Graves’ Disease Market Size to Reach USD 6,782 Million by 2035, Impelled by Advancements in Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Graves’ Disease Market Outlook 2025-2035:
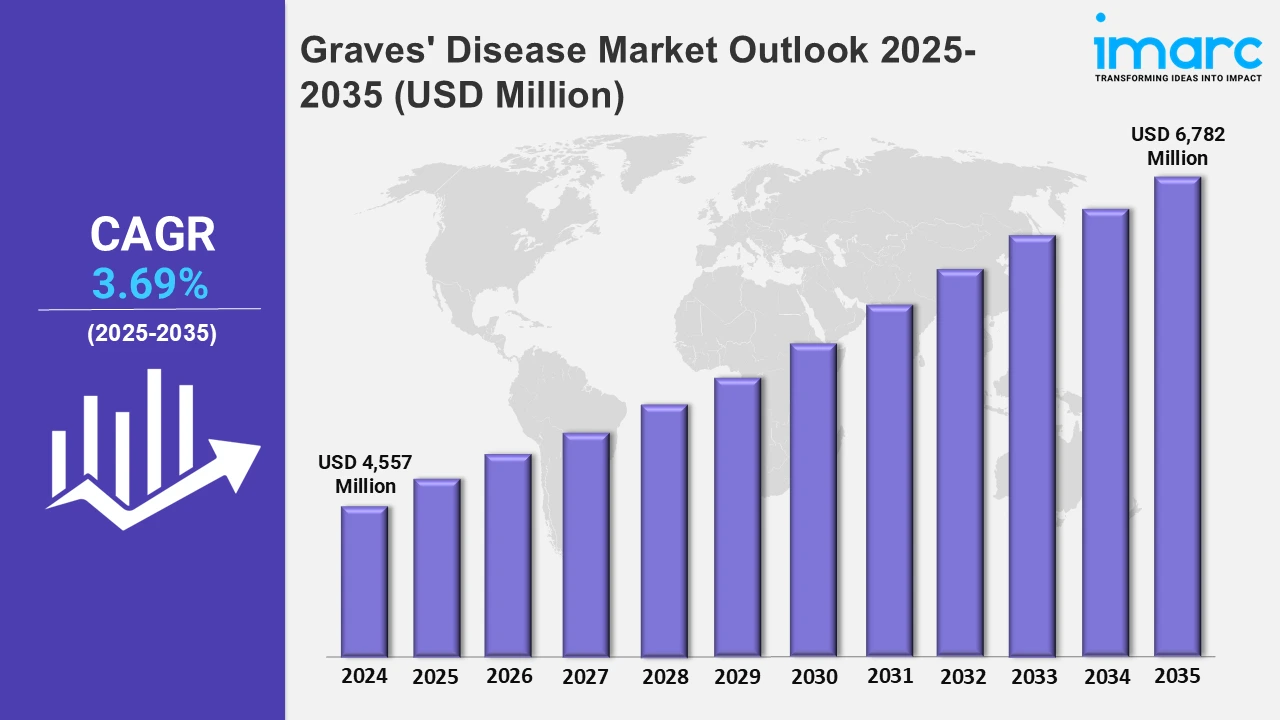
The 7 major Graves’ disease market reached a value of USD 4,557 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the 7MM to reach USD 6,782 Million by 2035, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.69% during 2025-2035. The market is fueled by the increasing demand for minimally invasive therapies like radiofrequency ablation and laser ablation due to their numerous benefits over traditional surgical interventions like reduced recovery times, less complications, and reduced chances of injury to adjacent tissues. Moreover, the increasing popularity of radioactive iodine therapy in patients with extreme symptoms or those with contraindications against the use of anti-thyroid medicines is further fueling the market growth.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Advances in Early Detection and Diagnostic Technologies: Driving the Graves’ Disease Market
The market for Graves' disease is growing substantially owing to advances in early detection and diagnostic technologies that are vital to timely intervention and successful disease control. Among the most significant advances in the diagnosis of Graves' disease is the development of high-sensitivity immunoassays for the detection of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) antibodies. These autoantibodies are key to the progress of the disease, and early detection means that diagnosis can be achieved promptly before serious symptoms develop. More advanced third-generation TSH receptor antibody (TRAb) tests provide enhanced sensitivity, which can distinguish between Graves' disease and hyperthyroidism from other causes. Ultrasound and Doppler scanning have also become routine diagnostic tests for Graves' disease. These imaging modalities assist in the evaluation of thyroid gland size, vascularity, and structural alterations, facilitating non-invasive and precise disease assessment. The application of thyroid scintigraphy with radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) also assists in distinguishing Graves' disease from other thyroid conditions, maximizing treatment choice. Moreover, developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enhancing the interpretation of thyroid function tests and imaging. AI-based diagnostic algorithms can examine huge amounts of patient information, facilitating earlier and more accurate detection of Graves' disease. The relentless enhancement of diagnostic technology is not just speeding up the identification of early disease but also making it possible to monitor the response to treatment and remission of the disease more effectively. With increasing availability of these innovations, they are fueling growth in the market by enhancing patient care, lowering complications, and allowing for more tailored treatment modalities for Graves' disease.
