
Australia Fish and Seafood Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product, Form, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Fish and Seafood Market Size and Share:
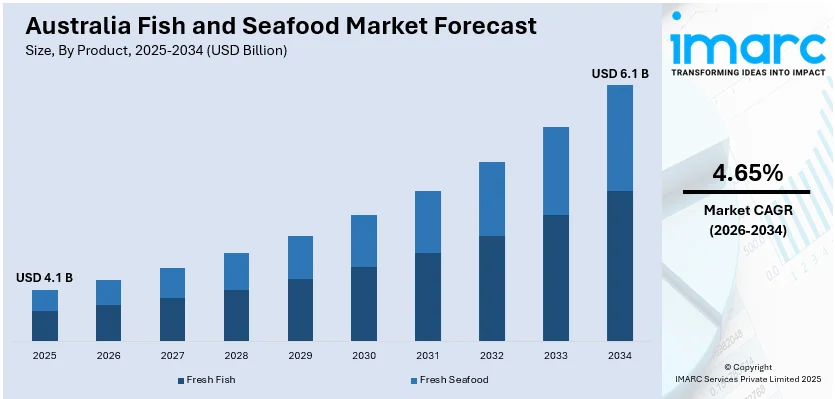
The Australia fish and seafood market size was valued at USD 4.1 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 6.1 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.65% from 2026-2034. The market is growing steadily, fueled by evolving consumer preferences for nutritious and sustainably sourced products. Advancements in aquaculture, strong export demand, and government support for sustainable fishing practices are further propelling the market. Moreover, innovation in seafood alternatives and convenience-driven products supports expansion in domestic and international markets.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 4.1 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 6.1 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 4.65% |
The Australia fish and seafood market is driven by growing consumer demand for sustainably sourced, high-quality products. Increasing health awareness has amplified seafood’s popularity, valued for its rich nutritional benefits, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Enhanced traceability systems and sustainability certifications have bolstered consumer trust, promoting market growth. Advancements in aquaculture and fishing practices have streamlined supply chains, ensuring the consistent availability of premium seafood. For instance, according to industry reports, Australia’s fisheries and aquaculture production value is expected to remain stable between 2024–25 and 2028–29, with an average of $3.48 billion. Additionally, technological innovations in processing and packaging have improved product quality and shelf life, meeting the evolving needs of consumers and contributing to the expansion of fresh, frozen, and value-added seafood products.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The expanding foodservice industry, encompassing restaurants, cafes, and catering businesses, drives growth by prominently including seafood in their offerings. Tourism, particularly in coastal areas, has amplified the demand for locally sourced seafood, as visitors seek fresh and authentic culinary experiences. Additionally, export opportunities to Asia and Europe, where Australian seafood is recognized for its premium quality, continue to contribute to the market’s robust growth. For instance, in August 2024, South Australia exported over 6,000 tonnes of tuna to Japan, valued at $58 million, primarily as frozen products, with a smaller portion sold fresh or chilled. Moreover, local exporters shipped 124 tonnes of oysters and mollusks during the same period, generating nearly $5 million in export revenue. This dynamic interplay of domestic and international demand ensures steady market expansion.
Australia Fish and Seafood Market Trends:
Growing Demand for Sustainable and Certified Seafood
Australia's fish and seafood market is experiencing increased consumer demand for sustainably sourced and certified products. This shift is driven by heightened awareness of environmental issues and overfishing. For instance, in November 2023, State and territory consumer affairs ministers announced an agreement for limited seafood labeling in restaurants, cafes, and clubs, which will take effect in 2025. Under the new policy, seafood will be labeled as Australian, imported, or mixed origin (AIM model), aligning eateries with seafood retailers, which already disclose the origin of their products. The Australian Marine Conservation Society (AMCS) stressed additional measures, emphasizing the need for labeling to include details such as the species name, fishing or farming methods, and the country of origin. This focus aligns with global trends, ensuring Australia remains competitive in the premium seafood segment while supporting the long-term health of marine ecosystems.
