
Biosimilar Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Molecule, Indication, Manufacturing Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Biosimilar Market 2025, Size and Share:
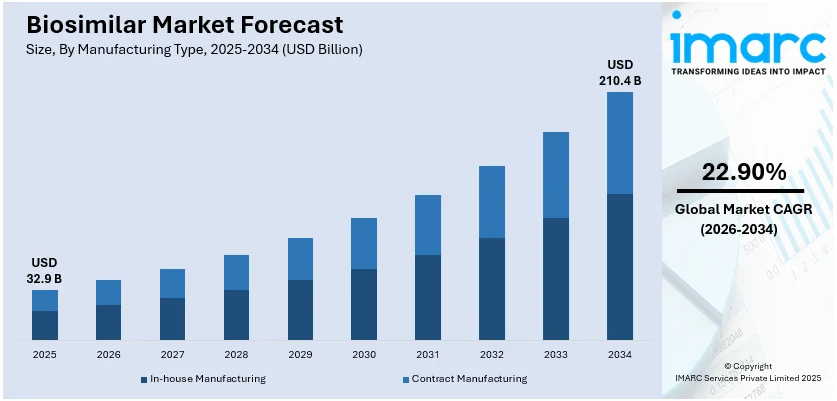
The global biosimilar market size was valued at USD 32.9 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 210.4 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 22.90% from 2026-2034. Europe currently dominates the market. The expiration of patents for major biological drugs, growing awareness about the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of biosimilars, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases worldwide, and continual advancements in biopharmaceutical manufacturing technologies are some of the major factors boosting the biosimilar market share.
Biosimilar Market Key Highlights:
- Rising global healthcare costs are driving demand for cost-effective treatment alternatives like biosimilars, as governments and healthcare providers seek affordable options to manage chronic diseases without compromising therapeutic efficacy or patient outcomes.
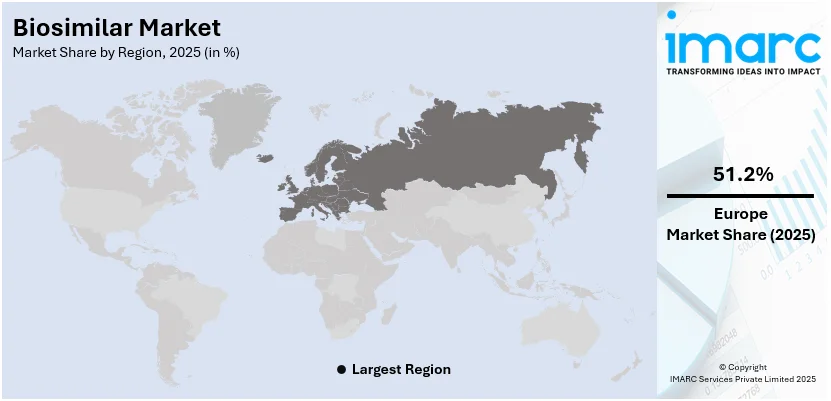
- In 2025, Europe leads the global biosimilar market due to supportive regulatory policies, high biosimilar adoption rates, and strong presence of key pharmaceutical companies driving growth.
- Infliximab dominates the biosimilar market in 2025 because of its widespread use in treating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease, ensuring strong market demand.
- Autoimmune diseases hold the largest biosimilar market share due to the rising prevalence of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel diseases demanding affordable treatment options.
