
Antibiotics Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Action Mechanism, Drug Class, Spectrum of Activity, Route of Administration, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
Antibiotics Market Size and Share:
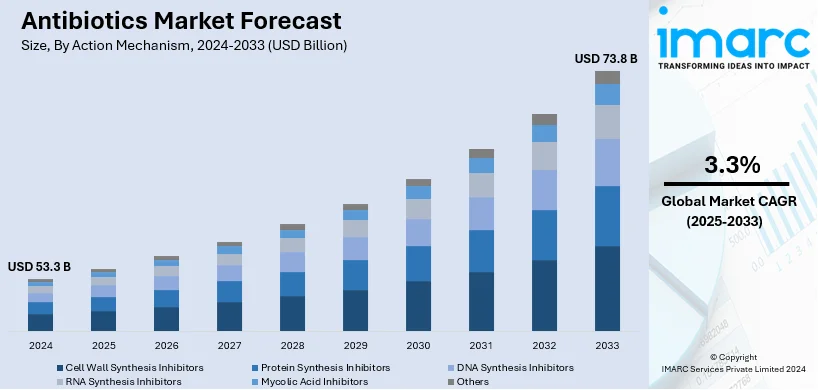
The global antibiotics market size was valued at USD 53.3 Billion in 2024. The market is projected to reach USD 73.8 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.3% during 2025-2033. Asia Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of around 44% in 2024. The market is fueled by the increasing cases of pneumonia, tuberculosis, and other infectious diseases among individuals. The increasing concerns over antimicrobial resistance are driving the development of new and more effective antibiotic therapies. Also, expanding healthcare access in developing regions is supporting greater antibiotic consumption. In addition to this, continual technological advancements in biotechnology and drug discovery techniques are some of the major factors augmenting the antibiotics market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033 |
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 53.3 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 73.8 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 3.3% |
Currently, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in the global population is contributing to the market growth. Moreover, the widespread availability of antibiotics through online and offline stores and increased demand for topical antibiotics are boosting the product demand. Antibiotics help reduce the risk of infection in the surgical wound area for individuals. This has strengthened the global demand for antibiotics. Rising employment of antibiotics for the health and welfare of livestock animals is also fueling the market growth. In addition, the increased consumer awareness of preventative health care measures and growing demand in aging population are supporting the antibiotics market growth.
The antibiotics market in the United States is witnessing lucrative growth, fueled by the ongoing need to treat bacterial infections and the growing issue of antibiotic resistance. Investments in research and government-backed initiatives are encouraging the development of more effective treatments. A notable example is the FDA’s approval in April 2023 of Zevtera (ceftobiprole medocaril sodium for injection), which is designed to treat Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (bacteremia), including right-sided infective endocarditis and acute bacterial skin infections.
Antibiotics Market Trends:
Rising Incidence of Infectious Diseases
Worldwide, the incidence of infectious diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, urinary tract infections (UTI), gastrointestinal infections and sepsis in the bloodstream is increasing among the population and people suffer more from these diseases because of inadequate sanitation. This contributes to the spread of bacterial infections. 10 out of 25 women and 3 out of 25 men have a urinary tract infection at some point in their lives. More powerful antibiotics are needed to help treat these infections. Antibiotics are specifically designed to target and eliminate bacterial infections. They effectively kill bacteria in the body and promote healing. Antibiotics are also used under the guidance of a health professional to optimize patient outcomes.
Increasing Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
There is a rise in the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) across the globe, which is driving the antibiotics market. AMR occurs when bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi evolve and become resistant to the drugs used to treat them. It reduces the effectiveness of antibiotics and causes longer and more severe infections, increased healthcare costs, and high mortality rates among individuals. In 2019, bacterial antimicrobial resistance (AMR) was directly linked to 1.27 million deaths worldwide. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics are contributing to the development of drug-resistant bacteria, which makes traditional antibiotics less effective. In addition, multidrug-resistant strains, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), are more prevalent. This necessitates the sales and development of advanced antibiotics, thereby contributing to the market growth.
