share in 2024. Polycrystalline, or multi-crystalline silicon/poly-silicon, is extensively employed in building-integrated photovoltaics. Since polycrystalline PV is generally less expensive to produce than single-crystal PVs, polycrystalline PVs are typically much more economical, especially for large installations. The polycrystalline solar cell manufacturing process is much less energy-intensive and wasteful than that of monocrystalline cells. Additionally, as polycrystalline panels have relatively better heat tolerance as compared to monocrystalline panels, they do not decay as quickly in high temperatures, which can be beneficial in humid climates.
In recent years, other types of solar technology, such as thin-film and perovskite solar cells, have also obtained traction for their utilization in BIPV applications due to their elasticity and appealing characteristics.
Analysis by Application:
- Roof
- Facades
- Glass
- Others
Roof lead the market with around 44.7% of market share in 2024. BIPVs are most frequently employed on roofs because they receive the most direct and unhindered exposure to sunlight, especially in high-rise structures. They are the proper place for photovoltaic systems needing the sun to produce power efficiently. Additionally, BIPV systems can be incorporated into roofing materials during renovation or construction, taking the place of traditional options. This helps in generating electricity but also provides weatherproofing and can enhance the building's aesthetic appeal. Thus, installing BIPVs on the roof is easy and less disruptive to the building and the residents. Rooftop integrated photovoltaics also help to build energy efficiency within a structure. They serve shading purposes and thus reduce cooling loads, imparting some measure of thermal insulation as well.
Analysis by End Use:
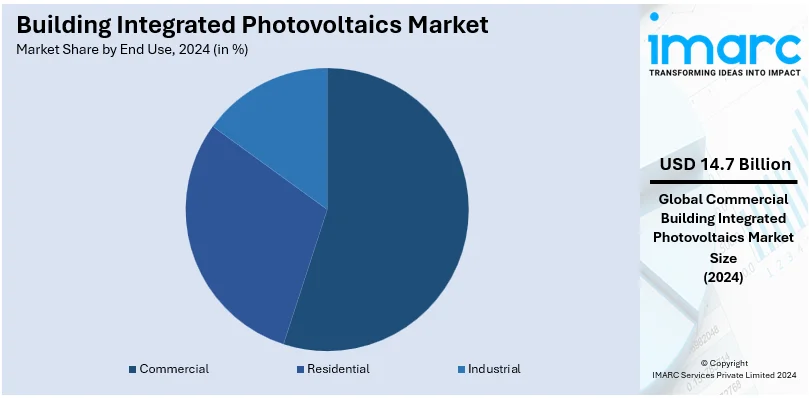
- Commercial
- Residential
- Industrial
Commercial leads the market with around 54.5% of market share in 2024. In the commercial sector, BIPV has been widely adopted. Compared to residential buildings, commercial buildings typically have larger facades and roof areas, which gives plenty of room for BIPV system installation. These buildings also have higher energy utilization during daylight hours, which corresponds with the electricity creation from BIPV systems. This orientation permits for more effective usage of the produced electricity, lowering dependence on the grid and resulting into significant cost savings. Furthermore, a lot of organizations and businesses are implementing sustainability goals as a component of their CSR campaigns. Implementing BIPV helps them to lower their carbon footprint and demonstrate their commitment to renewable energy and sustainable practices.
Regional Analysis:
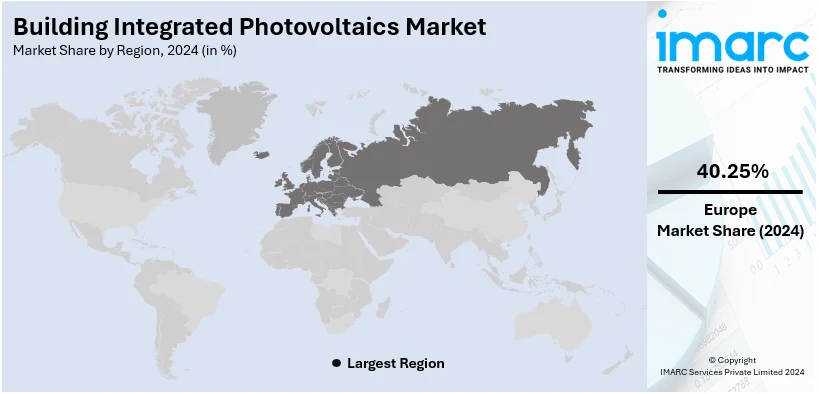
- Europe
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
- Latin America
In 2024, Europe accounted for the largest building integrated photovoltaics market share of 40.25%. The market in Europe is propelled by a strong regulatory framework that promotes the utilization of renewable energy sources. Incentives, such as feed-in tariffs and tax credit grant schemes are provided by many European countries, as well as provisions for encouraging renewable energy use. Europe is the major actor in the fight against climate change and committed reductions of GHG under the Paris Agreement (2015), spurring even more movement towards renewable energy sources such as BIPV. Additionally, Europe has many companies in the BIPV market that are at the forefront of technological innovations in this domain. The existence of these companies and the robust research and development (R&D) capabilities are driving the BIPV market growth across Europe.
