
Australia Pharmaceutical Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Therapeutic Class, Drug Type, Prescription Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Pharmaceutical Market Size and Share:
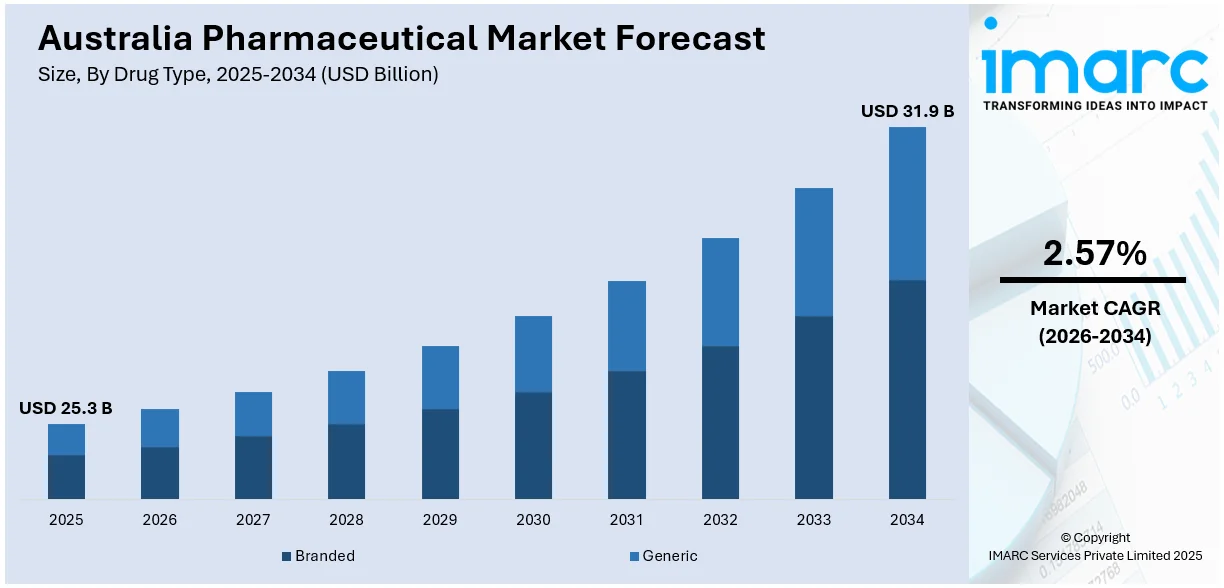
The Australia pharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 25.3 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 31.9 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.57% from 2026-2034. The market is driven by a growing geriatric population, rising chronic diseases, government healthcare funding, innovation in biopharmaceuticals, increasing demand for generic medicines, expanding telehealth and e-pharmacy services, and a heightened focus on preventive healthcare.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 25.3 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 31.9 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 2.57% |
The geriatric population in Australia is growing at a fast pace, which has huge implications for the pharmaceutical market. Life expectancy at birth was recorded for males as 81.1 years and for females as 85.1 years in the years 2021-2023 which will increase the population of older people in the near future. Such demographic changes lead to an increased prevalence of chronic illnesses like arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, dementia, etc., hence creating more demands for medications and health services. For example, it has been estimated that there will be an expansion from about 534,000 of the population aged 85 and over in Australia in the year 2021 to about 15,00,000 by the year 2041, representing a growth rate of 180%. Hence, this increase necessitates a hike in pharmaceuticals related to older people. An additional contribution of seniority is a larger requirement for health products of preventive and long-term medications, which creates drives consumption in the pharmaceutical market.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
It is also through the establishment of various policies and funding initiatives that the country’s government is majorly influencing the Australia pharmaceutical industry. Many medicines are provided through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) at an affordable price. This is also reflected in the public budget allocation of AUD 43 billion by the state government for the PBS in the federal budget for the FY2023-24. This funding ensures the accessibility of various essential medicines to the general populace while creating a demand for them and motivating the pharmaceutical companies to launch new products in the market. Other than that, it encourages and stimulates drug innovation and a growth atmosphere in the provisions of funding for healthcare infrastructure and research.