- In-house manufacturing leads the biosimilar market as companies prefer full control over production processes, quality assurance, and cost-efficiency, ensuring regulatory compliance and competitive advantage.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 32.9 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 210.4 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 22.90% |
The global market is majorly driven by the increasing incidence rates of chronic and autoimmune diseases, wherein biosimilars act as the best alternative options for patients. In addition to this, standard approval from the regulatory frameworks motivates manufacturers to develop and market biosimilars. For example, on May 21, 2024, Biocon Biologics announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its biosimilar aflibercept, Yesafili. Yesafili, a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor, is approved for treating several ophthalmic conditions, including neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema. Moreover, advances in biotechnology and manufacturing have improved the production efficiency and quality of biosimilars, meeting high criteria for safety and efficacy. Besides this, increased awareness of healthcare providers and patients about the therapeutic equivalence of biosimilars to reference biologics assists in strengthening market acceptance globally.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The United States stands out as a key regional market and is witnessing significant growth due to the need for cost-efficient healthcare, as biosimilars are one of the options for lowering the high cost of biologic drugs. In line with this, the implementation of supportive policies, such as the biologics price competition and innovation act (BPCIA), encourages the approval of biosimilars, thereby impelling the biosimilar market growth. Moreover, the growing number of collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and healthcare providers and strategic acquisitions have strengthened distribution networks, ensuring broader patient access to these therapies. For instance, on January 22, 2024, Sandoz announced an agreement to acquire the U.S. biosimilar ranibizumab, CIMERLI® (ranibizumab-eqrn), from Coherus BioSciences for USD 170 Million. This acquisition includes a biologics license application, product inventory, and ophthalmology sales and field reimbursement talent, aims to strengthen Sandoz's ophthalmology portfolio in the U.S. market. Also, the continued growth portfolio of biosimilars in high-need therapy areas such as oncology and endocrinology accelerate the integration of biosimilars into the U.S. healthcare system and, consequently, drives the market forward.
Biosimilar Market Trends:
Increasing Patent Expirations of Blockbuster Biologics
The expiration of patents for important biological pharmaceuticals is a primary source of biosimilar market demand. Many blockbuster biologics that have proved critical in treating many chronic diseases are nearing the end of their patent protection. For instance, chronic diseases responsible for 75% of all global deaths are rapidly increasing, driving urgent healthcare concerns worldwide. According to industry reports, big pharmaceutical companies such as Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, and Johnson & Johnson face a looming threat that will put tens of billions of dollars in sales at risk between now and 2030, as key blockbuster drugs approach patent expiration. When the patents of one or more of a company's leading branded drugs have expired, it opens the door for competitors to sell copycats of those drugs, often at a lower price. This tends to render the revenue down for drugmakers and costs down for patients, who can access more affordable options. The increased competition will lead to reduced prices, which makes these vital treatments more accessible to a larger patient population, thus likely to fuel the biosimilar market revenue.
Growing Regulatory Support and Streamlined Approval Processes
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA have established robust frameworks and guidelines to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of biosimilars. These supportive regulatory environments facilitate the approval and market entry of biosimilars. For instance, in February 2024, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) proposed to waive comparative efficacy studies (CES) for biosimilars with a straightforward mechanism of action (MOA), such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins to decrease the number of human investigations required to compare a biosimilar medicine under development to the reference product. Clear regulatory pathways and streamlined approval processes enhance confidence among healthcare providers and patients, encouraging the adoption of biosimilars. According to the biosimilar market forecast, the ongoing efforts to educate stakeholders about the benefits and safety of biosimilars are projected to influence the market growth positively over the coming years.
Rising Healthcare Costs and Demand for Affordable Treatments
The increasing cost of healthcare, particularly in the management of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders, is raising the demand for cost-effective alternatives to expensive biologics. For instance, in a recent study conducted by the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGI), it was found that the cost of cancer treatment during outpatient department (OPD) consultations are substantially higher than the costs accrued during hospitalization. The study, which surveyed 9,787 patients from seven cancer hospitals in India to estimate out-of-pocket expenses, sheds light on the financial issues that cancer patients and their families confront. Diagnostics accounted for a substantial 36.4% of the total expenditure, with medicines making up an additional 28%. Biosimilars offer similar therapeutic benefits at a fraction of the cost, which makes them an attractive option for both healthcare providers and patients. The push for affordable healthcare solutions is further supported by governments and insurance companies seeking to manage healthcare expenditures without compromising on the quality of care.
Biosimilar Market Key Takeaways:
- In 2025, Europe accounted for the largest market share in the biosimilar market across the globe.
- By molecule, infliximab accounts for the largest market share in 2025.
