
Australia Warehousing and Storage Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type of Warehousing, Ownership, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Warehousing and Storage Market Size and Share:
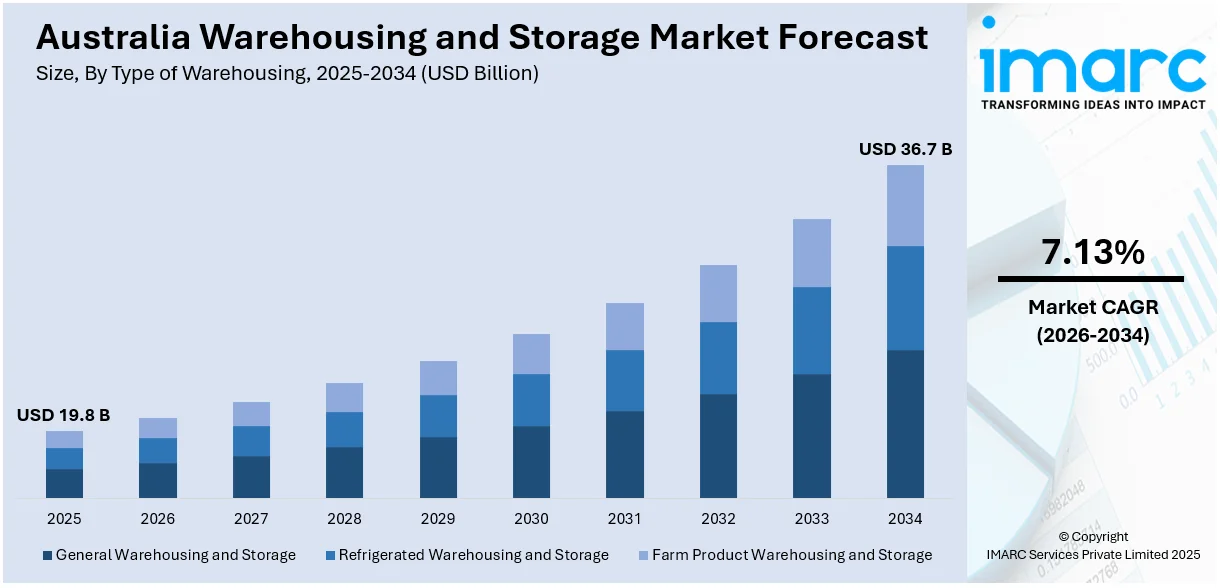
The Australia warehousing and storage market size was valued at USD 19.8 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 36.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.13% from 2026-2034. The rising e-commerce demand, fueling the need for fulfillment centers and automation, and infrastructure investments enhancing logistics efficiency. Additionally, growing cold storage requirements driven by pharmaceuticals and perishable goods, along with increased adoption of shared warehousing to reduce costs, thus increasing the Australia warehousing and storage market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 19.8 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 36.7 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 7.13% |
Expansion of e-commerce rapidly boosts the demand for advanced warehousing and storage in Australia. Fulfillment centers are the next investments being undertaken by retailers and logistics companies in order to enable last-mile delivery efficiency. As a result of increased online purchases, turnover increases, meaning more automated storage and real-time tracking of inventories. Increasing customer expectations regarding fast delivery are further prompting the creation of strategic, well-placed distribution hubs. Urban and regional warehouse expansions cater to omnichannel retail models, which enhance supply chain resilience. Growing adoption of warehouse robotics and AI-driven inventory management further strengthens operational efficiency in meeting the evolving Australia warehousing and storage market outlook.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Significant investment in infrastructure like road, rail, and ports upgrades the warehousing and storage facilities of Australia. Government-driven initiatives like Inland Rail boost connectivity in freight movement, and therefore, shortens transit time, which eventually helps optimize the efficiency of supply chain. Increasing volumes of trade have led to an increase in the construction of warehouses near major transport corridors. Industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing benefit from expanded smart logistics hubs with automated handling systems and cold storage facilities. Increased foreign direct investment in logistics real estate fuels the growth of large-scale distribution centers in Australia, further cementing it as a primary regional hub for storage and distribution.
Australia Warehousing and Storage Market Trends:
Automation and Smart Warehousing Adoption
The integration of automation and smart technologies is transforming Australia’s warehousing and storage market. Businesses are increasingly integrating robotics, AI-powered inventory management, and IoT-enabled tracking systems to boost operational efficiency. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic picking systems help mitigate workforce shortages while enhancing accuracy and speed. Cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) enable real-time data analytics, optimizing inventory control and order fulfillment. Moreover, AI-powered demand forecasting enables businesses to maintain optimal stock levels, lowering storage costs and reducing supply chain disruptions. The push for greater efficiency, coupled with rising labor costs, is accelerating the transition towards fully automated and data-driven warehousing solutions, enhancing competitiveness in a fast-evolving logistics landscape.
