
Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Raw Material, Application, and Region, 2025-2033
Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Size and Share:
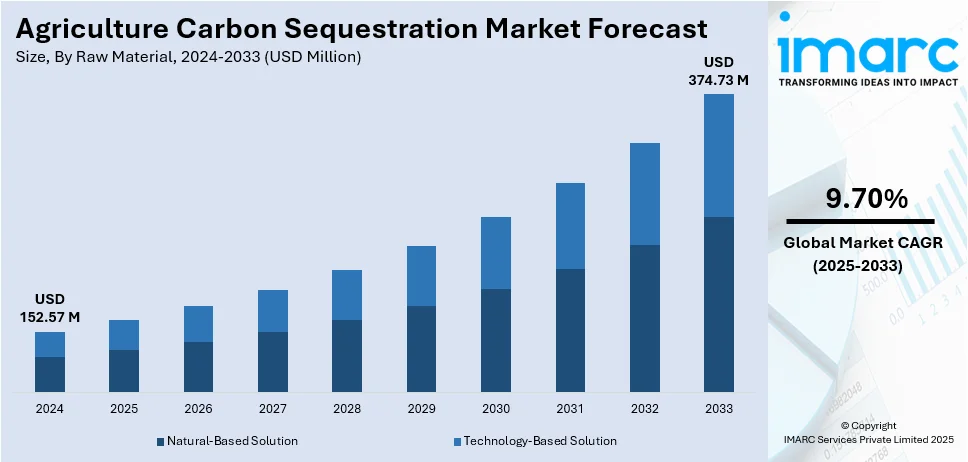
The global agriculture carbon sequestration market size was valued at USD 152.57 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 374.73 Million by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.70% from 2025-2033. North America currently dominates the market, holding a market share of over 40.5% in 2024. The growth of the North American region is driven by government incentives, carbon credit programs, regenerative farming adoption, advanced monitoring technologies, corporate sustainability commitments, and strong research collaborations.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 152.57 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 374.73 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2025-2033) | 9.70% |
Governing bodies worldwide are implementing subsidies, tax benefits, and grants to encourage farmers to adopt carbon sequestration techniques. The inclusion of soil carbon sequestration in voluntary and compliance-based carbon credit markets is providing additional revenue streams for farmers. Regulatory frameworks are being developed to ensure transparency in carbon credit trading, attracting more participants. Besides this, advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI)-driven predictive models, satellite imaging, and internet of things (IoT)-enabled soil sensors are improving the accuracy of carbon sequestration measurement. Blockchain technology is being integrated into carbon credit verification systems to enhance transparency and prevent fraud. The development of cloud-based platforms allows real-time monitoring of soil carbon levels, ensuring data-driven decision-making in carbon sequestration projects.
The United States is a crucial segment in the market, driven by government policies that promote carbon sequestration in agriculture. Additionally, corporations and institutional buyers are securing large volumes of carbon credits from agricultural sequestration projects to meet sustainability goals and offset emissions. The growing demand for verified soil carbon credits is motivating farmers to embrace regenerative methods like cover cropping and minimized tillage. Companies are also forming long-term partnerships with carbon credit providers, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality sequestration credits while supporting the financial sustainability of farmers. In 2024, Catona Climate secured 250,000 carbon credits from Indigo Ag's regenerative agriculture soil carbon project, marking the largest reservation by a single partner. The credits were to be generated by US farmers practicing sustainable methods like cover cropping and reduced tillage to sequester carbon.
Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Trends:
Expansion of Corporate Carbon Offsetting Programs
The increasing commitment of corporations to carbon neutrality is driving the demand for agricultural carbon sequestration projects as viable offset solutions. Companies across multiple industries are purchasing carbon credits generated from sustainable farming practices to meet emissions reduction targets. Large-scale corporate sustainability initiatives are directly funding agricultural carbon sequestration programs to integrate them into supply chain strategies. Businesses are forming partnerships with farmers and agritech companies to develop customized sequestration models aligned with corporate ESG goals. Carbon insetting, where companies invest in carbon reduction within their supply chains rather than external offsets, is gaining traction, further embedding sequestration into agricultural operations. For instance, in 2024, CinSOIL, a German startup, introduced AI-driven software to help AgriFood companies decarbonize their supply chains through soil carbon sequestration. By using satellite data, their tool monitored soil carbon dynamics, enabling companies to reduce emissions directly within their operations, promoting sustainable farming and improving soil health. CinSOIL focused on "insetting," integrating sustainability into a company's own value chain rather than relying on external carbon offset projects.