Technological Advancements in Antibiotics
Innovations in biotechnology, molecular biology, and drug discovery techniques are helping to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of antibiotic development. This, in turn, is enhancing the antibiotics market outlook. Genomics and high-throughput screening enable the identification of potential drug targets and the screening of large compound libraries. Many companies are investing in the technology. For example, in January 2021, Pfizer Inc. announced a $120 million investment in four clinical-stage biotechnology companies under the Pfizer Breakthrough Growth Initiative (PBGI). The partnership aims to advance promising clinical development programs in line with Pfizer's future strategic interests. Computer-aided drug design also allows for predicting drug efficacy and optimizing antibiotic candidates. These technological advances have streamlined the antibiotic discovery process and reduce the time and costs compared to traditional methods. In addition, advances in diagnostic techniques, such as rapid pathogen identification and sensitivity testing, help in choosing the right antibiotic to improve patient outcomes.
Rising Demand due to Disease Burden, Resistance, and Regional Disparities
The market is experiencing steady growth due to increasing global health pressures. The rising prevalence of infectious diseases, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, is driving higher demand for broad-spectrum antibiotics. Industry reports indicate that approximately 8.2 million new tuberculosis cases were recorded in 2023, reflecting an increase from 7.5 million cases in 2022. Respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and gastrointestinal disorders remain especially common, prompting healthcare systems worldwide to rely on antibiotics as frontline therapy. Concurrently, antimicrobial resistance is intensifying worldwide, reducing the effectiveness of older treatments and forcing the development of new drug classes. Resistance to first-line antibiotics has increased, leading to treatment failures and longer hospital stays. This has spurred public and private sector investments in novel compounds and improved diagnostics. Moreover, the geographic distribution of antibiotic usage and access varies significantly. High-income countries emphasize surveillance and stewardship, while many low- and middle-income regions face limited access, inconsistent quality, and misuse. This imbalance adds complexity to policy and supply chain strategies across the global market.
Antibiotics Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global antibiotics market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on action mechanism, drug class, spectrum of activity, route of administration, and end-user.
Analysis by Action Mechanism:
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
- DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- Mycolic Acid Inhibitors
- Others
Cell wall synthesis inhibitors action mechanism is the largest action mechanism in 2024, holding around 52% market share. Cell wall synthesis inhibitors is a class of antibiotics that target the bacterial cell wall. These antibiotics interfere with the process of cell wall synthesis, which causes cell wall damage and eventual bacterial death. In addition, penicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems are some of the cell wall synthesis inhibitors. They work by inhibiting enzymes called penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that are involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains. Moreover, cell wall synthesis inhibitors are particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria due to their thicker peptidoglycan layer, which provides a greater target for disruption.
Analysis by Drug Class:
- Cephalosporin
- Penicillin
- Fluoroquinolone
- Macrolide
- Carbapenem
- Aminoglycoside
- Others
Penicillin leads the market with around 26% market share in 2024. As per antibiotics market report segmentation, Penicillin is a widely used class of antibiotics that belongs to the beta-lactam drug class. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls that causes cell wall damage and bacterial death. It is considered an essential medicine and is widely available as generic drugs. Apart from this, it is increasingly used in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and outpatient settings. In addition, the rising utilization of penicillin, as it is effective against various bacterial infections, is contributing to the growth of the market.
Analysis by Activity:
- Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics
- Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotics
Broad-spectrum antibiotics segment leads the market with around 70% market share in 2024. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are a class of antibiotics that exhibit activity against a wide range of bacteria, such as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In line with this, the rising adoption of broader spectrum antibiotics, as they are effective against a broader range of microorganisms compared to narrow-spectrum antibiotics, is bolstering the growth of the market. Apart from this, broad-spectrum antibiotics assist in treating infections when the causative bacteria are unknown or when the infection involves multiple bacterial species. The appropriate use of broad-spectrum antibiotics minimizes the risks of infections in the body.
Analysis by Route of Administration:
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Topical
- Others
Parenteral leads the market with over 68% market share in 2024. Parenteral antibiotics are administered via routes other than the digestive tract, such as intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), or subcutaneous (SC) routes. These routes allow for direct delivery of the medication into the bloodstream or deep tissues, bypassing the gastrointestinal system. In addition, parenteral antibiotics provide rapid and predictable drug absorption and immediate therapeutic effect. They are also suitable for patients with compromised gastrointestinal function. Apart from this, it allows for accurate dosing and is particularly beneficial in cases where high drug concentrations are needed or when oral administration is not possible.