Key Trends of Australia Pharmaceutical Market:
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
In Australia, chronic illnesses are a major source of sickness and mortality, which has a big effect on the pharmaceutical industry. In 2023, chronic illness accounted for 78% of the fatal burden and 91% of the non-fatal burden, representing an overwhelming percentage of the illness load that needs continuous medication treatments. In the country, cancer continues to be the most common cause of early mortality among chronic illnesses, accounting for one-third (33%) of the overall burden. The demand for pharmaceuticals, such as painkillers, anti-inflammatory meds, and mental health therapies, is driven by the rising prevalence of these disorders. This pattern emphasizes the necessity of ongoing pharmacological innovation to meet the changing healthcare demands of chronic illnesses.
Expanding Telehealth and E-Pharmacies
One of the main factors driving the Australian pharmaceutical market size is the growing adoption of telehealth services and e-pharmacies. In 2022 and 2023 , 20% of general practitioners (GPs), 11% of non-GP specialists, 12% of allied health professionals, and 3% of other clinicians, including nurse practitioners and midwives, utilized telehealth, according to an analysis by Department of Health and Aged Care. The use of e-pharmacies has also increased dramatically in recent years, as seen by the sharp rise in online prescription orders. These digital platforms expedite the distribution of pharmaceutical supplies and improve patient convenience, especially in distant places. The pharmaceutical industry is changing as a result of the use of technology in healthcare delivery, which is encouraging accessibility and efficiency.
Focus on Preventive Healthcare
Preventive health care is a priority in Australia, altering consumption patterns of pharmaceutical products. In particular, public health campaigns and government agenda have considered vaccination and early detection of diseases. For instance, according to data from the Australian Immunization Register, approximately 8.7 million people were vaccinated against flu between March to July in the year 2023. This prevention approach goes beyond vaccinations. Rising demand for diagnostic and early-detection screening tools, matched in quality by ever-increasing numbers of Australians considering regular checkups at early stages for conditions such as cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases, is fostering the Australia pharmaceutical market growth.
Growth Drivers of Australia Pharmaceutical Market:
Government Support and Favorable Healthcare Policies
The Australian government plays a pivotal role in driving pharmaceutical market growth through programs like the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS), which subsidizes a wide range of essential medicines. This enhances accessibility and affordability of prescription drugs amongst the population, resulting in a jump in demand by all demographics. Moreover, regulatory systems like the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) make products safe and favourable to innovation. Research & development (R&D), clinical trial investment, and the health system are other investments that are driving global enterprises in the pharmaceutical sector to invest in Australia. Such policy-supported initiatives put the pharmaceutical firms in a robust and stable position to innovate, produce, and market various forms of drugs catering to the healthcare-related demands of a country.
Aging Population and Rising Healthcare Needs
Australia’s ageing population is a significant growth factor driving the Australia pharmaceutical market demand. As the proportion of people aged 65 and older continues to rise, so does the demand for medications related to age-associated conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, and neurodegenerative disorders. Older individuals generally require more frequent and complex medication regimens, which fuels both prescription and over-the-counter drug consumption. Additionally, senior citizens often rely on long-term care facilities, which in turn contribute to consistent pharmaceutical procurement. With longevity increasing and the government focused on elder care initiatives, the pharmaceutical industry stands to benefit from sustained demand for therapeutic solutions that enhance quality of life and manage chronic and acute conditions common in this demographic.
Growth of Biopharmaceutical and Specialty Drug Segments
The shift toward biopharmaceuticals and specialty drugs is reshaping the Australia pharmaceutical market share. These treatments, often targeting rare or complex diseases, are experiencing high demand due to their effectiveness and advancements in precision medicine. Biologics, immunotherapies, and gene-based therapies are increasingly prescribed, especially in areas like oncology, autoimmune diseases, and rare disorders. Australia’s supportive regulatory environment and skilled research base further encourage innovation and faster approval of specialty treatments. Pharmaceutical companies are investing in advanced production facilities and collaborating with biotech firms to bring these next-generation drugs to market. As public and private healthcare sectors adopt more personalized and targeted therapies, the biopharma segment is poised to drive substantial growth in both revenue and research investment.