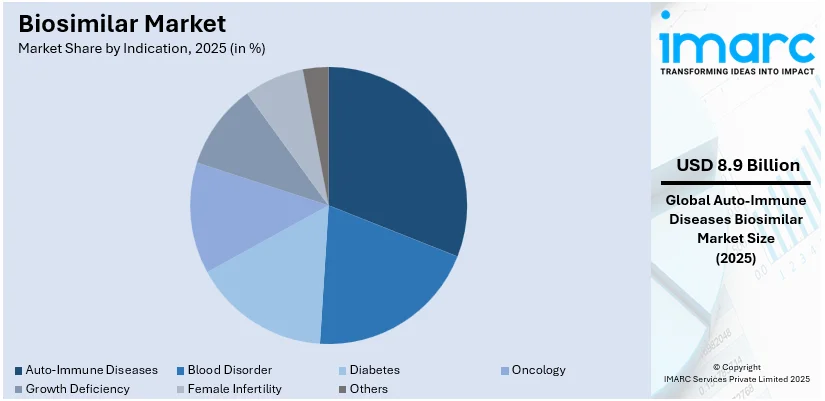
- By indication, auto-immune diseases lead the market share in 2025.
- By manufacturing type, in-house manufacturing accounts for the largest market share in 2025.
Market Dynamics:
Driver: Increased Accessibility and Cost Savings
Biosimilars offer a promising pathway to expanding access to advanced therapies for chronic diseases, including certain types of cancer. Their cost-effective production methods open doors for broader experimentation with pharmacological treatments. By reducing the financial strain of chronic illnesses on healthcare systems and improving access to high-quality drug therapies, biosimilars are positioned to drive substantial market growth. For this potential to materialize, physicians need greater confidence in prescribing biosimilars as alternatives to reference products, and the price gap between biosimilars and their original biologics must be significant.
Restraint: Complex Manufacturing and Analytical Processes
Biosimilar production presents unique challenges due to the intricate nature of large molecules and the rigorous requirements for demonstrating clinical safety. Differences in cell culture conditions can cause structural alterations, which may result in risks like contamination, the presence of viruses, or remnants of cell proteins and DNA. The limited availability of advanced analytical tools to accurately compare biosimilars with their reference biologics further complicates production. Together, these challenges create obstacles that hinder the growth of the biosimilar market size.
Opportunities: Technological Innovations
Advances in scientific research and technology have expedited the development of biosimilars, allowing for improvements to biologics introduced over a decade ago. Biosimilars are emerging as an important drug category, offering therapeutic options comparable to biologics in efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity, but at reduced costs. With patents on many biologics nearing expiration, the biosimilars market is set to grow as these cost-effective alternatives become more widely available. The streamlined clinical trial requirements for biosimilars, combined with their production in living cells, further support their market potential. Notably, CVS launched a new biosimilar brand in September 2023, signaling increasing investment in this space.
Biosimilar Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global biosimilar market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on molecule, indication, and manufacturing type.
Analysis by Molecule:
- Infliximab
- Insulin Glargine
- Epoetin Alfa
- Etanercept
- Filgrastim
- Somatropin
- Rituximab
- Follitropin Alfa
- Adalimumab
- Pegfilgrastim
- Trastuzumab
- Bevacizumab
- Others
Infliximab leads the market in 2025. Infliximab monoclonal antibody is used specifically in auto-immune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease. Infliximab ensures cost-efficient biological treatments due to the pressure by the healthcare systems to address the high costs of treatments. The patent expiration of Remicade, the original reference drug, raised the competition and led to the development and acceptance of infliximab biosimilars into the market. These products offer access to high-end therapies across a wide patient base in emerging markets, where the affordability issue is key. Furthermore, an expanding pipeline of biosimilars, support from the regulatory framework, and increasing acceptance among physicians enhance the adoption rate of infliximab biosimilars. The molecule possesses the potential to redefine treatment profiles by offering improved accessibility and cost reductions while promoting sustainable healthcare services, which is, therefore, a crucial growth driver for the market of biosimilars.