Analysis by End User:
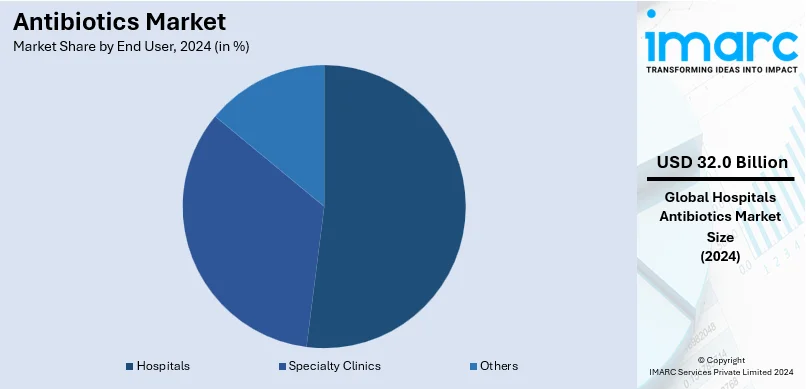
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Others
Hospitals leads the market with around 60% market share in 2024. Antibiotics are widely consumed in hospitals due to the increased number of patients staying in this healthcare setting. Antibiotics are administered to patients admitted with severe infections. They are also administered before surgical procedures to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination. In line with this, the rising utilization of antibiotics among individual post-surgical prophylaxis is contributing to the growth of the market. Apart from this, the increasing consumption of antibiotics due to the rising risk of multidrug-resistant infections in hospitals is supporting the growth of the market.
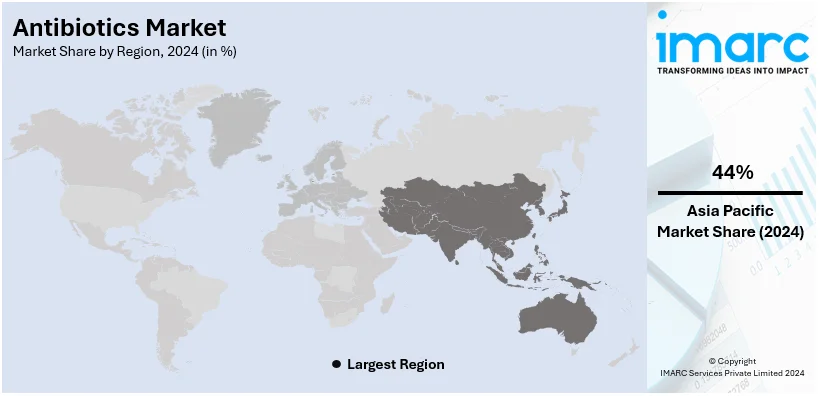
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
In 2024, Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market share of around 44%. The growing incidence of bacterial infections to poor sanitation is contributing to the growth of the market in the Asia Pacific region. Apart from this, the increasing demand for advanced antibiotics that can effectively combat multidrug-resistant bacteria is supporting the growth of the market. Furthermore, the presence of a large number of generic drug manufacturers is propelling the growth of the market in the region.
Key Regional Takeaways:
North America Antibiotics Market Analysis:
The North America antibiotics market is driven by the increasing incidence of infectious diseases, particularly respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections, as these conditions necessitate effective antibiotic treatments to combat rising bacterial resistance. Additionally, the aging population in the region contributes to heightened demand for antibiotics, as older adults are more susceptible to infections. Advances in antibiotic development, including novel formulations and combination therapies, are also critical in addressing antibiotic resistance challenges. Furthermore, strategic collaborations among pharmaceutical companies and increased investment in research and development are enhancing the pipeline of new antibiotics, ensuring the market remains responsive to evolving health needs.
United States Antibiotics Market Analysis:
United States accrued a market share of around 86% in the North America market in 2024. The increased incidence of bacterial illnesses, improvements in healthcare facilities, and significant R&D expenditures are the main factors propelling the U.S. antibiotics industry. Urinary tract infections and respiratory tract infections continued to be among the most frequently treated illnesses in 2023, which increased the need for a wide range of antibiotics. The market is greatly influenced by the aging population, which is expected to reach more than 78 million by 2040 and more than 88 million by 2060. This is because older people are more prone to illnesses. Also, one of the significant antibiotics market trends is the rise of strains of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, like MRSA, which is increasing the demand for next-generation antibiotics and sparked innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
Research on new antibiotic classes and quick diagnostics are supported by government programs to address antimicrobial resistance (AMR), such as the National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Additionally, market expansion is driven by the FDA's accelerated approval processes for important medicines and the robust presence of major pharmaceutical companies in the United States. Demand is being further fueled by healthcare facilities implementing stricter antibiotic regimens in response to an increase in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). The U.S. market for antibiotics is expanding despite issues with overuse and resistance, owing to strong healthcare spending and innovation.
