Japan Battery Market Expected to Reach 229.9 GWh by 2033 - IMARC Group
Japan Battery Market Statistics, Outlook and Regional Analysis 2025-2033
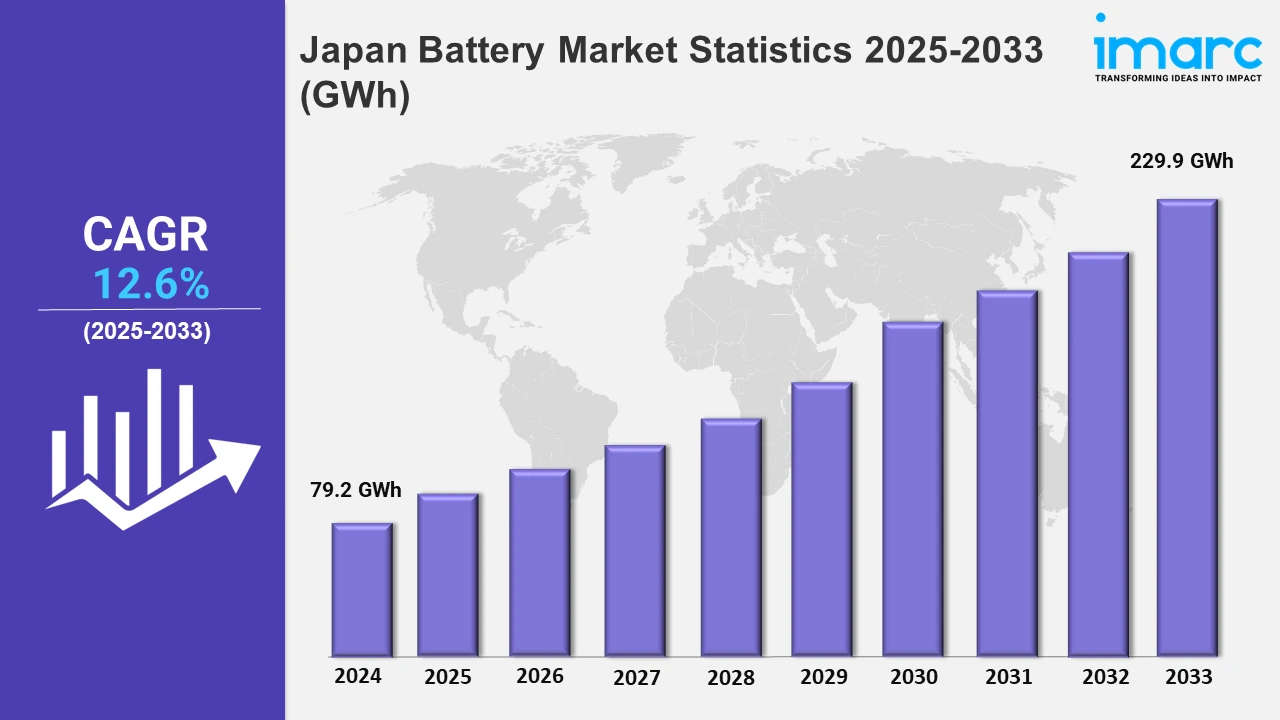
The Japan battery market size reached 79.2 GWh in 2024, and it is expected to reach 229.9 GWh by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 12.6% from 2025 to 2033.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The focus on energy efficiency is propelling innovations in the battery market, particularly in Japan. This market growth is fueled by increasing investments in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and next-generation battery technologies. Japan's commitment to reducing carbon emissions and its push towards clean energy solutions align with trends, making it a key player in the battery industry. Additionally, government subsidies to promote EV adoption further bolster the demand for innovative battery solutions. As a result, Japanese companies are intensifying research and development efforts to enhance battery performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, in January 2025, Mazda announced the establishment of a 10GWh lithium-ion battery module plant in Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan. This facility will utilize Panasonic’s cylindrical cells to support Mazda's EV initiatives, aligning with the company’s 2030 Management Policy. This development underpins Mazda's plans to launch a dedicated platform EV by 2027, marking a significant step in its electrification journey.
Similarly, in November 2024, Honda inaugurated a manufacturing line for all-solid-state batteries in Sakura City, Japan. Spanning 27,400 square meters, this facility is dedicated to developing mass-production processes for solid-state batteries. These batteries aim to improve energy density, reduce costs, and revolutionize EV performance. Honda’s goal is to commence production by January 2025, showcasing its commitment to battery innovation. Moreover, advancements in battery technology are reshaping the competitive landscape of the Japanese market, with a strong emphasis on solid-state batteries. These batteries offer optimal safety, greater energy storage capacity, faster charging, etc., compared to traditional counterparts. For instance, in April 2024, Nissan unveiled its project for an all-solid-state battery pilot line at its Yokohama Plant in Japan. This initiative aligns with Nissan Ambition 2030, targeting the integration of these advanced batteries into EVs by 2028. Solid-state batteries are expected to significantly reduce costs, improve charging efficiency, and offer superior performance, positioning Nissan as a leader in next-generation battery technology.
Japan Battery Market Statistics, By Region
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Kanto region, Kinki region, Central/Chubu region, Kyushu-Okinawa region, Tohoku region, Chugoku region, Hokkaido region, and Shikoku region. The rising focus on elevating domestic innovations is stimulating the market.