Rising Exports to Asian Markets
The Australian fish and seafood market is benefitting from rising exports to Asian markets, driven by high demand for premium-quality products such as tuna, lobster, and abalone. Countries like Japan, China, and South Korea view Australian seafood as a luxury item due to its freshness, sustainability, and stringent quality standards. This export growth is encouraging investment in processing facilities and cold-chain logistics to maintain quality and expand market share. Additionally, government initiatives are playing a crucial role in supporting this growth. For instance, in September 2024, the Australian Government launched the NEXDOC system to simplify seafood export documentation, supporting the USD 1.8 billion trade. The digital platform streamlines permits and certifications, reducing costs and manual processes. Exporters benefit from secure QR-coded certificates, faster approvals, and improved tracking. Part of a USD 322.9 million digital initiative, it enhances efficiency and strengthens Australia's reputation in global markets.
Increased Adoption of Technology in Aquaculture
Technology adoption is transforming Australia’s aquaculture sector, which is a significant contributor to the fish and seafood market. Advanced systems like automated feeding, real-time water quality monitoring, and data analytics are improving productivity and sustainability. The use of recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) is also gaining momentum, allowing for fish farming in controlled environments with reduced environmental impact. For instance, in July 2024, Huon Aquaculture announced an investment of $110 million to expand its freshwater Atlantic salmon nursery at Whale Point, Port Huon, Tasmania. The new recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) will grow larger fish on land, reducing marine time. Moreover, the project creates 150 construction jobs, 8 permanent roles, and boosts local businesses. These innovations are enhancing yields, reducing costs, and ensuring consistent supply to both domestic and international markets. Furthermore, the Australian government and private sector investments in research and development are further accelerating the adoption of these technologies, reinforcing the country’s reputation for high-quality and sustainably produced seafood.
Australia Fish and Seafood Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Australia fish and seafood market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on product, form, and distribution channel.
Analysis by Product:
- Fresh Fish
- Fresh Seafood
Fresh fish is one of the dominant segments in the Australian fish and seafood market, driven by local sourcing and high consumer demand for quality, nutritious products. Fish such as barramundi, snapper, and tuna are readily available in coastal regions and are commonly sold at fishmongers, supermarkets, and directly to consumers via local seafood markets. Fresh fish is preferred for its superior taste, texture, and health benefits, making it a staple in Australian households and restaurants. Besides, Australia's rich fishing industry, a sustainable approach toward marine products, and emerging interest in clean eating and organic foods continue to foster growth in the fresh fish category.
Fresh seafood, including shellfish, crustaceans, and mollusks, is another key product segment in the Australian market. Demand for fresh seafood is fueled by both domestic consumption and export opportunities. Products such as prawns, oysters, and mussels are often sold live or chilled, ensuring their premium quality and preserving their delicate flavors. Fresh seafood is popular in Australian cuisine, particularly for special occasions and feasts. With the increased spotlight on sustainability and traceable sourcing, fresh seafood is becoming a major focus in the marketplace, as consumers continue to choose locally sourced, responsibly farmed, and wild-caught options.
Analysis by Form:
- Fresh
- Frozen
- Canned
- Cured
Fresh fish and seafood remain the most popular form in the Australian market, primarily due to consumer demand for quality, tasteful, and healthy food. The segment holds strong position in the coastal regions, where seafood originates locally and is directly delivered into the local markets and restaurants. On the whole, fresh seafood is sold through specialist fishmongers, supermarkets, and local seafood markets. This is promoted by the proximity of Australia to the ocean and established fishing industries, which ensure supplies of fresh and sustainable produce. Consumer demand for freshness, supported by convenience-driven retail models, continues to drive this segment.
The frozen fish and seafood segment is accelerating on rising consumer convenience and shelf-life. It gives consumers and food service operators the flexibility of having to hold the product for long periods of time. Supermarkets and specialty retailers have responded by carrying frozen seafood selections usually pre-packaged for convenient use. The frozen segment is also boosted by the export market, where frozen products are shipped globally. Technological advancements in freezing processes have also helped maintain the quality and nutritional value of frozen seafood, supporting its popularity among consumers.