Opportunities of Australia Pharmaceutical Market:
Expansion of Clinical Trials and R&D Investment
Australia presents a prime location for clinical trials due to its diverse population, high healthcare standards, and streamlined ethics approval processes. The government also offers R&D tax incentives and grants, making it attractive for both domestic and international pharmaceutical firms to invest in drug development. The country’s well-regulated environment and access to world-class research institutions further support the scaling of clinical studies, especially in oncology, neurology, and infectious diseases. Additionally, Australia’s strong data protection laws and electronic health record systems enhance patient recruitment and tracking, which reduces time-to-market for new therapies. This creates vast opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to innovate locally, form partnerships with research organizations, and bring new, cutting-edge treatments to global markets.
Growing Demand for Mental Health Medications
Australia has seen a marked increase in mental health awareness and diagnosis, creating a substantial opportunity for the pharmaceutical industry. With rising cases of anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders, particularly among young adults and working professionals, the demand for antidepressants, anxiolytics, and mood stabilizers is accelerating. Government initiatives, including mental health funding and public awareness campaigns, are reducing stigma and encouraging treatment-seeking behavior. According to the Australia pharmaceutical market analysis, this trend is further supported by easier access to general practitioners and psychologists, who often prescribe these medications as part of integrated care. Pharmaceutical companies focusing on central nervous system (CNS) drugs and novel psychiatric treatments can tap into this growing market by offering effective, low side-effect therapies tailored to mental wellness.
Increased Role of Generic and Biosimilar Drugs
As healthcare systems seek cost-effective solutions, the Australian pharmaceutical market is experiencing rising demand for generic and biosimilar drugs. With patent expirations on key branded drugs, generics are gaining traction in both hospital and retail segments. The government supports their use through PBS listings and prescribing guidelines, helping reduce overall healthcare expenditure. Biosimilars, particularly for biologics in oncology and autoimmune treatment, present further opportunity for market growth. Companies capable of ensuring quality and affordability can penetrate underserved therapeutic areas while meeting regulatory requirements. This shift also allows domestic manufacturers to compete effectively with multinationals, enabling a more balanced and accessible pharmaceutical supply landscape across Australia.
Australia Pharmaceutical Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Australia pharmaceutical market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on therapeutic class, drug type, and prescription type.
Analysis by Therapeutic Class:
- Alimentary Tract and Metabolism
- Blood and Blood Forming Organs
- Cardiovascular System
- Dermatologicals
- Genito Urinary System and Sex Hormones
- Systemic Hormonal Preparations
- Anti-infectives for Systemic Use
- Antineoplastic and Immunomodulating Agents
- Musculoskeletal System
- Nervous System
- Antiparasitic Products, Insecticides, and Repellents
- Respiratory System
- Sensory Organs
- Others
The alimentary tract and metabolism segment is focused primarily on the treatment of diabetes, metabolic syndromes, as well as gastrointestinal ailments. In 2023, around 4.3% and 2.9% of Australians suffered from Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, respectively. Furthermore, an increase in gastrointestinal therapies for conditions such as acid reflux and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is stimulated by dietary and lifestyle changes. While the public grows more aware, the PBS is likely to support the growth of the probiotic and enzyme replacement therapy industries through subsidies, as per the Australia pharmaceutical market forecasts.
Anemia and clotting problems and some blood-related malignancies are handled through the blood and blood-forming organs. Erythropoiesis-stimulating medicines and iron supplements have been more in demand along with increased diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia especially among women and children. Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs remain a necessity in the management of age-related cardiovascular diseases, especially in the prevention of stroke. Blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma continue to drive the development of target-specific and biological products. Increased funding for research on blood health is also adding to the anticipated growth of this segment through support for treatment derived from plasma.