Europe Antibiotics Market Analysis:
The growing cases of infectious diseases and the numerous government programs designed to fight antibiotic resistance are the main factors affecting the antibiotics market in Europe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Europe uses a diverse range of antibiotics and has a high rate of resistant bacterial strains, including Klebsiella pneumonia and E. coli. As a result, the players are investing in the creation of novel antibiotics and stewardship initiatives to maximize their use.
Leading countries in this sector include Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, bolstered by their sophisticated healthcare systems and proactive AMR regulations. Additionally, the EMA has expedited the approval procedures for antibiotics that fulfill unmet medical requirements. The increase of outpatient care services and the increasing use of quick diagnostic techniques for bacterial infections are driving the market demand further.
Asia Pacific Antibiotics Market Analysis:
The high incidence of infectious diseases, rising healthcare costs, and growing awareness of contemporary treatments are all contributing to the Asia-Pacific antibiotics market's rapid expansion. Antibiotic demand is fueled by the high incidence of bacterial illnesses, such as pneumonia and tuberculosis, in nations like China, Indonesia, and India. According to time-series research, a total of 16,290 million doses of antibiotics were sold in India in 2020, which is slightly less than the amount in 2018 and 2019. Apart from this, the antibiotics market worth is further increased by the expanding middle class and better access to healthcare services in emerging markets.
The region's governments are tackling issues such as antibiotic resistance by supporting antibiotic stewardship initiatives and providing funds for research into novel medication classes. As significant producers of antibiotics, China and India also gain from export prospects. Additionally, the use of telemedicine platforms is expanding the availability of antibiotic treatments in remote locations.
Latin America Antibiotics Market Analysis:
The incidence of infectious disorders, such as gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, is propelling the Latin American market growth. Advanced antibiotics are being adopted by nations like Brazil and Mexico to fight infections that are worsened by inadequate access to healthcare and poor sanitation. The industry is expanding owing to government programs like vaccination campaigns that use preventative antibiotics and investments in healthcare infrastructure. Furthermore, the region's expanding pharmaceutical sector and collaborations with international pharmaceutical companies are opportunistic for the market growth.
Middle East and Africa Antibiotics Market Analysis:
The high incidence of infectious diseases, including respiratory infections, malaria, and tuberculosis, has an impact on the demand for antibiotics. Antibiotics are becoming more widely available in the Middle East due to the investments made in healthcare modernization by nations like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. International agencies like UNICEF and WHO are assisting antibiotic supply chains in Africa to address healthcare issues. While government programs are encouraging local production to lessen reliance on imports, awareness campaigns and measures to combat antibiotic resistance are gradually improving usage patterns.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players in the industry are investing in research and development (R&D) activities to discover and develop new antibiotics and focus on antibiotic resistance, expanding the spectrum of activity, and improving the efficacy and safety profiles of antibiotics. Apart from this, they are engaging in collaboration with research institutions, academic organizations, and government bodies to leverage their expertise and address the challenges associated with antibiotic development, such as high costs and regulatory compliances. Moreover, antibiotic companies are actively promoting antibiotic stewardship programs that encourage responsible and appropriate use of antibiotics to avoid overdosage and misuse. According to antibiotics market research report, companies are increasingly conducting clinical trials and adhering to safety and efficacy standards to obtain regulatory approvals for their antibiotics.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the market. Detailed profiles of all major companies have also been provided. Some of the key players in the market include:
- Allergan Plc (AbbVie Inc.)
- Basilea Pharmaceutica AG
- GlaxoSmithKline Plc
- Johnson & Johnson
- Melinta Therapeutics
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Nabriva Therapeutics Plc
- Paratek Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi SA
- Spero Therapeutics
- Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: Mumbai‑based Wockhardt announced plans to pursue regulatory approvals and launch its novel antibiotic Zaynich (WCK 5222) across the U.S., Europe, India, and emerging markets. Following a successful pre‑NDA meeting with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in May 2025, Wockhardt intends to file its New Drug Application in Q2 FY26 with the aim of launching in FY26–27, while European and Indian filings are slated for the second half of FY25. The Phase III data supporting Zaynich demonstrated approximately 20% superior cure rates over meropenem in treating serious gram‑negative and carbapenem‑resistant infections, reflecting its potential to address a major unmet global medical need.