Development of Novel Therapies and Pharmacological Treatments: Contributing to Market Expansion
Graves' disease is a growing market with the progress in the novel treatments and drugs offering better management of the disease in a targeted and effective way. One of the most promising developments in the treatment of Graves' disease is the establishment of biologic therapies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) antibodies. Novel monoclonal antibodies, including teprotumumab, initially created for thyroid eye disease (TED), have shown potential in managing autoimmune activity in Graves' disease. These targeted treatments create a more specific mechanism of action with less autoimmune attack on the thyroid gland and less progression of the disease. Furthermore, small-molecule inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs have been studied as alternatives to classic ATDs methimazole and propylthiouracil. The new compounds aim to repress autoimmunity with reduced adverse effects, keeping liver toxicity and agranulocytosis risks that arise from earlier interventions to a bare minimum. TKIs and various other immune-modulating agents have been researched regarding their capacity in managing hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease. Additionally, genetic profiling and personalized medicine are facilitating individualized treatment strategies. With the ability to comprehend individual patient reactions to treatment, clinicians are able to optimize drug choice, minimize side effects, and enhance long-term disease control. As ongoing R&D in new therapies continues to enhance the Graves' disease market, the disease will be treated more effectively, precisely, and safely, enhancing patients' quality of life.
Marketed Therapies in Graves’ Disease Market
Propylthiouracil: Teva Pharmaceuticals
Propylthiouracil is a thiourea antithyroid medication used to treat hyperthyroidism caused by an overactive thyroid gland (Graves’ disease). Propylthiouracil binds to thyroid peroxidase, which hinders the conversion of iodide to iodine. Thyroid peroxidase generally converts iodide to iodine (with hydrogen peroxide as a cofactor) and then catalyzes the integration of the resultant iodide molecule into both the 3 and/or 5 positions of the phenol rings of tyrosines found in thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin is destroyed to create the thyroid gland's major hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thus, propylthiouracil efficiently suppresses the generation of new thyroid hormones.
Tapazole (Methimazole): Pfizer
Tapazole (Methimazole) is a thionamide antithyroid drug used to treat persons with Graves' disease or toxic multinodular goiter who have an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Methimazole's major mechanism of action appears to be interfering with an early step in thyroid hormone synthesis called thyroid peroxidase (TPO). TPO, coupled with hydrogen peroxide, generally catalyzes the conversion of iodide to iodine and then further catalyzes the integration of this iodine onto the 3 and/or 5 positions of the phenol rings of tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin. The thyroglobulin molecules then breakdown within thyroid follicular cells to yield either T4 or T3, which are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
Emerging Therapies in Graves’ Disease Market
ATX-GD-59: Worg Pharmaceuticals
ATX-GD-59, manufactured Worg Pharmaceuticals, uses antigen-specific immunotherapy to re-establish immunological tolerance to the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR), the principal target in Graves' disease. This essentially prevents the immune system from attacking the thyroid gland by exposing it to specific TSHR peptides that promote tolerance rather than an immunological response. The result is achieved by attaching to HLA-DR molecules on dendritic cells without activating them, therefore lowering the danger of additional immunological activation.
Linsitinib: Sling Therapeutics
Linsitinib, developed by Sling Therapeutics, works by inhibiting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), effectively blocking downstream signaling pathways such as AKT and ERK. These pathways are critical for the development and progression of inflammation associated with Graves' disease, particularly in the context of thyroid eye disease (TED), where it is currently being studied. Essentially, it inhibits the immunological response in orbital tissue by targeting the IGF-1R pathway.