Conditions like high blood pressure, heart failure, and increased cholesterol levels fall under the segment cardiovascular system. As per a survey by Australian Bureau of Statistics, in 2023, heart diseases account for nearly 9.2% as the primary cause of death in Australia. This ensures a steady demand for antihypertensives, statins, and anticoagulants. Lifestyle and an ever-growing aging population also increase the need for cardiovascular treatments, while combined therapies and minimally invasive drug delivery continue to innovate and drive growth in this segment. Furthermore, government-supported initiatives and patient awareness campaigns are key enablers for growth in this therapeutic class.
Analysis by Drug Type:
- Branded
- Generic
Branded medicines represent a significant aspect of the pharmaceutical market in Australia, because of the innovation with their efficacies as well as the large number of intensive clinical trials that accompany them. Most often, these are used in the case of complex and chronic ailments such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and cardiovascular disorders. Branded drugs may be costly, but because of highly proven effectiveness and high science formulation, they are trusted by patients and healthcare providers alike. Branded drugs represent a huge revenue stream for the market as the emergence of new biologics and precision medicines drive this value. Pharmaceutical companies have also continued making large investments in research and development to gain competition advantage, fortified by strong intellectual property rights and exclusive period.
Generic drugs are becoming more popular since they are less expensive than branded ones. Their popularity is increasing as greater numbers of patients and healthcare professionals embrace them. These medications, which offer the same therapeutic advantages as branded counterparts at a fraction of the price, are frequently used to treat common ailments including infections, diabetes, and hypertension. Government regulations supporting generics and the growing emphasis on affordable healthcare options are the main factors propelling this market. Furthermore, the anticipated expiration of patents for significant branded medications is anticipated to hasten the expansion of generic medications in Australia.
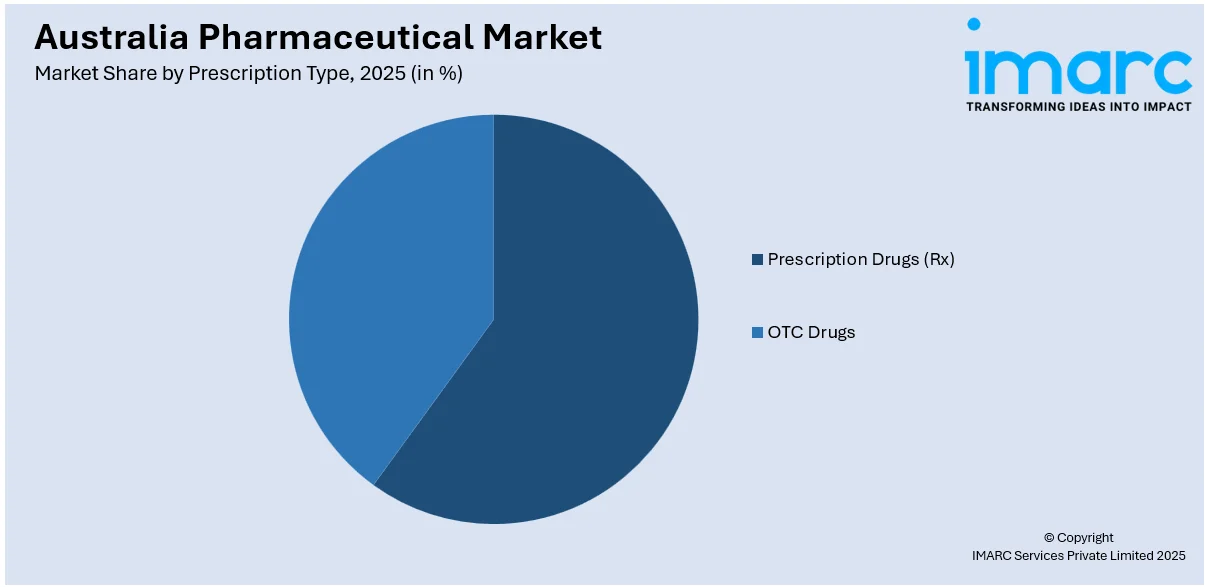
Analysis by Prescription Type:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Prescription Drugs (Rx)
- OTC Drugs
Prescription drugs, which address urgent medical needs, complicated disorders, and chronic diseases, make up a substantial portion of the Australia pharmaceutical market size. They are restricted substances that can only be obtained with a prescription from a physician in order to guarantee that their usage is monitored and targeted. The rise in the prevalence of long-term conditions including diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders drives the segment growth. Antidepressants and antihypertensives are the most frequently used medications in this group. The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme also facilitates the availability of various prescription drugs. As a result, numerous prescription drugs are now available to patients at lower expenses.