Key Regional Takeaways:
North America Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Analysis
The market in North America is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy solutions, government incentives, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and state-level renewable portfolio standards. Energy-efficient building codes and certifications, such as LEED, encourage adoption in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Technological advancements in solar materials and designs enhance BIPV performance and aesthetic integration, making them appealing to modern architecture. Rising energy costs and the push for carbon neutrality by corporations and governments also play a significant role. Additionally, urbanization, smart city projects, and a focus on sustainable infrastructure further boost the demand for BIPVs. For instance, in October 2024, Sustainable Buildings Canada (SBC) announced that Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) has chosen SBC to spearhead two important multi-year projects that greatly improve sustainability in Canada's built environment. Both new and existing affordable housing are the subject of these projects. For new construction, the Codes Acceleration Project will support Building Officials in accelerating the adoption of higher Tier Building Codes in several regions across the country. The goal of SBC's EnergySPRING initiative is to assist Ontario's Social Housing and Indigenous Communities in implementing deep-energy, scalable retrofits in their low-rise, multi-unit residential structures for present affordable housing. The growing consumer awareness about environmental benefits and long-term cost savings accelerates the market growth in the region.
United States Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Analysis
In 2024, the United States accounted for a market share of over 85.60%. The growing emphasis on sustainable building practices and the incorporation of renewable energy sources is propelling the BIPV industry in the United States. The Energy Independence and Security Act and numerous state-level renewable portfolio standards (RPS) have provided a supportive regulatory framework for solar systems, including BIPV. One important motivator is California's Title 24 regulations, which impose solar systems on newly constructed residential buildings.
In order to achieve net-zero energy targets, the business sector—in particular, big IT firms like Apple and Google—is implementing BIPV technologies. Due to advancements in solar technology, including flexible and transparent photovoltaic materials, BIPVs are now a practical and aesthetically pleasing option for urban construction. Adoption is further aided by government tax incentives such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which offers a 30% tax credit for solar setups. The demand for integrated energy solutions, such as BIPV, is anticipated to rise in response to the U.S. Department of Energy's goal of having 100% clean electricity by 2035. The market also gains from developments in energy storage, which make it possible to integrate BIPV with grid systems seamlessly and solve intermittency problems. In order to meet the demands of this developing industry, companies, such as Tesla, SunPower, and First Solar, are adding BIPV products to their portfolios.
Asia Pacific Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Analysis
The BIPV market in Asia-Pacific is expanding quickly because of supporting government policies, rising energy demand, and urbanisation. With significant expenditures in renewable energy projects, including BIPV installations in urban high-rise buildings, China is acting as the region leader. Another important element is Japan's emphasis on environmentally friendly building practices, which is fuelled by its Zero Energy Building (ZEB) program. Adoption of BIPV is being promoted by India's Smart Cities Mission and solar subsidies through programs like the PM-KUSUM initiative.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), despite making up 9% of the world's population, 6% of its GDP, and 5% of its energy demand, Southeast Asia only receives 2% of global renewable energy investment. Over the previous three years, the average annual energy investment was USD 72 billion. The IEA’s ‘Net Zero Emissions’ (NZE) scenario calls for USD 190 Billion in annual investment from 2026–2030. Southeast Asia's energy transitions depend heavily on foreign development funding and assistance. Launched in 2021 in Vietnam and Indonesia, the Just Energy Transition Partnerships (JETPs) offer a framework for raising money for clean energy investments and assisting in the phase-out of coal-fired power generation. A major milestone for the JETP was reached in November 2023 with the announcement of the Indonesia Comprehensive Investment and Policy Plan, which is anticipated to mobilise USD 97 Billion in the power industry. BIPV is becoming a more appealing choice for businesses and households in Australia because to rising electricity rates and government subsidies for solar systems. Additionally, the area gains from the cost-effective production of solar materials, especially in China, which reduces the barriers to entry for BIPV solutions.