Analysis by Indication:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Auto-Immune Diseases
- Blood Disorder
- Diabetes
- Oncology
- Growth Deficiency
- Female Infertility
- Others
Auto-immune diseases lead the market in 2025. Autoimmune diseases are among the most prevalent diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. The demand for effective but affordable treatment options increased the adoption of biosimilars in autoimmune indications. These biosimilars, being much cheaper than biologics, render chronic diseases treatable. An increasing number of developers in the biosimilar space only heightened the competition level while reducing the costs of treatment. Advances in regulations and physician perception of biosimilars' efficacy and safety have fueled belief in biosimilars. Since most autoimmunity diseases are lifetime conditions, the affordability of biosimilars improves patient access and adherence considerably. This market segment shows the promise of biosimilars in addressing unmet medical needs while providing support for the economic sustainability of healthcare systems.
Analysis by Manufacturing Type:
- In-house Manufacturing
- Contract Manufacturing
In-house manufacturing leads the market in 2025. In-house manufacturing allows the company to have control over the quality, cost, and scalability of its production. This method of manufacturing enables biosimilar developers to streamline processes, maintain stringent quality standards, and respond quickly to market demands. Since the production of biosimilars is complex, maintaining consistency and efficacy for obtaining regulatory approval and competing well in the market is better ensured with in-house facilities equipped with advanced technologies. By reducing dependency on third-party manufacturers, companies can lower production costs, improve profit margins, and enable competitive pricing for biosimilars. In-house manufacturing also fosters innovation, which enables firms to refine processes and develop expertise that can be applied across their biosimilar portfolios. This method aligns with the industry's need to produce high-quality, affordable biologics at scale, which is driving adoption and expanding access to biosimilars worldwide.
Regional Analysis:
To get more information on the regional analysis of this market Request Sample
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- United Kingdom
- Rest of Europe
- United States
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of the World
In 2025, Europe accounted for the largest biosimilar market share. The region has a supportive regulatory environment, allowing several biosimilars to enter the European market before other regions. This early start enables Europe to gain a significant share of the market. Furthermore, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has been a forerunner in creating a clear and supportive regulatory framework for the approval of biosimilars since 2005, earlier than many other regions. This framework encourages the development and marketing of biosimilars in the region. Apart from this, the increasing awareness and acceptance of biosimilars among healthcare professionals and patients in Europe increases its uptake, which in turn is creating a positive market outlook across the region. For instance, in January 2024, Sandoz, the global leader in generic and biosimilar medicines, announced the launch of Tyruko® (natalizumab) in Germany on February 1. Tyruko®, developed by Polpharma Biologics, is the first and only biosimilar designed to treat RRMS.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Biosimilar Market Analysis
As per the biosimilar market trends, biosimilars are witnessing increased adoption in recent years, primarily driven by the expansion of healthcare investments. According to reports, the US accounts for about USD 4.3 Trillion of the USD 10 Trillion global healthcare expenditure, driving growing investments in healthcare. This trend is helping the biosimilar industry by increasing innovation and access. More funds are being invested in medical infrastructure and advanced treatments, such as biosimilars, which are more accessible and affordable. Biosimilars can be included in more healthcare funding lists of health systems, which would lower the cost burden of biologic therapies. This trend is apparent in the United States, as several healthcare systems are adapting to offer cheaper, rather than expensive, forms of biologics. The increase in government spending and private involvement via strategic partnerships creates a conducive environment for the application of biosimilars. These investments raise research and development (R&D) activities, consequently accelerating the entry of these biosimilars into the market. This has made more patients accessible to affordable therapies that were otherwise limited to traditional biologics, thus reinforcing the demand for biosimilars and enhancing healthcare outcomes.