Self-medication in the form of over-the-counter medicines is mainly driven by customer needs for convenience and do-it-yourself solutions. These over-the-counter medications, ranging from vitamins to painkillers and antihistamines, are found in about all pharmacies, across supermarkets, and online retailers without requiring any prescription. The OTC market witnessed massive spikes in demand due to growing health awareness. In this regard, sales of vitamins and those used for boosting immunity, such as zinc and vitamin C, are rising. The industry is also driven by the aging population of Australia, as well as the increase in the attention towards preventive care.
Regional Analysis:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and New South Wales (NSW) is one of the most significant markets in Australia, mainly driven by the high population density of the region and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Sydney, being one of the major hubs, leads to robust pharmaceutical consumption, particularly for chronic disease management and specialty medicines. There are well-established hospitals, research institutions, and pharmacies in the region. Government health programs, such as PBS, and high health literacy among the residents enhance the market in this region.
Victoria and Tasmania are dynamic markets, and Melbourne is a key center for medical research and pharmaceutical innovation. The region increasingly invests in biopharmaceuticals and clinical trials. Thus, it is a prime destination for drug development. The growth in Victoria is because of chronic disease medications and preventive care products. The Tasmanian region has an elderly population, and the need for geriatric medicines is increasing with age-related diseases such as arthritis and cardiovascular diseases. Steady growth in this region is ensured by the presence of healthcare facilities and government support.
Queensland's pharmaceutical market is growing at a fast pace due to a high population growth rate and rising lifestyle diseases. There is a higher demand for chronic disease management drugs, such as diabetes and hypertension, among patients. The healthcare network in urban and rural facilities supports the market of the area. Queensland's developed interest in health innovation and digital health, such as telehealth and e-prescription, has increased access to pharmaceutical products, especially in remote areas.
Northern Territory and South Australia market is characterized by unique healthcare challenges. In NT's remote areas, there is increased focus on access to essential drugs and indigenous healthcare needs. South Australia, with the city of Adelaide as an economic hub, has a well-established health infrastructure that supports growth in pharmaceuticals. In this region, demand has primarily been driven by the treatments for respiratory illnesses, chronic conditions, and preventive care, hence growing rapidly.
The pharmaceutical market in Western Australia is driven by its mining-driven economy and increasing urbanization. Perth is the health and pharmaceutical hub of the region, with demand concentrated on chronic disease management, mental health treatments, and pain management drugs. The vast geography of the state requires innovative distribution channels, such as e-pharmacies and telehealth services, to provide access to medications in rural and remote areas. Healthcare infrastructure investments and government-backed programs are also driving the growth of this market.
Competitive Landscape:
The leading companies in the industry are engaging in diversifying their partnerships, innovating, and focusing on patient-centered services. They are investing their resources in projects aimed at developing new classes of therapies, including vaccines, biologics, and precision medicines for complex and chronic diseases. One strategy that various organizations keep harnessing to enhance access to medicines while promoting innovation has been establishing partnerships with local health providers and research institutes. Digital transition is another area of focus, as companies are using patient assistance programs to integrate telehealth and create e-prescribing platforms to enhance healthcare delivery. To provide a matching response to the growing need for drug affordability, manufacturers are also expanding their portfolio of products under generic labels. Also, major firms are now in the process of executing sustainability strategies such as carbon footprint reduction and environmentally friendly packaging to meet customer expectations as well as global environmental goals.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Australia pharmaceutical market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- AbbVie Inc.
- Amgen Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- CSL Limited
- Eli Lilly Australia Pty Ltd
- GSK plc
- Merck KGaA
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty Ltd.
- Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd.
- Roche Australia
- Sanofi
Latest News and Developments:
- In December 2024, Neuren Pharmaceuticals stated that its partner Acadia Pharmaceuticals had finished selling the Rare Pediatric Disease Priority Review Voucher. The voucher was issued by the US FDA following the regulatory approval of DAYBUE (trofinetide) for the treatment of Rett Syndrome. Acadia and Neuren agreed that the latter would receive one-third of the revenues, net of any relevant costs.
- In December 2024, Cartherics, an Australian biotechnology firm, announced that it had received a US$300,000 G-Rex grant to enable clinical production of its main medicine CTH-401 for forthcoming clinical trials. ScaleReady, Wilson Wolf Manufacturing, and CellReady launched the G-Rex Grant Program, a $20 million effort aimed at advancing cell and gene treatments.
- In December 2024, FivepHusion, a clinical-stage biotechnology startup, signed a commercial agreement with the University of Wollongong for their ResectAssist Drug Delivery Platform. This drug-eluting biodegradable implant allows for the targeted delivery of a wide spectrum of licensed and experimental medications directly into solid tumors with significant unmet medical needs. Their flagship medication candidate, ResectAssist-FOLFIRINOX, is being developed for unresectable locally-advanced pancreatic cancer with the goal of downgrading these tumors to be resectable and curable.
- In November 2024, Race Oncology announced that it has completed an FTO-targeted drug development program at Monash University's Fragment Platform. According to the company, the method employed fragment-based NMR screening to find 39 molecular candidates that bind exclusively to the m6A RNA demethylase protein, FTO. These validated FTO-binding chemical scaffolds serve as a foundation for the development of unique and patentable compounds that may lead to new therapeutics targeting the m6A RNA epigenetic pathway.
- In November 2024, Amplia Therapeutics announced a research agreement with Korean preclinical drug screening startup Next&Bio. This cooperation will investigate the efficacy of Amplia's FAK inhibitors against patient-derived pancreatic cancer cells with known oncogenic mutations. The company is claimed to be interested in investigating the possible synergistic effect of its FAK inhibitors with a new class of medications under development that block the strong oncogene Kras. These medications may be utilized to treat pancreatic cancer in the coming years.
Australia Pharmaceutical Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Therapeutic Classes Covered | Alimentary Tract and Metabolism, Blood and Blood Forming Organs, Cardiovascular System, Dermatologicals, Genito Urinary System and Sex Hormones, Systemic Hormonal Preparations, Anti-infectives for Systemic Use, Antineoplastic and Immunomodulating Agents, Musculoskeletal System, Nervous System, Antiparasitic Products, Insecticides, and Repellents, Respiratory System, Sensory Organs, Others |
| Drug Types Covered | Branded, Generic |
| Prescription Types Covered | Prescription Drugs (Rx), OTC Drugs |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Companies Covered | AbbVie Inc., Amgen Inc., AstraZeneca, CSL Limited, Eli Lilly Australia Pty Ltd, GSK plc, Merck KGaA, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty Ltd., Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd., Roche Australia, Sanofi, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia pharmaceutical market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia pharmaceutical market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia pharmaceutical industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The pharmaceutical market in Australia was valued at USD 25.3 Billion in 2025.
The Australia pharmaceutical market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 2.57% during 2026-2034.
The Australia pharmaceutical market is projected to reach a value of USD 31.9 Billion by 2034.
The market is witnessing a shift toward digital therapeutics, real-world evidence adoption, and integration of AI in clinical decision-making. Growth in home-based care and wearable health tech is influencing drug delivery methods. Additionally, pharma companies are embracing data-driven strategies to optimize product lifecycle management and patient adherence programs.
The expanding health insurance penetration and increased funding for rare disease treatment are key growth drivers. The rising demand for innovative drug delivery systems, such as sustained-release formulations, along with strong intellectual property protections and government-backed research collaborations, also attracts global pharma companies to invest in and expand across the Australian market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