Canned fish and seafood products, such as tuna, salmon, and sardines, have remained a stable segment within the Australian market, with a focus on affordability, convenience, and long shelf life. These products are popular in households and foodservice due to their versatility, as they can be used in a wide range of dishes from salads to pastas. The canned segment is also seeing growth as more consumers focus on sustainable sourcing, with eco-friendly packaging and traceability becoming key factors. Canned seafood appeals to budget-conscious consumers and has a strong presence in retail stores, especially for products like canned tuna, which is a household staple.
Cured fish and seafood products, such as smoked salmon, salted cod, and other preserved items, represent a niche yet growing segment in the Australian market. These products offer a unique flavor profile and longer shelf life, making them popular in premium foodservice establishments and specialty retailers. The cured segment benefits from the increasing consumer interest in traditional and artisanal food preservation methods, which align with broader trends toward gourmet and sustainable foods. The segment’s growth is also fueled by demand for high-quality, ready-to-eat seafood options that are perceived as both convenient and indulgent.
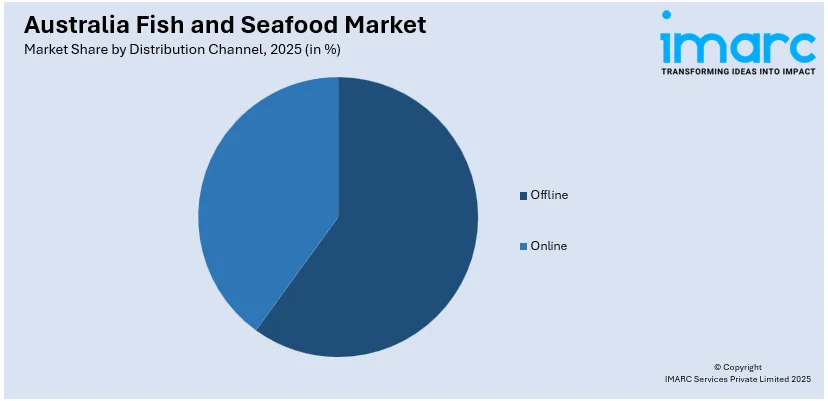
Analysis by Distribution Channel:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Offline
- Online
The offline distribution channel for Australia's fish and seafood market remains crucial, particularly for traditional retail and foodservice sectors. Supermarkets, local fishmongers, and seafood markets continue to be dominant players, offering consumers fresh seafood in-store. Restaurants, cafes, and caterers also form a significant part of the offline distribution, with a growing emphasis on quality and sustainability. Additionally, the wholesale market plays a key role in supplying large quantities to retailers and foodservice operators. The offline sector relies heavily on established distribution networks, which ensure product availability and freshness, and it continues to cater to those who prefer in-person shopping experiences.
The online distribution channel for the Australian fish and seafood market has seen significant growth, driven by consumer convenience and the rise of e-commerce platforms. Major supermarkets, independent retailers, and specialized seafood distributors have expanded their digital presence, offering home delivery services and subscription models. The online market also caters to niche segments, including sustainably sourced and premium seafood products. Additionally, online seafood marketplaces have emerged, providing consumers with access to fresh, high-quality options directly from producers, increasing both national and international sales opportunities. As online shopping becomes more prevalent, convenience and product transparency continue to shape purchasing behavior.
Regional Analysis:
- Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales
- Victoria and Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory and Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and New South Wales (NSW) represent a significant market for fish and seafood in Australia, driven by strong demand in urban centers like Canberra and Sydney. NSW has a diverse fishing industry, including both wild-caught and farmed seafood, with key ports such as Sydney and Eden supporting seafood production. The region has also seen a growing trend toward sustainable fishing practices and a focus on high-quality products like Australian lobsters and prawns. In recent years, seafood consumption has remained steady, supported by both local demand and exports to Asia.
Victoria and Tasmania play a crucial role in Australia's fish and seafood market, with Tasmania being renowned for its premium seafood products, including Atlantic salmon, oysters, and abalone. The state's clean waters and advanced aquaculture techniques make it a key producer for both domestic consumption and export markets, especially in Asia. Victoria, with its ports like Melbourne, has a vibrant seafood sector, benefiting from a diverse culinary culture and growing demand for sustainable, traceable seafood. Both regions are investing in sustainable fishing technologies, positioning them as leaders in the eco-friendly seafood sector.