Development of Carbon Farming Certification Programs
The establishment of carbon farming certification programs is enhancing the credibility and marketability of agricultural carbon sequestration initiatives. Certification bodies are creating standardized protocols for measuring, reporting, and verifying soil carbon sequestration, ensuring consistency in carbon credit markets. Farmers who implement certified carbon sequestration practices gain access to premium pricing opportunities, attracting greater participation in carbon credit trading. Blockchain and digital ledger technologies are being integrated into certification processes to enhance transparency and prevent fraudulent carbon credit claims. Additionally, multinational corporations are prioritizing certified carbon credits in their sustainability investments, increasing the demand for verifiable sequestration projects. In 2024, BeZero Carbon launched an innovative regenerative agriculture credit rating system aimed at evaluating and supporting carbon credit projects that prioritized soil health and CO2 sequestration. The system provided independent, risk-based ratings to help investors identify high-impact projects. This move reflected the growing importance of agriculture in mitigating climate change, with the first project receiving a BBB rating for its potential in CO2 removal.
Rise of Regenerative Agriculture Practices
Farmers are implementing regenerative techniques such as cover cropping, no-till farming, agroforestry, and rotational grazing to enhance soil health and carbon storage. These practices improve soil organic matter content, promoting long-term carbon sequestration while increasing crop resilience and productivity. Growing research on soil microbiomes is further optimizing regenerative farming methods to maximize carbon retention. Agricultural cooperatives and organizations are promoting knowledge-sharing initiatives, accelerating the transition to regenerative models. Financial incentives and premium pricing for regeneratively farmed products are encouraging large-scale adoption. Additionally, integration of regenerative agriculture into sustainability frameworks of multinational corporations and governments is strengthening the market growth. In 2024, the Odisha Government and ICRISAT launched the "Compendium of Regenerative Agriculture" at the International Symposium on Shree Anna in Bhubaneshwar. The compendium introduced sustainable farming practices, including soil health improvement, crop diversity, and climate resilience. It aimed to guide farmers and policymakers in adopting regenerative agriculture methods to enhance carbon sequestration, improve sustainability, and reduce carbon emissions.
Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global agriculture carbon sequestration market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on raw material and application.
Analysis by Raw Material:
- Natural-Based Solution
- Technology-Based Solution
Natural-based solution represents the largest segment, accounting 72.5% in 2024. Natural-based solution is a crucial segment in the market due to their cost-effectiveness, scalability, and environmental benefits. Practices such as cover cropping, agroforestry, biochar application, and rotational grazing are gaining traction as farmers prioritize soil health and long-term sustainability. These methods enhance soil organic carbon levels, improve water retention, and boost biodiversity while reducing reliance on chemical inputs. Government programs and carbon credit markets are incentivizing adoption by providing financial rewards for farmers implementing regenerative practices. Continuous advancements in soil microbiology and organic soil amendments are further optimizing carbon sequestration potential. Companies are developing innovative models to measure, verify, and monetize sequestration outcomes, ensuring greater market participation. Strong collaborations between research institutions, policymakers, and agribusinesses are driving awareness and large-scale implementation. With increasing consumer demand for sustainable food production, natural-based solutions offer a viable path toward decarbonizing agriculture while maintaining high productivity and economic viability.
