Japan Wound Care Market Expected to Reach USD 1,127.4 Million by 2033 - IMARC Group
Japan Wound Care Market Statistics, Outlook and Regional Analysis 2025-2033
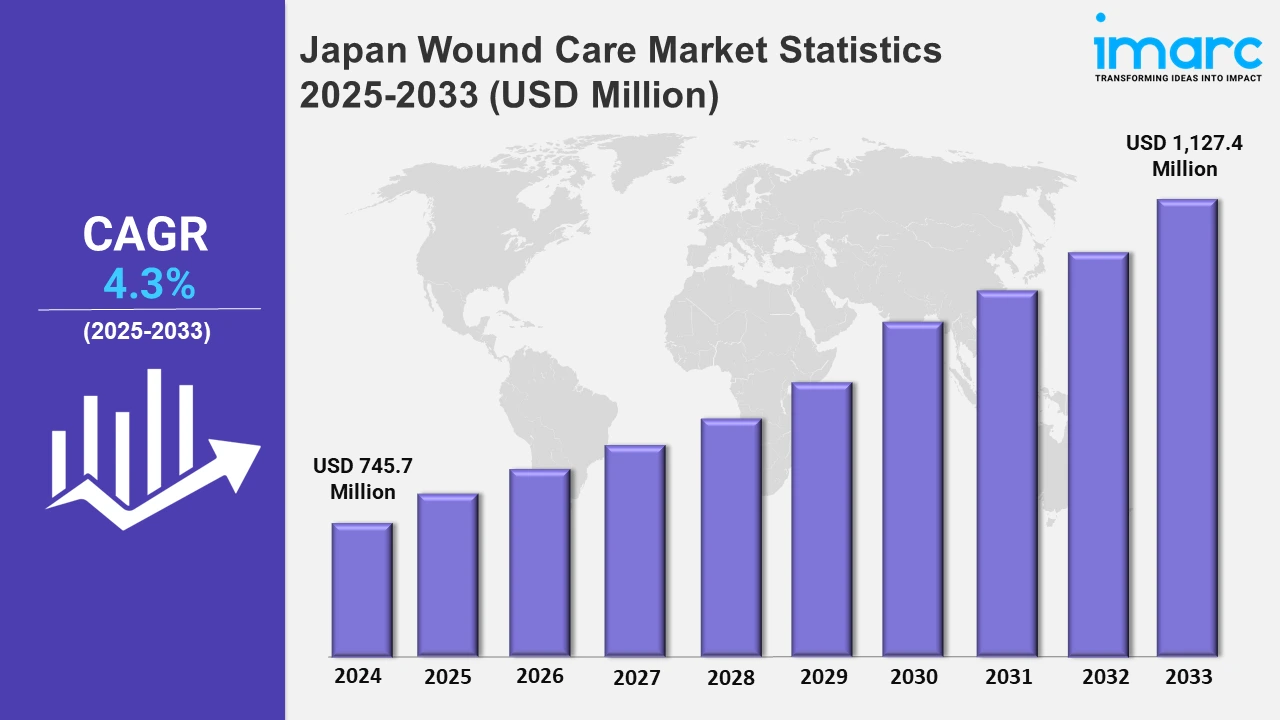
The Japan wound care market size was valued at USD 745.7 Million in 2024, and it is expected to reach USD 1,127.4 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2025 to 2033.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
In Japan, there is a growing focus on the direct distribution of advanced wound care products, including specialized dressings and medical devices. This approach enhances accessibility and supports more effective treatment for both chronic and acute wound conditions nationwide. For example, in April 2023, Gunze Medical, a leading medical device manufacturer, expanded its wound care sales network in Japan. The company now directly markets its artificial dermis product, PELNAC, along with wound dressings including fiber pads that are used for debridement and other medical devices designed for wound care.
Moreover, the wound care market in Japan is increasingly focused on advanced enzymatic therapies for burn treatment. New procedures are being developed to handle severe partial-thickness and full-thickness burns, expanding treatment choices for both adults and children in hospital settings across the country. For instance, Kaken Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, introduced NexoBrid in Japan for the treatment of burns in adults and children. Furthermore, the market is experiencing an increasing demand for advanced wound care solutions over traditional choices, owing to their higher efficacy in treating chronic and severe wounds. Companies in the region are investing in R&D activities to provide novel solutions that improve healing time and patient outcomes. For example, Japanese companies such as Nichiban and Tokuyama specialize in bioengineered wound care products and advanced dressings. Nichiban's proficient hydrocolloid dressings are extensively used in hospitals, including Tohoku University Hospital, which employs them to treat chronic wounds efficiently. These advances reflect the market's commitment to innovation and meeting the rising need for effective and user-friendly wound management products.
Japan Wound Care Market Statistics, By Region
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include the Kanto region, Kinki region, Central/Chubu region, Kyushu-Okinawa region, Tohoku region, Chugoku region, Hokkaido region, and Shikoku region. They are introducing numerous reimbursement policies, which is creating a favorable outlook for the market.
Kanto Region Wound Care Market Trends:
The Kanto region, which includes Tokyo, has a significant need for innovative wound care products due to its aging population and top-tier medical institutions. To treat chronic wounds, hospitals such as St. Luke's International use negative pressure wound therapy devices. Tokyo's high population also stimulates innovation in wound care technology, with firms manufacturing smart wound monitoring devices to improve treatment efficiency.