Queensland is a significant player in the Australian fish and seafood market, driven by its vast coastline and rich marine biodiversity. The state is a major producer of prawns, tuna, and reef fish, with large-scale commercial fishing operations along its coast, particularly in the Great Barrier Reef region. Queensland's seafood industry is supported by both wild-caught fisheries and aquaculture, especially for prawns and barramundi. With a focus on sustainability and traceability, Queensland is well-positioned to meet the growing domestic demand and export opportunities, particularly in Asia and Europe, where Australian seafood is highly valued.
The Northern Territory and South Australia contribute to Australia's fish and seafood market through their unique aquatic ecosystems and specialized fisheries. The Northern Territory is known for its barramundi and mud crab, with a focus on sustainable wild-catch practices. South Australia, with its rich marine environment, is famous for its abalone, tuna, and kingfish production, alongside its growing aquaculture industry. The region has also been making significant strides in sustainable aquaculture practices, particularly for shellfish. Both regions are integral to the domestic seafood supply, as well as key exporters, especially to Asian markets.
Western Australia plays a crucial role in the Australian fish and seafood market, with a strong presence in both wild-caught and aquaculture sectors. The state is a major exporter of seafood, including Western rock lobster, abalone, and prawns. Its expansive coastline, abundant marine resources, and focus on sustainability have made it a leader in the Australian seafood industry. Perth's seafood trade hub and ports like Geraldton contribute to the state's high seafood exports, especially to China and other parts of Asia. Additionally, the state is investing in innovative fishing and aquaculture technologies to meet growing demand while maintaining eco-friendly practices.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the Australia fish and seafood market is characterized by a mix of large-scale seafood companies, regional fishers, and aquaculture enterprises. Key players focus on sustainable sourcing, advanced processing technologies, and strong distribution networks to maintain market share. For instance, in January 2024, Genics, sn Australian biotech firm, launched Shrimp MultiPath2.0, a cutting-edge technology for early detection of shrimp diseases. It identifies 18 pathogens in a single test, enhancing precision and efficiency. This innovation protects aquaculture health, prevents stock losses, and boosts farm profitability, positively impacting Australia's fish and seafood market through improved disease management and increased harvest value. Moreover, retail giants and specialty seafood stores compete for domestic market dominance, while the foodservice industry fuels demand for premium and fresh seafood products. Furthermore, collaboration between stakeholders ensures adherence to sustainability standards, further enhancing market competitiveness.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Australia fish and seafood market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2024, Clean Seas Seafoods received an automatic feeder barge, "Eyre Spirit," valued at USD 6 million, at Port Adelaide. The barge is designed by Southern Ocean Solutions and built in Vietnam; hence, it will support yellowtail kingfish farming near Port Lincoln. It improves efficiency, reduces waste, and enables remote feeding for 90% of operations, driving significant cost savings
Australia Fish and Seafood Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Products Covered | Fresh Fish, Fresh Seafood |
| Forms Covered | Fresh, Frozen, Canned, Cured |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Offline, Online |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory and Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia fish and seafood market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia fish and seafood market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia fish and seafood industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
Fish and seafood refer to edible aquatic animals, including finfish (e.g., salmon, tuna) and shellfish (e.g., shrimp, crabs, mollusks). These products serve as vital protein sources globally, utilized in diverse culinary applications, including fresh, frozen, canned, and processed forms. Their demand spans retail, foodservice, and industrial sectors, driving significant economic activity.
The Australia fish and seafood market was valued at USD 4.1 Billion in 2025.
IMARC estimates the Australia fish and seafood market to exhibit a CAGR of 4.65% during 2026-2034.
The Australian fish and seafood market is driven by strong demand for high-quality, sustainable products, increasing export opportunities in Asian markets, and technological advancements in aquaculture. Moreover, government initiatives supporting sustainability and streamlined export processes, coupled with growing awareness of health benefits, further bolster market growth and attract domestic and international investment.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