Analysis by Application:
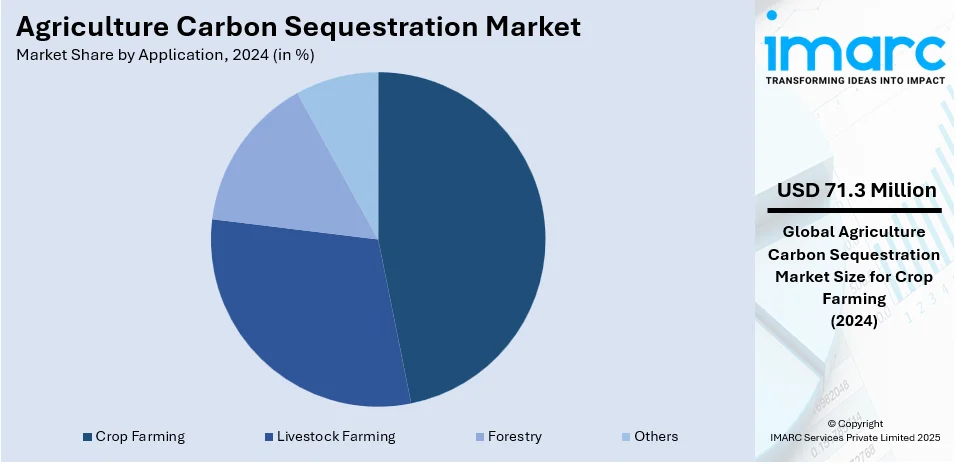
- Crop Farming
- Livestock Farming
- Forestry
- Others
Crop farming leads the market, holding 46.7% of market share in 2024. The agriculture carbon sequestration market in crop farming is expanding rapidly due to the adoption of regenerative practices that enhance soil health and carbon storage. Farmers are implementing cover cropping, no-till farming, and crop rotation to increase organic matter and reduce emissions. The integration of biochar, composting, and microbial soil amendments is further improving carbon sequestration efficiency. Precision agriculture technologies, including AI-driven soil monitoring and drone-based analysis, are optimizing carbon capture in farmlands. Governments and private entities are incentivizing farmers through carbon credit programs, providing additional revenue streams. Advancements in sustainable fertilizers and biological inputs are reducing dependency on synthetic chemicals, contributing to lower carbon footprints. Strong partnerships between research institutions, agribusinesses, and policymakers are driving innovation and adoption.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East
- Africa
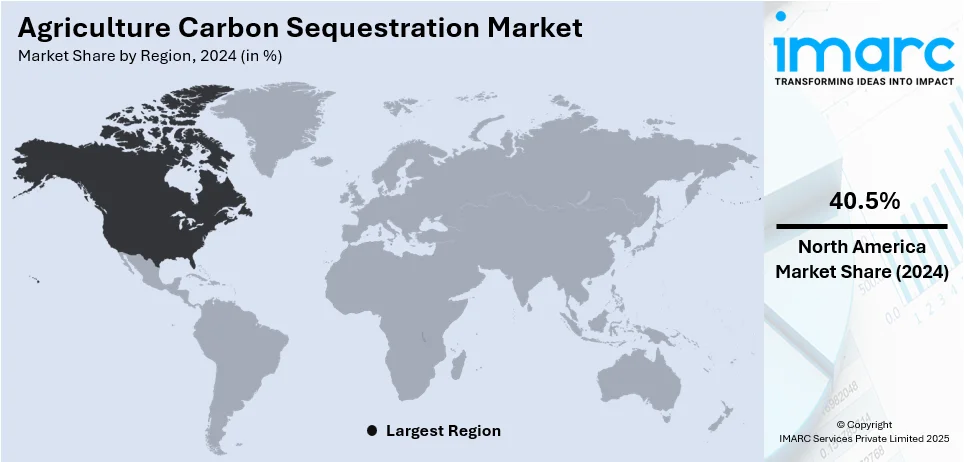
In 2024, North America dominated the market, accounting 40.5% of market share. North America dominates the market due to strong government policies, extensive carbon credit programs, and widespread adoption of regenerative farming practices. The region benefits from advanced precision agriculture technologies, including AI-driven soil monitoring, remote sensing, and blockchain-based carbon tracking, ensuring accurate measurement and verification. Leading agribusinesses and research institutions are actively investing in innovative sequestration techniques, such as biochar application, agroforestry, and microbial soil enhancements. Financial incentives and corporate sustainability commitments are driving large-scale implementation, providing farmers with additional revenue streams. In 2024, Mars, Incorporated announced partnerships to support regenerative agriculture in North America's pet food supply chain. The initiative, involving companies like ADM, The Andersons, Inc., Riceland Foods, and the Soil and Water Outcomes Fund, aimed to transition 150,000 acres to regenerative practices in 2024. This effort was part of Mars' broader climate strategy, contributing to carbon reductions and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Key Regional Takeaways:
United States Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Analysis
In North America, the market portion held by the United States was 87.20% of the overall total. The agriculture carbon sequestration market in the US is expanding rapidly due to strong government incentives, corporate sustainability goals, and the growth of voluntary carbon markets. Advances in precision agriculture, soil health initiatives, and carbon credit trading platforms are driving adoption. Major agribusinesses and technology firms are investing in scalable sequestration methods, including no-till farming, cover cropping, and agroforestry. The presence of research institutions and collaborations between stakeholders further enhances innovation. Favorable policies, such as USDA programs and private-sector funding, support widespread implementation, positioning the US as a leader in carbon sequestration efforts within agriculture. In 2023, the USDA released a comprehensive assessment on agriculture and forestry in US carbon markets, highlighting current barriers and opportunities for farmers and forest landowners to participate. The report, part of the Growing Climate Solutions Act, emphasized the need for improved access to carbon markets and solutions to reduce transaction costs. The USDA also announced a $300 million investment to improve greenhouse gas measurement and carbon sequestration in climate-smart agriculture.