Asia Pacific Biosimilar Market Analysis
According to the biosimilar market outlook, the rapid increase in diabetes cases across Asia-Pacific is a key factor fueling the rise in biosimilar adoption. According to WHO, approximately 77 Million adults in India suffer from type 2 diabetes, with nearly 25 Million others at high risk due to prediabetes. This growing prevalence underlines the need for effective diabetes management and prevention strategies. There is an increased demand for affordable treatments in the region due to several diabetes-related health issues. Biosimilars assist in overcoming this challenge as they can be sold at a relatively affordable price without compromising on quality treatment that branded drugs might inflict financially on patients. In countries with large diabetic populations, healthcare systems use biosimilars to reduce the economic burden that diabetes care imposes. These drugs, among others, provide alternatives to effective drugs that help them reduce financial pressures for patients and providers. As the regional healthcare system continues to emerge, biosimilars are likely take on a growing role in diabetes management to allow more patients to receive high-quality care.
Europe Biosimilar Market Analysis
The rising number of cancer cases in Europe is one of the major reasons for the increased use of biosimilars. Cancer fatalities climbed by 2.4% in 2022 compared to 2020, while new cancer cases grew by 2.3% to 2.74 million, according to figures from the European Commission in the European Cancer Information System (ECIS). The increasing incidence of cancer suggests that biosimilars may be a more cost-effective solution. As the number of cancer patients in the area rises, creative and affordable treatment becomes essential. Compared to original biologics, biosimilars are a practical way for patients to obtain biological therapies at a reduced cost. Patients can obtain biological therapies at a much lower cost using biosimilars, which are a good substitute for the original biologics. Cancer is among the most costly diseases for healthcare systems. In order to save costs without sacrificing the quality of available treatments, European healthcare systems are incorporating biosimilars into their medication regimens. The use of biosimilars in cancer treatment was also accepted and approved by regional authorities. Biosimilars are one of the most promising approaches for pushing clinical and economic challenges inflicted upon patients due to cancer.
Latin America Biosimilar Market Analysis
The growing pharmaceutical sector in Latin America plays a key role in driving the adoption of biosimilars in the region. Brazil ranks sixth in the world for medications and pharmaceuticals, according to the International Trade Administration, with a 26.2% rise in sales in 2022 over 2021. Because biosimilars provide more affordable treatment choices, this growth is encouraging their uptake. The industry's expansion is supporting the creation and accessibility of biosimilar treatments. Biosimilars are a cost-effective alternative to pricey biologic medications, making them a good therapeutic option for patients as well as healthcare professionals. Acknowledging the safety and effectiveness of biosimilars fosters clarity and trust, which also aids in overcoming early mistrust. The pharmaceutical business keeps expanding its range of biosimilars as market circumstances and regulatory frameworks evolve. As the health infrastructure in the region develops, biosimilars form an important part of the sustainable healthcare growth process.
Middle East and Africa Biosimilar Market Analysis
Government policies and measures to expand healthcare services in the Middle East and Africa are driving the biosimilars market. According to International Trade Administration, Saudi Arabia allocated 60% of the GCC's healthcare expenditure, and in 2023, it has budgeted for USD 50.4 Billion for healthcare and social development, which represents 16.96% of the national budget. The sector remains a key priority for the government. These regions try to bridge gaps in healthcare delivery and increase access to much-needed medicines while biosimilars provide cost-efficient treatment options for patients. Focuses on disease management are increased, with the rise of cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Biosimilars are seen as a solution to burdening healthcare funds. Favorable initiatives, regulatory support and international collaboration encourage healthcare providers to include biosimilars in their treatment protocols. As a result, biosimilars have become an essential element of healthcare programs focusing on expanding access of patients in the region to high-quality, inexpensive medications.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the global market is characterized by increasing demand for cost-effective alternatives to biologics. Regulatory frameworks in major countries such as the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific are being modified to encourage development and adoption while maintaining rigid safety and efficacy standards. This attracted a diverse range of players, from established pharmaceutical companies to specialized biotech firms, creating intense competition. Patent expirations of biologics, price pressures, and the need for affordable treatment options influence market dynamics. There is stiff competition, with a blend of traditional pharmaceutical firms and specialist biotechnology companies competing to obtain market share. These companies focus on developing biosimilars that would meet stringent regulatory requirements and also present cost-efficient healthcare systems. High technological expertise, distribution networks, and stakeholder education mainly determine success in the market.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the biosimilar market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Sandoz International GmbH
- Pfizer Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
- Celltrion Inc.