Batoclimab: HanAll Biopharma/Harbour BioMed/Immunovant
Batoclimab is a fully human anti-FcRn (neonatal Fc receptor) monoclonal antibody designed to reduce pathogenic autoantibodies in autoimmune diseases, including Graves’ disease. By selectively inhibiting FcRn, Batoclimab prevents the recycling of immunoglobulin G (IgG), leading to a dose-dependent reduction in circulating IgG autoantibodies, including thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibodies, which drive hyperthyroidism in Graves’ disease. This mechanism helps restore immune balance and reduces excessive thyroid stimulation.
| Drug Name | Company Name | MOA | ROA |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATX-GD-59 | Worg Pharmaceuticals | Thyrotropin stimulants | Intradermal |
| Linsitinib | Sling Therapeutics | IGF type 1 receptor antagonists; Insulin receptor antagonists; Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Receptor protein-tyrosine kinase antagonists | Oral |
| Batoclimab | HanAll Biopharma/Harbour BioMed/Immunovant | Neonatal Fc receptor antagonists | Subcutaneous |
Detailed list of emerging therapies in Graves’ Disease is provided in the final report…
Leading Companies in the Graves’ Disease Market:
The market research report by IMARC encompasses a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the market. Across the global Graves’ disease market, several leading companies are at the forefront of developing integrated platforms to enhance the management of Graves’ disease. Some of the major players include Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceuticals. These companies are driving innovation in the Graves’ disease market through continuous research, diagnostic tools, and expanding their product offerings to meet the growing demand for the illness.
Key Players in Graves’ Disease Market:
The key players in the Graves’ Disease market who are in different phases of developing different therapies are Teva Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Worg Pharmaceuticals, Sling Therapeutics, HanAll Biopharma, Harbour BioMed, Immunovant, Horizon Therapeutics, Novartis, and Others.

Regional Analysis:
The major markets for Graves’ disease include the United States, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, and Japan. According to projections by IMARC, the United States has the largest patient pool for Graves’ disease while also representing the biggest market for its treatment. This can be attributed to the emergence of monoclonal antibodies, FcRn inhibitors (e.g., Batoclimab), and immune-modulating therapies that offers more precise and effective treatment options, increasing physician and patient preference for innovative therapies.
Moreover, a major driver is the increasing prevalence of Graves’ disease and autoimmune thyroid disorders in the U.S. Factors such as genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and lifestyle changes have contributed to a rising incidence of autoimmune diseases, prompting greater demand for effective treatment options. Additionally, advancements in diagnostic tools, including high-sensitivity thyroid function tests and imaging techniques like ultrasound and radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) scans, are enabling early and accurate detection, leading to better disease management and market expansion.
Besides this, strong R&D investments, supported by the U.S. FDA’s fast-track and orphan drug designations, are accelerating the approval of novel therapies, further driving market growth. Expanding healthcare infrastructure, better insurance coverage, and growing patient awareness programs also contribute to improved access to advanced treatments, reinforcing the U.S. as a key market for Graves’ disease therapeutics.
Recent Developments in Graves’ Disease Market:
- In January 2025, Sling Therapeutics, Inc. announced topline efficacy and safety data from the Phase 2b/3 LIDS trial of linsitinib in patients with active, moderate to severe thyroid eye disease. The LIDS trial met its primary endpoint with statistical significance for the 150mg BID dose.
Key information covered in the report
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Period: 2019-2024
- Market Forecast: 2025-2035
Countries Covered
- United States
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Japan
Analysis Covered Across Each Country
- Historical, current, and future epidemiology scenario
- Historical, current, and future performance of the Graves’ disease market
- Historical, current, and future performance of various therapeutic categories in the market
- Sales of various drugs across the Graves’ disease market
- Reimbursement scenario in the market
- In-market and pipeline drugs
Competitive Landscape:
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of current Graves’ disease marketed drugs and late-stage pipeline drugs.
In-Market Drugs
- Drug Overview
- Mechanism of Action
- Regulatory Status
- Clinical Trial Results
- Drug Uptake and Market Performance
Late-Stage Pipeline Drugs
- Drug Overview
- Mechanism of Action
- Regulatory Status
- Clinical Trial Results
- Drug Uptake and Market Performance
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world’s most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. Across the six major continents and 100+ countries, we work alongside our business partners as one team with a common ambition to achieve unparallelled results, gain a competitive edge, and transform industries. IMARC Group excels in understanding its clients’ business priorities and delivering tailored solutions that drive meaningful outcomes. Our client base spans over 3,000 organizations in the private, public, and social sectors, ranging from high-growth startups to Fortune 500 companies.
Contact US
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: Sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
Phone Number: - +1 631 791 1145, +91-120-433-0800
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure




.webp)




.webp)