Europe Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Analysis
Europe is at the forefront of agriculture carbon sequestration, driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing corporate commitments to carbon neutrality. Farmers and agribusinesses are rapidly adopting regenerative farming, biochar application, and agroforestry to enhance soil carbon storage. For instance, in 2024, Mars launched initiatives to promote regenerative agriculture across Europe, partnering with organizations like Cargill, ADM, and Soil Capital. These programs aimed to transition thousands of hectares of farmland to sustainable practices, focusing on soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. Mars planned to convert over one million acres to regenerative agriculture by 2030 to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. Apart from this, advanced carbon tracking technologies, digital platforms, and strong financial support are fostering market expansion. The presence of leading agritech firms and research institutions contributes to continuous innovation. With growing consumer demand for sustainably sourced food, Europe remains a highly attractive market for agricultural carbon sequestration investments and projects.
Asia Pacific Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Analysis
Asia Pacific is witnessing growth in agriculture carbon sequestration due to rising awareness, government incentives, and increasing participation in carbon trading programs. Countries such as China, India, and Australia are investing in regenerative agriculture and sustainable soil management practices. Advancements in agri-tech, remote sensing, and AI-driven monitoring systems are improving carbon capture efficiency. For example, in 2024, Diageo India launched a regenerative agriculture program in Telangana, focusing on rice cultivation to reduce carbon emissions and water usage in its supply chain. The program, in partnership with the Centre for Sustainable Agriculture, promoted carbon sequestration through practices like alternate wetting and drying (AWD) to reduce Scope 3 emissions and enhance soil health. It covered 500 hectares in its first year, benefiting small-holder farmers and improving climate resilience.
Latin America Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Analysis
Latin America offers vast opportunities for agriculture carbon sequestration due to its extensive agricultural lands, biodiversity, and strong agribusiness sector. Countries like Brazil and Argentina are implementing large-scale carbon farming programs, supported by international investments and regional sustainability initiatives. Adoption of conservation agriculture, agroforestry, and soil restoration practices is increasing. Growing participation in international carbon credit markets is creating financial incentives for farmers. With supportive policies and rising interest from multinational companies, Latin America is emerging as a critical player in global agricultural carbon sequestration. In 2024, Yazaki North America launched a sustainability project in Mexico, in collaboration with TOWING Co. and Nagase Enterprise Mexico. The initiative focused on using TOWING’s biochar technology, Soratan, to improve soil health, boost yields, and promote carbon sequestration. The project, which began in November 2024, aimed to address soil degradation, enhance agricultural sustainability, and contribute to long-term carbon sequestration efforts.