Latin America Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Analysis
Growing awareness of renewable energy and the region's plentiful solar resources are driving the BIPV market in Latin America. According to IEA data, Brazil, Chile, Costa Rica, and Colombia are among the nearly half of the 33 Latin America and Caribbean (LAC) nations that have committed to achieving net zero emissions by 2050. To meet these targets, the average annual investment in clean energy for the 2026–2030 timeframe must rise from the previous decade, meaning that fossil fuel usage will peak during this decade. With the help of net metering laws and government incentives that make solar energy economically feasible, Brazil and Mexico are the countries with the highest adoption rates. Opportunities for BIPV installations in residential and commercial buildings are being created by the drive for sustainable building standards and rapid urbanisation. Furthermore, interest in self-sustaining energy systems, where BIPV is essential, is fuelled by concerns about energy reliability in nations like Argentina. Advanced photovoltaic technology adoption in the region is accelerated through partnerships with international solar enterprises.
Middle East and Africa Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Analysis
Growing investments in sustainable urban development projects and renewable energy are driving growth in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) BIPV market. The Middle East is aimed to take USD 75.63 Billion of investment in various renewable energy projects through to 2030. This is according to a new report released by the Energy Industries Council, one of the world's largest energy trade associations for corporations distributing goods and services to the energy businesses worldwide. Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates are major participants; projects like Masdar City in Abu Dhabi demonstrate how BIPV is incorporated into smart city plans. Africa's difficulties with electrification and dependence on off-grid alternatives encourage the use of BIPV, particularly in urban areas. Growth is being stimulated by government incentives and international cooperation, while regional issues are being addressed by developments in resilient PV materials made for harsh climates.
Competitive Landscape:
The key players in the global building integrated photovoltaics market are continuously innovating to further improve the energy conversion efficiency of their photovoltaic materials. Additionally, they have concentrated on improving the aesthetics and adaptability of photovoltaic materials, such as transparency, color, and size-customizable photovoltaic glass. Thin-film photovoltaic cells, which are more affordable, lighter, and more flexible than conventional silicon cells, are also being developed by market players. Several key players are offering complete BIPV solutions that are designed to integrate seamlessly with specific parts of a building. They have also developed software systems to optimize the generation, storage, and use of solar power. With the help of weather forecasts, these systems can forecast future energy output, manage energy distribution and storage to optimize efficiency, and track energy production in real-time.
The report has provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the global building integrated photovoltaics market. Detailed profiles of all major companies have also been provided. Some of the key players in the market include:
- Ankara Solar AS
- Ertex Solartechnik GmbH
- Viasolis
- Hanergy Holding Group Ltd.
- HermansTechniglaz
- ISSOL sa
- Sphelar Power Corporation
- Navitas Green Solutions Pvt. Ltd.
- NanoPV Solar Inc.
- Polysolar Ltd.
Recent Developments:
- January 2025: Researchers from Nagoya University introduced a novel building-integrated photovoltaic system integrating ventilated louvers for passive cooling and heat recovery. The system enhances solar panel efficiency while maintaining indoor temperature control without extra energy input. Numerical models showed it reduced energy consumption and improved heating efficiency, highlighting its sustainability potential.
- November 2024: GoodWe launched a residential solar carport featuring Polaris building-integrated PV panels, available in 4.8 kW and 8.0 kW variants for one or two vehicles. The carport combines a modular, lightweight design with wind resistance up to 240 km/h, offering efficiency and durability. Its bifacial TOPCon modules achieve 21.5% efficiency, highlighting innovation in residential solar solutions.