- May 2025: Innoviva Specialty Therapeutics (a subsidiary of Innoviva) and partner Basilea Pharmaceutica officially launched antibiotics ceftobiprole (marketed as Zevtera®), marking it as the first FDA-approved cephalosporin in the United States for treating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (including right-sided endocarditis), acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP). Originally approved in April 2024, the antibiotic fills a critical gap in combating serious drug-resistant S. aureus infections across both adult and pediatric populations.
- March 2025: Roche announced the initiation of a Phase III clinical trial for its investigational antibiotic zosurabalpin (RG6006), designed specifically to combat carbapenem‑resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) infections. The compound, developed in partnership with Harvard University, targets a novel mechanism—lipopolysaccharide transporter inhibition—and builds on promising early-stage data. This advancement marks a critical step toward addressing one of the most urgent global antimicrobial resistance threats.
- August 2023: Bugworks Research, a biopharmaceutical company with R&D facilities in Bengaluru, India, formed a partnership with the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP) based in Switzerland. The collaboration seeks to expedite the development of an antibiotic compound for treating serious infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria.
- July 2023: Orchid Pharma Ltd, Chennai, India signed a technology transfer agreement with a prominent multinational biotechnology company for its fermentation-based '7ACA project' under the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
- April 2023: Baxter International Inc. announced the U.S. launch of ZOSYN (piperacillin and tazobactam) Injection. Zosyn premix is approved for treating various infections caused by susceptible bacteria and is offered in Baxter’s exclusive single-dose Galaxy containers.
- October 2021: Sandoz, a Novartis division, successfully completed the acquisition of GlaxoSmithKline’s (GSK) cephalosporin antibiotics business. This acquisition provides them rights to three established brands (Zinnat, Zinacef and Fortum) in more than 100 markets to Sandoz.
- January 2020: Merck & Co. Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a New Drug Application (NDA) for DIFICID® (fidaxomicin) for oral suspension, and a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for DIFICID tablets for the treatment of Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) in children aged six months and older.
Antibiotics Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Action Mechanisms Covered | Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors, Protein Synthesis Inhibitors, DNA Synthesis Inhibitors, RNA Synthesis Inhibitors, Mycolic Acid Inhibitors, Others |
| Drug Classes Covered | Cephalosporin, Penicillin, Fluoroquinolone, Macrolide, Carbapenem, Aminoglycoside, Others |
| Spectrum of Activities Covered | Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics, Narrow-spectrum Antibiotics |
| Routes of Administration Covered | Oral, Parenteral, Topical, Others |
| End Users Covered | Hospitals, Specialty Clinics, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Allergan Plc (AbbVie Inc.), Basilea Pharmaceutica AG, GlaxoSmithKline Plc, Johnson & Johnson, Melinta Therapeutics, Merck & Co. Inc., Nabriva Therapeutics Plc, Paratek Pharmaceuticals Inc., Pfizer Inc., Sanofi SA, Spero Therapeutics, Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals, etc.. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Antibiotics market from 2019-2033.
- The Antibiotics market research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Antibiotics industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The antibiotics market was valued at USD 53.3 Billion in 2024.
The antibiotics market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.3% during 2025-2033, reaching a Svalue of USD 73.8 Billion by 2033.
The market is driven by the growing prevalence of pneumonia, tuberculosis, and other infectious diseases among individuals, rising occurrence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and technological advancements in biotechnology and drug discovery techniques.
Asia Pacific currently dominates the antibiotics market, accounting for a share of 44% in 2024. The dominance is fueled by a high prevalence of infectious diseases, growing healthcare infrastructure, increasing population, and rising demand for effective antimicrobial treatments in the region.
Some of the major players in the antibiotics market include Allergan Plc (AbbVie Inc.), Basilea Pharmaceutica AG, GlaxoSmithKline Plc, Johnson & Johnson, Melinta Therapeutics, Merck & Co. Inc., Nabriva Therapeutics Plc, Paratek Pharmaceuticals Inc., Pfizer Inc., Sanofi SA, Spero Therapeutics, and Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals, among others.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