Middle East and Africa Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Analysis
The Middle East and Africa are witnessing a growing interest in agriculture carbon sequestration, supported by initiatives promoting climate resilience and sustainable land management. Investments in soil regeneration, agroforestry, and biochar projects are increasing, particularly in arid regions. Governments and international organizations are providing funding for carbon farming initiatives, enhancing regional participation in carbon markets. With growing commitments from agribusinesses and policymakers, the region is developing innovative strategies to enhance soil health and carbon storage, contributing to sustainable agricultural development and climate adaptation. In 2024, AgraME 2024, held at the Dubai World Trade Centre, focused on sustainable agriculture, including soil health and carbon sequestration. The event highlighted regenerative practices to improve resilience and mitigate climate change. It also introduced the "Plant the Emirates" initiative to enhance the UAE's food security, sustainability, and promote carbon sequestration efforts in agriculture.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players in the market are focusing on expanding carbon credit programs, developing advanced soil carbon measurement technologies, and forming strategic partnerships with farmers and agribusinesses. They are investing in research to enhance sequestration techniques, including regenerative farming, biochar application, and microbial soil amendments. Companies are integrating digital platforms and remote sensing for accurate carbon accounting, ensuring transparency in carbon offset trading. They are also focusing on data-driven approaches to measure and verify carbon sequestration and environmental impact. This enhances transparency, boosts credibility, and encourages greater participation in sustainable farming practices and carbon credit markets. In 2024, AHDB, supported by Quality Meat Scotland (QMS), launched a £2.5m pilot project to baseline environmental data on up to 170 farms across Great Britain. The project focused on measuring carbon sequestration, emissions, and soil health to provide accurate data on farming's environmental impact. This initiative aimed to demonstrate agriculture's role in carbon storage, improve soil health, and enhance reporting toward net-zero targets.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the agriculture carbon sequestration market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Indigo Ag, Inc.
- Soil Capital
- Yara
- Carbon8 Systems Ltd.
- The Cool Farm
- Corteva
- BASF
- Syngenta
- Carbo Culture
- Charm Industrial
Latest News and Developments:
- November 2024: the EU Council endorsed a regulation that creates a certification system for permanent carbon removals, carbon farming, and carbon retention in products. This voluntary framework was designed to promote high-quality carbon removal and soil emission reduction efforts, assisting the EU in reaching climate neutrality by 2050. It included strict criteria for certification, monitoring, and third-party verification to ensure environmental integrity and transparency.
- September 2024: Corteva Agriscience launched a program to support two million women in India’s agri-value chain by 2030, focusing on sustainable practices like carbon sequestration. The initiative empowered women as farmers, researchers, and entrepreneurs by providing tools, resources, and education to promote environmental stewardship, food security, and economic growth.
- May 2024: Syngenta Group and The Nature Conservancy (TNC) renewed their collaboration to advance regenerative agriculture, focusing on land restoration and climate resilience in regions like Brazil, China, and the US. Their partnership aimed to improve soil health, boost carbon sequestration, and enhance resource efficiency.
- January 2024: Grow Indigo raised over US$8 million to support sustainable agriculture practices, including carbon sequestration. The company operated a carbon farming platform for smallholder farmers in India, aiming to remove 20MtCO2e annually through soil carbon sequestration. Grow Indigo's biological products also helped reduce chemical inputs and improved soil health across 4 million acres.
Agriculture Carbon Sequestration Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Raw Materials Covered | Natural-Based Solution, Technology-Based Solution |
| Applications Covered | Crop Farming, Livestock Farming, Forestry, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East, Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Indigo Ag, Inc., Soil Capital, Yara, Carbon8 Systems Ltd., The Cool Farm, Corteva, BASF, Syngenta, Carbo Culture, and Charm Industrial, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the agriculture carbon sequestration market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global agriculture carbon sequestration market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the agriculture carbon sequestration industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The agriculture carbon sequestration market was valued at USD 152.57 Million in 2024.
The agriculture carbon sequestration market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.70% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 374.73 Million by 2033.
Key factors driving the agriculture carbon sequestration market include the increasing demand for sustainable farming practices, growing awareness about climate change, government incentives, technological advancements in soil management, and the need to reduce carbon emissions, promoting carbon capture through agricultural methods.
North America currently dominates the agriculture carbon sequestration market, accounting for a share of 40.5%. The dominance of the region is because of government incentives, carbon credit programs, regenerative farming adoption, advanced monitoring technologies, corporate sustainability commitments, and strong research collaborations.
Some of the major players in the agriculture carbon sequestration market include Indigo Ag, Inc., Soil Capital, Yara, Carbon8 Systems Ltd., The Cool Farm, Corteva, BASF, Syngenta, Carbo Culture, and Charm Industrial, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