Expansion of Cold Storage Facilities
The growing need for temperature-controlled storage is fueling the expansion of cold chain warehousing in Australia. Growth in the pharmaceutical, perishable food, and online grocery sectors necessitates advanced refrigerated storage solutions. The increasing popularity of meal delivery services and fresh food e-commerce platforms further fuels investment in climate-controlled warehouses. Energy-efficient refrigeration technologies and solar-powered cold storage facilities are gaining traction to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Regulatory compliance with strict food safety and pharmaceutical storage standards also propels investments in high-tech monitoring systems for temperature and humidity control. As supply chains become more reliant on cold logistics, the market for specialized temperature-controlled warehousing continues to expand.
Growth of Multi-Client and Shared Warehousing
Companies are increasingly using multi-client and shared warehousing solutions to reduce costs and increase flexibility. Increasing real estate costs and volatile inventory levels force companies to opt for shared warehouse space, where multiple businesses use the same facility to store goods. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer scalable solutions that allow businesses to increase storage capacity as needed, minimizing capital investment. This trend favors small and medium enterprises (SMEs) who need affordable warehousing with no long-term agreements. Also, shared distribution centers facilitate the retail and manufacturing industry to rationalize their logistics so that the last-mile delivery is faster. Pay-per-use storage models are revolutionizing the way Australia warehouses and making it flexible to changes in the market.
Australia Warehousing and Storage Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Australia warehousing and storage market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on type of warehousing, ownership, and end use.
Analysis by Type of Warehousing:
- General Warehousing and Storage
- Refrigerated Warehousing and Storage
- Farm Product Warehousing and Storage
According to the Australia warehousing and storage market forecast, the general warehousing involves the storage of non-perishable goods, including retail inventory, industrial equipment, and consumer products. These facilities focus on inventory management, order fulfillment, and distribution. Increasing e-commerce activity and supply chain optimization drive demand, with automation and smart warehousing improving operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Concurrently, refrigerated warehousing specializes in temperature-controlled storage for perishable goods, including food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology products. These facilities ensure product integrity through advanced cooling, monitoring, and energy-efficient solutions. Growing demand for frozen and fresh food, along with stringent regulations for pharmaceutical storage, is fueling expansion in this sector.
Along with this, the farm product warehousing supports agricultural supply chains by storing grains, seeds, and other raw materials. These facilities safeguard crops against spoilage and pest damage through controlled environments and fumigation. Rising global food demand, advancements in storage technology, and government initiatives supporting food security are key drivers of this segment.
Analysis by Ownership:
- Private Warehouses
- Public Warehouses
- Bonded Warehouses
Privately owned warehouses are operated by businesses to store their own goods. They offer greater control over inventory, security, and operational efficiency. Common in manufacturing, retail, and e-commerce, these facilities are strategically located for supply chain optimization. Higher investment costs are offset by long-term savings and logistical advantages.
Public warehouses offer storage services to multiple businesses on a rental basis, providing flexible solutions without requiring significant capital investment. Equipped with advanced inventory management systems, these facilities accommodate seasonal demand fluctuations, support small businesses, and serve companies needing temporary or overflow storage capacity.
Moreover, bonded warehouses store imported goods before customs duties are paid, enabling businesses to defer taxes until the products are released for distribution. Used for international trade, these facilities are strictly regulated and often equipped with security measures. They support exporters, importers, and manufacturers dealing with high-value or duty-taxable goods like alcohol and tobacco.