- October 2024: Trinasolar Evergreen, a building-integrated photovoltaic unit of Trina Solar, launched four new products for public, industrial, and infrastructure projects. These include solar tiles, industrial walls, PV noise barriers, and colored PV glass, all featuring TOPCon solar cell technology with up to 21.9% efficiency. The launch aligns with China’s green construction policies and aims to tap into the growing BIPV market.
- September 2024: Germany's Fraunhofer CSP announced the 'AluPV' project, a research collaboration on manufacturing processes and material optimization for building-integrated photovoltaics. The initiative involves partners like Baltic Renewable Partners and MN Metall, aiming to advance sustainable solar technology. The project will continue at Fraunhofer's Center for Silicon Photovoltaics until the end of 2025.
- August 2024: China’s largest port-based building-integrated photovoltaics project, a 7.3 MW system at Guangzhou’s Nansha Port, achieved full-capacity grid connection. Designed to generate 6.8 million kWh annually and reduce 4,338 tonnes of carbon emissions, it integrates advanced waterproofing and energy efficiency innovations. Plans include expanding to 20 MW of distributed photovoltaic capacity by year-end.
- October 2024: A new building-integrated photovoltaic system was devised by Chinese scientists that uses 30 mm of phase change material on each side of the wall.
- May 2024: A commercial partnership to develop and promote "Building Integrated Photovoltaics" (BIPV) was announced by YKK AP Inc. and Kandenko Co., Ltd.
- April 2023: Canadian solar company Mitrex plans to launch a 2.5 GW solar panel factory in the USA, with the final location declaration pending. The new facility will significantly expand its capacity, complementing its current 500 MW plant in Toronto. This development highlights Mitrex's commitment to advancing solar energy adoption and contributing to North America's clean energy goals.
- March 2023: Sphelar Power Corporation developed a Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) for evaluating the power generation capabilities of spherical solar cells (I-V characteristic measurement). The new standard will increase the use of spherical cells in BIPV and other commercial applications.
- October 2021: NanoPV announced that it would invest over $36 million to establish a production and distribution plant in Georgia, USA.
Building Integrated Photovoltaics Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered | Polycrystalline, Thin Film, Others |
| Applications Covered | Roof, Facades, Glass, Others |
| End Uses Covered | Commercial, Residential, Industrial |
| Regions Covered | Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa, Latin America |
| Companies Covered | Ankara Solar AS, Ertex Solartechnik GmbH, Hanergy Holding Group Ltd., HermansTechniglaz, ISSOL sa, Navitas Green Solutions Pvt. Ltd., NanoPV Solar Inc., Polysolar Ltd., Sphelar Power Corporation and VIASOLIS |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, building integrated photovoltaics market forecast, and dynamics of the market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global building integrated photovoltaics market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the building integrated photovoltaics industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) are solar panels seamlessly incorporated into building materials, such as roofs, walls, windows, or facades. They generate renewable energy while serving dual functions like insulation, weather protection, and aesthetics. BIPV systems enhance energy efficiency, reduce carbon footprints, and minimize the need for standalone solar installations.
The building integrated photovoltaics market was valued at USD 26.89 Billion in 2024.
IMARC estimates the global building integrated photovoltaics market to exhibit a CAGR of 15.76% during 2025-2033.
The key factors driving the building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) market are rising demand for renewable energy, government incentives, growing awareness of sustainable architecture, advancements in solar technologies, energy-efficient building regulations, and increasing urbanization. Aesthetic appeal, multifunctionality, and long-term cost savings further boost BIPV adoption in modern construction projects.
According to the report, polycrystalline represented the largest segment by type, due to its affordability, reliable energy efficiency, widespread availability, and suitability for diverse applications.
Roof leads the market by application as they offer ample sunlight exposure, easy integration, dual functionality, and significant energy generation potential.
Commercial is the leading segment by end use, due to high energy demands, cost-saving potential, sustainability goals, and larger installation spaces.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa, wherein Europe currently dominates the global market.
Some of the major players in the global building integrated photovoltaics market include Ankara Solar AS, Ertex Solartechnik GmbH, Hanergy Holding Group Ltd., HermansTechniglaz, ISSOL sa, Navitas Green Solutions Pvt. Ltd., NanoPV Solar Inc., Polysolar Ltd., Sphelar Power Corporation and VIASOLIS.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