Kanto Region Battery Market Trends:
The Kanto region, home to Tokyo, is seeing growth in electric vehicle (EV) battery production, driven by Japan’s push for carbon neutrality by 2050. Major companies like Panasonic in Yokohama are expanding facilities to meet demand. The region's advanced infrastructure supports lithium-ion battery recycling initiatives. For instance, Saitama prefecture has implemented recycling programs to reclaim battery materials, thereby bolstering sustainability and reducing dependency on raw material imports.
Kinki Region Battery Market Trends:
In the Kinki region, Osaka leads advancements in solid-state battery technology. Kyoto-based companies such as Murata Manufacturing are heavily investing in research to commercialize these batteries for electronics and EVs. With Kansai's proximity to international markets and strong innovation hubs, the region attracts partnerships, such as Panasonic’s collaboration with Tesla, enhancing its overall competitiveness in battery innovation.
Central/Chubu Region Battery Market Trends:
Centra/Chubu is focusing on industrial battery systems for renewable energy storage. Toyota’s facilities in Aichi prefecture are developing next-generation batteries for hybrid vehicles. The region is also leveraging its strong manufacturing base to integrate battery systems into smart grids to reduce energy wastage. Toyota’s recently announced solid-state battery breakthrough exemplifies Chubu’s leadership in pushing for efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Kyushu-Okinawa Region Battery Market Trends:
Fukuoka and the rest of the Kyushu region are becoming leaders in battery recycling technologies. In addition, rare metal recovery from discarded batteries is being improved by businesses such as Nippon Magnetic Dressing. Okinawa, whose islands rely mostly on renewable energy, is also investing in energy storage to maintain supplies. Kagoshima's renewable energy storage initiatives demonstrate the area's strategic importance in elevating Japan's energy transition objectives.
Tohoku Region Battery Market Trends:
The Tohoku region is focusing on advancing energy storage systems for its growing renewable energy sector. Prefectures such as Miyagi are collaborating with battery manufacturers to enhance grid stability and efficiency. For instance, Sumitomo Electric has deployed advanced redox flow battery systems in the region to support large-scale wind farms. Tohoku's strategic emphasis on renewable energy integration positions it as a critical player in Japan's energy transformation.
Chugoku Region Battery Market Trends:
Chugoku, with Hiroshima as its core, is advancing batteries for marine and industrial applications. The port of Hiroshima supports innovation in lithium-ion batteries for electric ships, aligning with decarbonization goals. Companies like GS Yuasa in Okayama are driving research into long-cycle life batteries for industrial equipment. This industrial focus underscores Chugoku’s contribution to diversifying battery applications across Japan’s key economic sectors.
Hokkaido Region Battery Market Trends:
Hokkaido region is making significant investments in battery storage to help its expanding renewable energy industry. The prefecture's massive wind and solar farms need effective battery systems to handle excess energy. For example, wind farms in Kushiro are paired with battery installations to ensure stable power supply during demand fluctuations. The region’s geographic isolation further underscores the importance of robust energy storage solutions for grid reliability.
Shikoku Region Battery Market Trends:
Shikoku, with Ehime prefecture as a hub, is focusing on residential and small-scale commercial battery solutions. Solar panel adoption across rural areas has spurred the requirement of compact energy storage systems. Companies in Matsuyama are innovating modular batteries for households to store renewable energy. Shikoku’s emphasis on localized battery solutions ensures energy independence for remote communities, contributing to Japan’s broader energy diversification strategy.
Top Companies Leading in the Japan Battery Industry
Some of the leading market companies include EEMB Japan, GS Yuasa International Ltd., Maxell, Ltd, NGK Insulators Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, The Furukawa Battery Co., Ltd, Toshiba Corporation, among many others. Panasonic Holdings resumed operations at its Wakayama Prefecture facility to begin manufacturing its new generation of EV batteries.
Japan Battery Market Segmentation Coverage
- On the basis of the type, the market has been bifurcated into primary battery and secondary battery. Primary batteries are single-use and non-rechargeable energy sources. Besides this, secondary batteries are rechargeable, designed for multiple cycles, and widely used in portable devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems.
- Based on the product, the market is categorized into lithium-ion, lead acid, nickel metal hydride, nickel cadmium, and others. Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density and efficiency. Moreover, lead-acid batteries are cost-effective. In contrast, nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium batteries are durable, while emerging chemistries enhance niche applications.
- On the basis of the application, the market has been divided into automotive batteries, industrial batteries, and portable batteries. Automotive batteries power vehicles, including EVs. Industrial batteries support large-scale operations like manufacturing and grid backup. In contrast, portable batteries provide energy for personal devices, ensuring mobility, and convenience in daily use.
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | 79.2 GWh |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | 229.9 GWh |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 12.6% |
| Units | GWh |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Primary Battery, Secondary Battery |
| Products Covered | Lithium-Ion, Lead Acid, Nickel Metal Hydride, Nickel Cadmium, Others |
| Applications Covered | Automotive Batteries, Industrial Batteries, Portable Batteries |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Companies Covered | EEMB Japan, GS Yuasa International Ltd., Maxell, Ltd, NGK Insulators Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, The Furukawa Battery Co., Ltd, Toshiba Corporation, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.





.webp)




.webp)