- Biocon Limited
- Samsung Biologics
- Amgen, Inc.
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited
- Stada Arzneimittel Ag.
Latest News and Developments:
- December 2024: Intas Pharmaceuticals, through its U.S. division Accord BioPharma, expanded its cancer therapy biosimilar portfolio by acquiring Coherus BioSciences' UDENYCA® business. UDENYCA® is the only biosimilar to Amgen’s NEULASTA® in the U.S., used to reduce infection risk after chemotherapy. This acquisition positions Accord for growth in the biosimilar sector. Additionally, Intas entered a global licensing agreement with Xbrane Biopharma to co-develop Xbrane's nivolumab biosimilar, aiming for a 2028 U.S. launch, enhancing access to cancer treatments and improving healthcare system efficiency.
- December 2024: Biocon Biologics received USFDA approval to launch its Stelara biosimilar by February 2025, targeting autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and plaque psoriasis. Despite facing competition from five other biosimilars, the launch is expected to significantly enhance Biocon's revenue and profitability. The move positions Biocon to capture a larger share of the growing biosimilars market, particularly in autoimmune treatments.
- May 2024: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Bkemv (eculizumab-aeeb), the first interchangeable biosimilar to Soliris (eculizumab), for treating rare diseases. Bkemv is approved for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) to reduce hemolysis and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) to inhibit thrombotic microangiopathy. This approval aims to expand access to effective treatments for individuals with rare life-threatening conditions.
- May 2024: Teva Pharmaceuticals, a U.S. affiliate of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Alvotech announced that SIMLANDI (adalimumab-ryvk) injectable is now available in the United States as an interchangeable biosimilar to Humira for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, adult rheumatoid arthritis, adult psoriatic arthritis, adult ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, adult ulcerative colitis, adult plaque psoriasis, adult hidradenitis suppurativa, and adult uveitis.
- May 2024: Celltrion USA announced that adalimumab-aaty, the company's high-concentration (100 mg/mL) and citrate-free formulation biosimilar to HUMIRA ® (adalimumab), is now available at a low wholesale acquisition cost (WAC). Adalimumab-aaty will be priced as a WAC list price at an 85% discount to the current WAC list price of HUMIRA. Celltrion USA is available under the brand name YUFLYMA,™ that launched in July 2023 and is available with a 5% discount from the current WAC list price of HUMIRA.
Biosimilar Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Molecules Covered | Infliximab, Insulin Glargine, Epoetin Alfa, Etanercept, Filgrastim, Somatropin, Rituximab, Follitropin Alfa, Adalimumab, Pegfilgrastim, Trastuzumab, Bevacizumab, Others |
| Indications Covered | Auto-Immune Diseases, Blood Disorders, Diabetes, Oncology, Growth Deficiency, Female Infertility, Others |
| Manufacturing Types Covered | In-house Manufacturing, Contract Manufacturing |
| Regions Covered | Europe |
| Countries Covered | Germany, France, Italy, Spain, United Kingdom, United States, Japan, India, South Korea, Rest of the World |
| Companies Covered | Sandoz International GmbH, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Limited, Celltrion Inc., Biocon Limited, Samsung Biologics, Amgen, Inc., Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited, Stada Arzneimittel Ag. etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the biosimilar market from 2020-2034.
- The biosimilar market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the biosimilar industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The biosimilar market size was valued at USD 32.9 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 210.4 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 22.90% from 2026-2034.
The global market is majorly driven by increasing healthcare costs, patent expirations of major biologics, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Growing demand for affordable treatment options and advancements in biotechnology further propel market growth.
Europe currently dominates the market, driven by its supportive regulatory environment, increasing awareness and acceptance of biosimilars among healthcare professionals and patients, and the rising number of cancer cases.
Some of the major players in the biosimilar market include Some of the major players in the global biosimilar market include Sandoz International GmbH, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Limited, Celltrion Inc., Biocon Limited, Samsung Biologics, Amgen, Inc., Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited, Stada Arzneimittel Ag., etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