Analysis by End Use:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
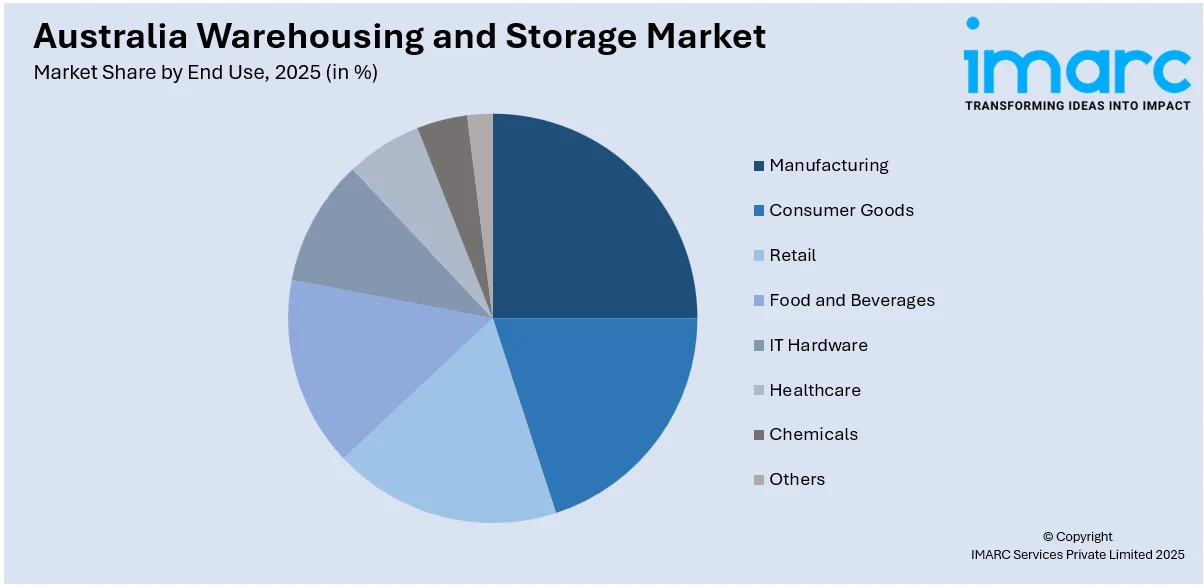
- Manufacturing
- Consumer Goods
- Retail
- Food and Beverage
- IT Hardware
- Healthcare
- Chemicals
- Others
Warehousing for manufacturing supports raw material storage, component handling, and finished goods distribution. Facilities often integrate automation, inventory management, and just-in-time delivery systems to optimize production efficiency. Growing domestic manufacturing and export activities drive demand for specialized storage, including bulk handling and climate-controlled environments for sensitive materials.
Similarly, high volume and efficient networks are the thrust of warehousing in consumer goods. E-commerce growth is leading to demand fulfillment centers with an advanced logistics ability. Rapid turnover of inventory, seasonal fluctuations of demand, and last-mile efficiency in delivery dictate the need for more investment in automated and strategically located warehouses.
Also, the retail warehousing supports both brick-and-mortar stores and online shopping. Distribution centers prioritize quick order fulfillment, inventory visibility, and efficient logistics to meet consumer expectations. The rise of omnichannel retailing is increasing demand for flexible storage solutions, urban warehouses, and last-mile delivery hubs to ensure faster product availability.
Besides this, the warehousing for food and beverage requires specialized facilities, including refrigerated and frozen storage for perishable goods. Compliance with food safety regulations, temperature control, and efficient supply chain management are critical. Rising demand for fresh and packaged foods, along with export growth, fuels investment in advanced cold storage solutions.
Furthermore, the IT hardware warehousing involves secure storage for electronics, components, and finished products. Facilities must have climate control to prevent damage from humidity and temperature fluctuations. Just-in-time supply chain models, global sourcing, and increasing demand for cloud computing and smart devices drive the need for efficient, high-tech storage solutions.
Likewise, the healthcare warehousing supports pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and hospital supplies. Stringent regulatory compliance, temperature-controlled environments, and real-time tracking are essential. The growth of telemedicine, an aging population, and increased pharmaceutical production drive demand for specialized storage solutions, including cold chain logistics for vaccines and biologics.
Along with this, the Chemical warehousing requires specialized facilities with strict safety protocols, hazardous material handling, and compliance with environmental regulations. Storage solutions must prevent contamination and ensure proper ventilation. Growth in industrial production, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals increases demand for high-security, temperature-controlled, and bulk liquid storage facilities.
Other areas include the automotive, textile, energy, and aerospace industries, which warehouse in a completely different manner than any other, requiring bulk material handling to temperature-controlled environments. It is always customizable and constantly advanced with technological solutions such as robotics and AI-based inventory management systems. This kind of warehouse expansion is mostly in emerging industries and sustainability.
Regional Analysis:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Westen Australia
Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales serves as Australia’s economic hub, with Sydney driving warehousing demand due to high consumer activity, e-commerce growth, and strong port operations. Infrastructure developments, such as Western Sydney’s logistics hubs, enhance supply chain efficiency. Rising land costs and urban expansion influence warehousing strategies and automation adoption.
In line with this, Victoria, supported by Melbourne's larger logistics hubs and port, supports critical supply chain functions across the country. Wholesale, retailing, manufacturing, and agriculture spur demand for warehouses. In Tasmania, the main focus of warehouses is on storing foodstuffs for export to other countries that are using superior cold chains with improved connectivity back to mainland markets.