Kinki Region Wound Care Market Trends:
In the Kinki region, particularly Osaka, the prevalence of diabetic foot ulcers drives the adoption of specialized wound care solutions. Osaka University Hospital emphasizes advanced wound care for diabetes patients by using bioactive products and antimicrobial dressings. With the rising number of diabetes cases, clinics in Kyoto and Kobe also see increased demand for preventive wound management. This trend underscores the region’s focus on managing diabetes-related wounds to reduce hospitalization rates and improve patient quality of life.
Central/Chubu Region Wound Care Market Trends:
The Central/Chubu region, centered around Nagoya, experiences high usage of traditional wound care products due to its strong industrial base. Factory workers frequently rely on items like gauze and adhesive bandages for treating workplace injuries. Nagoya University Hospital actively partners with local manufacturers to promote better occupational safety practices. Nichiban, a prominent company in the region, produces adhesive bandages specifically designed for industrial applications, ensuring quick and effective treatment of minor injuries.
Kyushu-Okinawa Region Wound Care Market Trends:
In the Kyushu-Okinawa region, the subtropical climate leads to a higher occurrence of skin infections, creating demand for antimicrobial wound dressings. The University of the Ryukyus Hospital in Okinawa addresses these cases using advanced wound care solutions to prevent infections. Saraya Co., headquartered in Fukuoka, manufactures antimicrobial cleansers and dressings tailored to the region’s needs, supporting both hospitals and clinics in managing wounds effectively in humid conditions.
Tohoku Region Wound Care Market Trends:
The Tohoku region, with its aging rural population, has a rising demand for home-based wound care solutions. Tohoku University Hospital in Sendai offers specialized care for pressure ulcers and guides using easy-to-apply dressings for home treatment. Tokuyama Corporation supplies advanced wound care materials to local healthcare providers, ensuring that residents in remote areas have access to effective products for managing long-term wound care needs.
Chugoku Region Wound Care Market Trends:
The Chugoku region, with its focus on the agriculture industry, often deals with minor injuries among farmers. Hiroshima University Hospital frequently treats such injuries and emphasizes the importance of accessible wound care products like gauze and antiseptics. Daio Paper Corporation, a company based in the region, produces wound care essentials, ensuring rural clinics and pharmacies are well-stocked to meet the needs of local communities for quick and effective treatment.
Hokkaido Region Wound Care Market Trends:
Hokkaido’s cold climate often leads to skin dryness, cracks, and frostbite, increasing the need for wound care products. Sapporo Medical University Hospital provides specialized care for cold-related wounds, focusing on protective ointments and advanced dressings. Hokuyaku, a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Sapporo, supplies a wide range of wound care solutions, including moisturizing treatments and dressings tailored to prevent and manage wounds caused by the region’s harsh winters.
Shikoku Region Wound Care Market Trends:
In the Shikoku region, where access to large medical facilities is limited, telemedicine plays a vital role in wound care. Ehime University Hospital in Matsuyama offers remote consultations to assist patients in managing wounds in remote locations. Nichiban Co., a trusted provider of adhesive wound care products, supplies easy-to-use dressings, allowing patients and caregivers in the region to handle wound care needs effectively from the comfort of their homes.
Top Companies Leading in the Japan Wound Care Industry
Some of the leading Japan wound care market companies have been included in the report. Competitive analysis, such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant, has been covered in the report.
Japan Wound Care Market Segmentation Coverage
- Based on the product type, the market has been classified into advanced wound care products (foam dressing, hydrocolloid dressing, film dressing, alginate dressing, hydrogel dressing, collagen dressing, and others), surgical wound care products (sutures, staplers, tissue adhesive, sealants, and hemostats, and anti-effective dressing), traditional wound care products (medical tapes and cleansing agent), active wound care products (biological skin substitutes and topical agents), and wound therapy devices products (negative pressure wound therapy, oxygen and hyperbaric oxygen equipment, electric stimulation devices, pressure relief devices, wound assessment and monitoring devices, and others). Chronic wounds are better treated using advanced wound care products such as hydrocolloids and foams, which promote quicker healing. Post-operative therapies mostly consist of surgical wound care products such as stitches and staples. Traditional wound care products, including gauze and bandages, continue to be widely utilized for basic wound management. Active wound care products rely on bioengineered solutions, while wound therapy device products, such as NPWT systems, improve treatment efficiency.
- Based on the wound type, the market has been categorized into chronic wounds (diabetics ulcers, pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and others) and acute wounds (surgical traumatic wounds and burns). Chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers, require long-term treatment using improved solutions. Acute wounds, including surgical incisions and trauma injuries, require prompt treatment with standard bandages, surgical solutions, and wound therapy devices.
- Based on the end user, the market has been divided into hospitals and clinics, long-term care facilities, home care setting, and others. Hospitals and clinics are primary adopters, which use advanced devices to treat acute and surgical wounds. Long-term care facilities concentrate on chronic wound treatment for older people. The home care setting encourages convenience-driven wound care, emphasizing simple dressings and portable therapeutic equipment.
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 745.7 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1,127.4 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 4.3% |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Product Types Covered |
|
| Wound Types Covered |
|
| End Users Covered | Hospitals & Clinics, Long-Term Care Facilites, Home Care Setting, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Browse IMARC Related Reports on Plywood Market:
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.





.webp)




.webp)