Also, the Queensland’s warehousing market is bolstered by its agricultural exports, mining activities, and growing e-commerce sector. Brisbane, as a logistics hub, supports regional and national distribution. Expanding trade routes and infrastructure projects, including port expansions and road networks, enhance storage and distribution capabilities, driving warehousing investments across the state.
Apart from this, the Northern Territory’s warehousing sector supports resource extraction and remote supply chains, with Darwin as a strategic logistics gateway to Asia. South Australia, driven by Adelaide’s manufacturing and wine industries, sees growing demand for cold storage and general warehousing. Government incentives promote infrastructure investments, strengthening regional logistics operations.
Furthermore, Western Australia’s warehousing market is dominated by mining exports and trade through Perth’s ports. The demand for industrial storage, particularly for equipment and bulk commodities, remains high. Growing e-commerce and agricultural exports drive warehousing expansion, while investments in transport infrastructure improve supply chain connectivity across the vast region
Competitive Landscape:
The Australian warehousing and storage market is highly competitive, fueled by the growing demand for advanced logistics solutions. Market players range from large-scale providers offering integrated supply chain management to specialized firms focusing on cold storage, e-commerce fulfillment, and automated warehousing. The rise of third-party logistics (3PL) providers has intensified competition, with businesses seeking flexible and cost-effective storage solutions. Innovation in automation, AI-driven inventory management, and sustainability practices is a key differentiator, as companies invest in smart warehousing to enhance efficiency. Strategic warehouse locations near major transport corridors provide a competitive edge, enabling faster deliveries. Additionally, rising real estate costs push market players to optimize storage space and adopt multi-client warehousing models to remain cost-effective.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Australia warehousing and storage market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Aurizon Holdings Limited
- DHL Group
- Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Linfox Pty Ltd.
- Qube Holdings Ltd.
- G&S Logistics
- Race Couriers
- UC Logistics Australia
- eStore Logistics
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2024, DP World Australia announced the acquisition of Silk Logistics through a binding Scheme Implementation Deed, valuing the deal at A$174.5 million. Silk Logistics manages 21 logistics hubs and 25 warehousing sites across Australia, providing port-to-door and contract logistics services. The acquisition, pending shareholder and regulatory approvals, is expected to be completed in the first half of 2025. With this strategic move, DP World aims to strengthen its integrated logistics capabilities and broaden its service offerings.
- In November 2024, StorHub Group acquired three prime self-storage facilities in Sydney for over A$110 million, marking one of Australia’s largest self-storage deals. This acquisition expands StorHub’s Australian portfolio to over 110,000 sqm of GFA and 8,500 storage units, valued at over A$420 million. The newly acquired sites in Homebush, Forestville, and Revesby will be rebranded under StorHub, reinforcing its rapid growth since entering the market earlier this year.
- In September 2024, FranklinWH Australia Pty Ltd. has partnered with AC Solar Warehouse to advance solar and energy storage solutions in Australia and New Zealand. This collaboration combines FranklinWH’s expertise in home energy management with AC Solar Warehouse’s extensive distribution network. The alliance aims to provide homeowners with integrated solar, battery, and smart energy management solutions, promoting energy independence. This partnership strengthens sustainable energy adoption and efficiency across the region.
Australia Warehousing and Storage Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types of Warehouse Covered | General Warehousing and Storage, Refrigerated Warehousing and Storage, Farm Product Warehousing and Storage |
| Ownerships Covered | Private Warehouses, Public Warehouses, Bonded Warehouses |
| End Uses Covered | Manufacturing, Consumer Goods, Retail, Food and Beverage, IT Hardware, Healthcare, Chemicals, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Companies Covered | Aurizon Holdings Limited, DHL Group, Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd., Linfox Pty Ltd., Qube Holdings Ltd., G&S Logistics, Race Couriers, UC Logistics Australia, eStore Logistics, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia Warehousing and Storage market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia Warehousing and Storage market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia Warehousing and Storage industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia warehousing and storage market was valued at USD 19.8 Billion in 2025.
The Australia warehousing and storage market was valued at USD 36.7 Billion in 2034 exhibiting a CAGR of 7.13% during 2026-2034.
The growth of Australia’s warehousing and storage market is driven by rising e-commerce, increasing demand for cold storage, and infrastructure development. Automation and smart warehousing enhance efficiency, while third-party logistics (3PL) services offer cost-effective solutions. Expanding trade volumes and urbanization further boost the need for advanced storage and distribution facilities.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












